Abstract
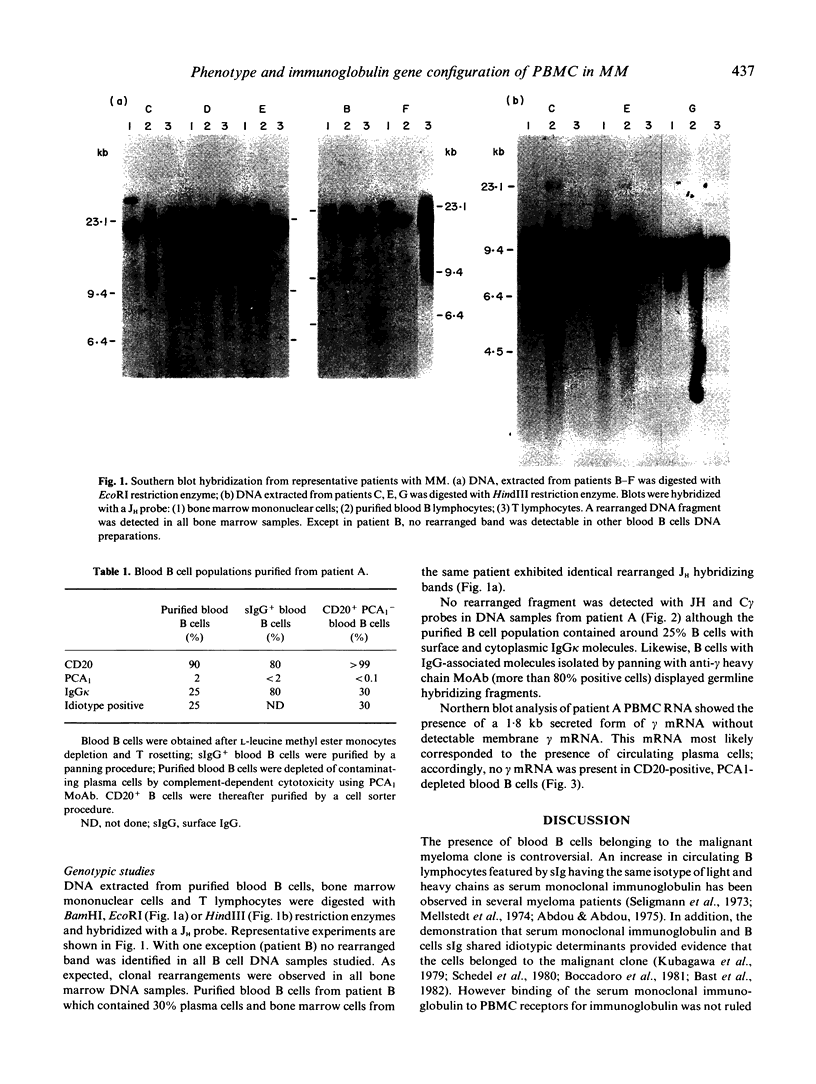
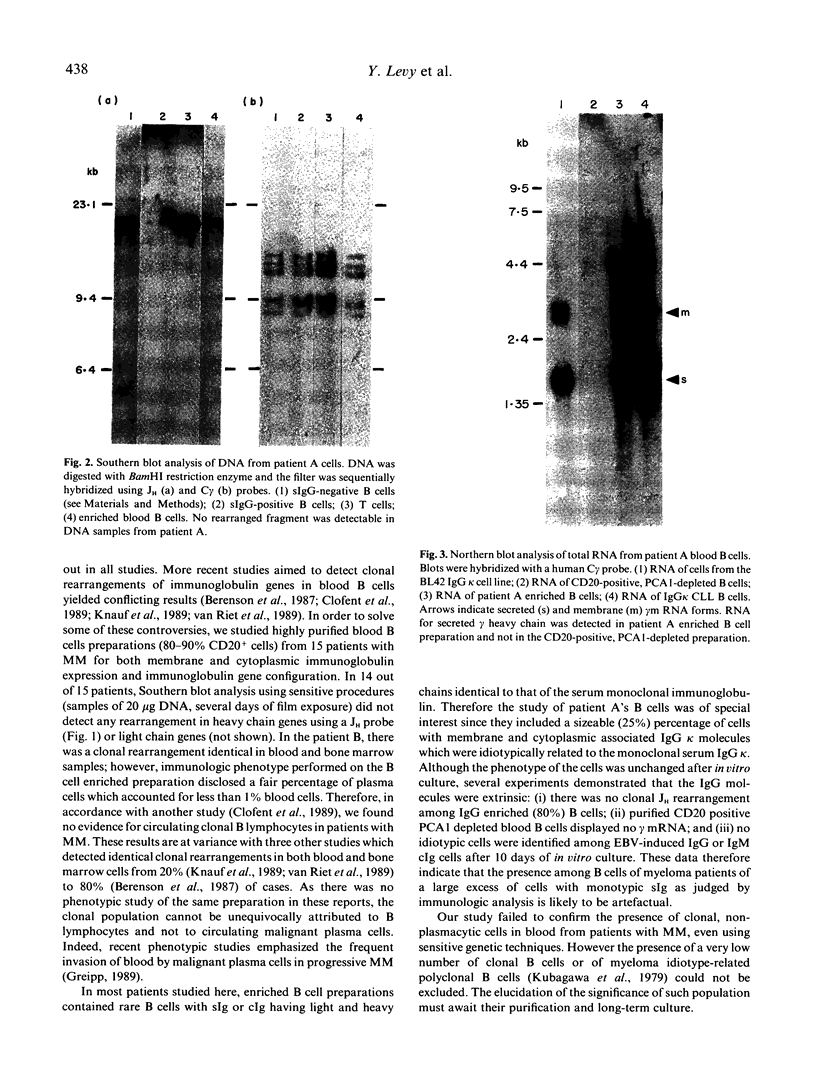
We have studied the phenotype and the immunoglobulin gene configuration of blood B cells from 15 patients with stage III multiple myeloma (MM) at diagnosis. Highly purified B cells (greater than 90% CD20 positive cells) were obtained after L-leucine methyl ester monocyte depletion and elimination of T cells by rosetting. The percentage of B cells with surface immunoglobulin (sIg) featuring the same light and heavy chain isotype as the serum monoclonal immunoglobulin was very low, except in one patient, in whom 25-30% of B cells displayed surface and cytoplasmic immunoglobulin (cIg) sharing idiotypic determinants with the serum monoclonal IgG kappa. In all cases but one the percentage of circulating plasma cells accounted for less than 2% of the enriched B cell preparations. In one patient purified B cell population contained 30% of plasma cells and the immunoglobulin gene study revealed a rearranged JH hybridizing fragment identical in bone marrow and blood B cell DNA samples. In the other 14 cases no rearranged fragment was detected although we used a technique allowing the detection of at least 2% clonal cells. The absence of clonal cells in the patient whose B cells contained a high percentage of cells featuring surface IgG molecules was confirmed on purified sIgG-positive cells. In addition CD20-positive cells from this patient did not contain gamma mRNA. Therefore the IgG molecules were clearly extrinsic. Although the existence of clonal B lymphocytes or of myeloma idiotype related B cells cannot be ruled out, they escape detection by sensitive genetic studies of immunoglobulin genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Abdou N. L. The monoclonal nature of lymphocytes in multiple myeloma. Effects of therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jul;83(1):42–45. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-1-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander A., Steinmetz M., Barritault D., Frangione B., Franklin E. C., Hood L., Buxbaum J. N. gamma Heavy chain disease in man: cDNA sequence supports partial gene deletion model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3260–3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bast E. J., van Camp B., Reynaert P., Wiringa G., Ballieux R. E. Idiotypic peripheral blood lymphocytes in monoclonal gammopathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):677–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenson J., Wong R., Kim K., Brown N., Lichtenstein A. Evidence for peripheral blood B lymphocyte but not T lymphocyte involvement in multiple myeloma. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1550–1553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergui L., Schena M., Gaidano G., Riva M., Caligaris-Cappio F. Interleukin 3 and interleukin 6 synergistically promote the proliferation and differentiation of malignant plasma cell precursors in multiple myeloma. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):613–618. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccadoro M., Van Acker A., Pileri A., Urbain J. Idiotypic lymphocytes in human monoclonal gammopathies. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1981 Jan-Feb;132C(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0769-2625(81)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clofent G., Klein B., Commes T., Ghanem N., Lefranc M. P., Bataille R. No detectable malignant B cells in the peripheral blood of patients with multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 1989 Mar;71(3):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb04292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greipp P. R. Monoclonal gammopathies: new approaches to clinical problems in diagnosis and prognosis. Blood Rev. 1989 Dec;3(4):222–236. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(89)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillot-Courvalin C., Labaume S., Brouet J. C. Differentiation by interleukin 2 of a subpopulation of human B cells. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Jun;23(6):679–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan T. M., Durie B. G., Lomen C., Spier C., Wirt D. P., Nagle R., Wilson G. S., Richter L., Vela E., Maxey V. Delineation of a novel pre-B cell component in plasma cell myeloma: immunochemical, immunophenotypic, genotypic, cytologic, cell culture, and kinetic features. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):932–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubagawa H., Vogler L. B., Capra J. D., Conrad M. E., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Studies on the clonal origin of multiple myeloma. Use of individually specific (idiotype) antibodies to trace the oncogenic event to its earliest point of expression in B-cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):792–807. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellstedt H., Hammarström S., Holm G. Monoclonal lymphocyte population in human plasma cell myeloma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):371–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Labaume S. Immunofluorescent staining of human lymphocytes for the detection of surface immunoglobulins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:254–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedel I., Peest D., Stünkel K., Fricke M., Eckert G., Deicher H. Idiotype-bearing peripheral blood lymphocytes in human multiple myeloma and Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(4):437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. L., Kurosaka M., Lipsky P. E. Phenotype of the accessory cell necessary for mitogen-stimulated T and B cell responses in human peripheral blood: delineation by its sensitivity to the lysosomotropic agent, L-leucine methyl ester. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2282–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsapis A., Bentaboulet M., Pellet P., Mihaesco E., Thierry D., Seligmann M., Brouet J. C. The productive gene for alpha-H chain disease protein MAL is highly modified by insertion-deletion processes. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3821–3827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp B., Reynaert P., Broodtaerts L. Studies on the origin of the precursor cells in multiple myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia and benign monoclonal gammopathy. I. Cytoplasmic isotype and idiotype distribution in peripheral blood and bone marrow. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Apr;44(1):82–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Riet I., Heirman C., Lacor P., De Waele M., Thielemans K., Van Camp B. Detection of monoclonal B lymphocytes in bone marrow and peripheral blood of multiple myeloma patients by immunoglobulin gene rearrangement studies. Br J Haematol. 1989 Nov;73(3):289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]