Abstract
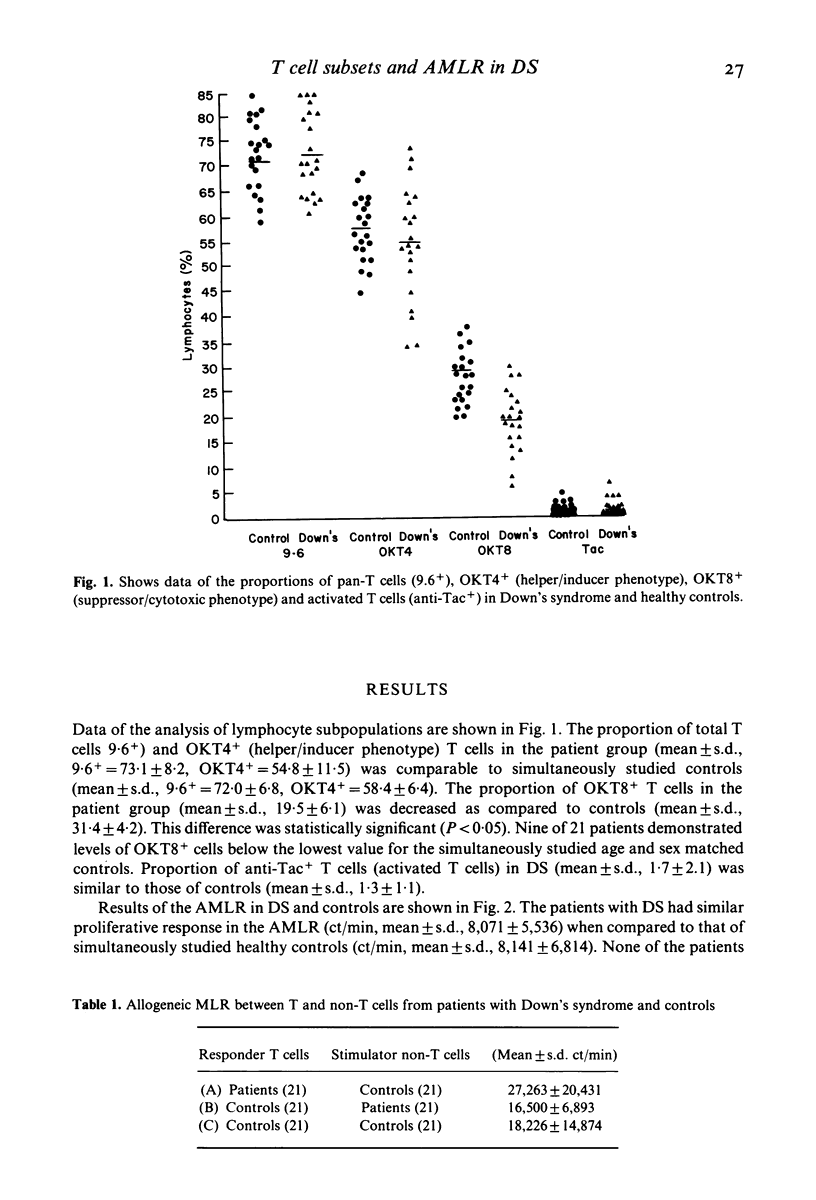
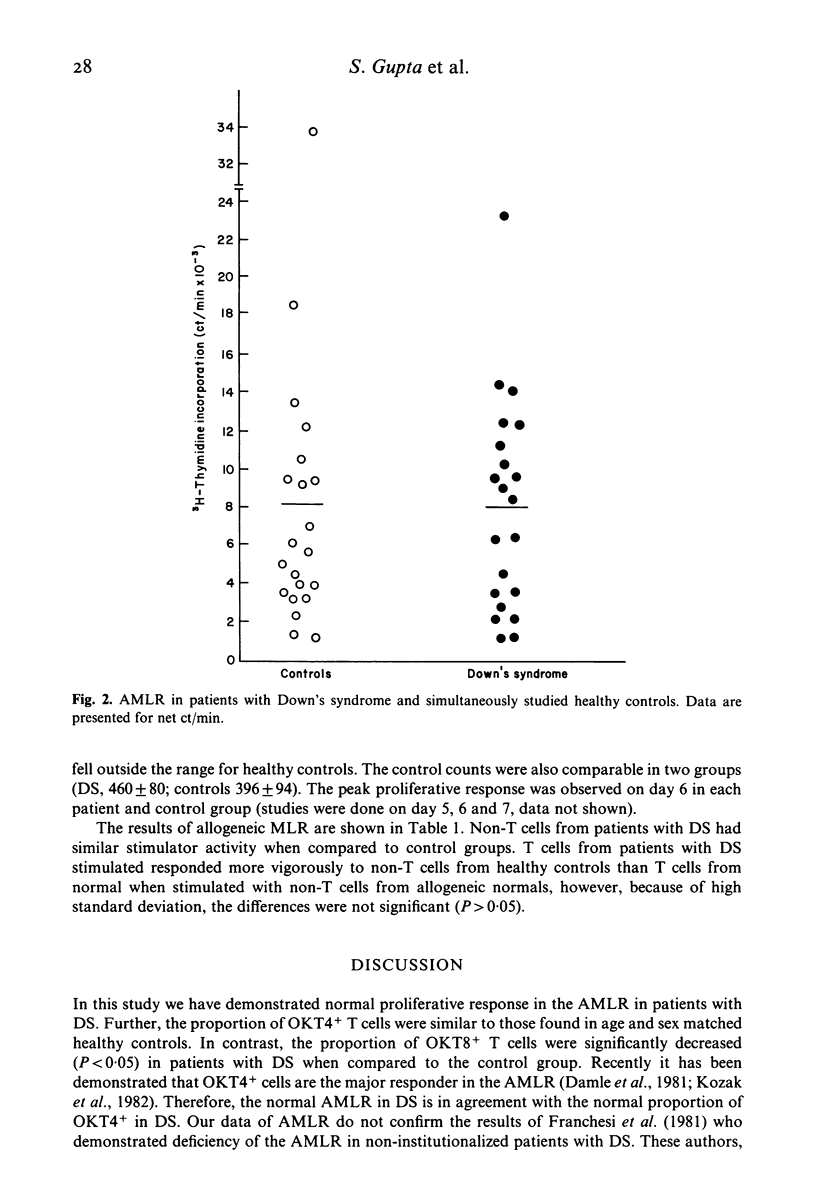
Peripheral blood from 21 non-institutionalized children with Down's syndrome (DS) and 21 age and sex matched simultaneously studied healthy controls, was analysed for monoclonal antibody defined T cells and T cell subsets, using a fluorescence activated cell sorter, and the autologous (AMLR) and allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR). Total T cells (9.6+), OKT4+ (helper/inducer phenotype) and anti-Tac+ (activated T) cells were present in comparable proportions to that observed in the control group. In contrast, the proportion of OKT8+ (suppressor/cytotoxic phenotype) cells were significantly (P less than 0.05) decreased when compared to healthy controls. The proliferative response in the AMLR and MLR were comparable to control group. The significance of these results are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgio G. R., Ugazio A. G. Immunity in Down's syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1978 Apr 20;127(4):293–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00493546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgio G. R., Ugazio A. G., Nespoli L., Marcioni A. F., Bottelli A. M., Pasquali F. Derangements of immunoglobulin levels, phytohemagglutinin responsiveness and T and B cell markers in Down's syndrome at different ages. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Sep;5(9):600–603. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Hansen J. A., Good R. A., Gupta S. Monoclonal antibody analysis of human T lymphocyte subpopulations exhibiting autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5096–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M. Are the Ir genes expressed by macrophages? Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):105–105. doi: 10.1038/267105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi C., Licastro F., Chiricolo M., Bonetti F., Zannotti M., Fabris N., Mocchegiani E., Fantini M. P., Paolucci P., Masi M. Deficiency of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactions and serum thymic factor level in Down's syndrome. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2161–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi C., Licastro F., Paolucci P., Masi M., Cavicchi S., Zannotti M. T and B lypmhocyte subpopulations in Down's syndrome. A study on non-institutionalised subjects. J Ment Defic Res. 1978 Sep;22(3):179–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1978.tb00975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin M. E., Crinella F. M., Castles J. J., Trent J. K. Immunologic characteristics of Down's syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1977 Dec;21(4):237–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1977.tb01587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Brown M. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of a human T lymphocyte surface protein associated with the E-rosette receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):207–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak R. W., Moody C. E., Staiano-Coico L., Weksler M. E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. XII. Quantitative and qualitative differences between human autologous and allogeneic reactive T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1723–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S., Schlesinger M., Handzel Z., Hahn T., Altman Y., Czernobilsky B., Boss J. Thymic deficiency in Down's syndrome. Pediatrics. 1979 Jan;63(1):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez V., Ochs H. D., Thuline H. C., Davis S. D., Wedgwood R. J. Defective antibody response to bacteriophage phichi 174 in Down syndrome. J Pediatr. 1975 Feb;86(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. E., Innes J. B., Staiano-Coico L., Incefy G. S., Thaler H. T., Weksler M. E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. XI. The effect of age on the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. Immunology. 1981 Oct;44(2):431–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Möller G. HLA-DR antigens render resting T cells sensitive to interleukin-2 and induce production of the growth factor in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Obara Y. Hypersensitivity of lymphocytes in Down's syndrome shown by mixed leukocyte culture experiments. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):596–598. doi: 10.1038/222596b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutnick A. I., London W. T., Blumberg B. S., Gerstley B. J. Susceptibility to leukemia: immunologic factors in Down's syndrome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Nov;47(5):923–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugazio A. G., Maccario R., Duse M., Burgio G. R. T-lymphocyte deficiency in Down syndrome. Lancet. 1977 May 14;1(8020):1062–1062. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Pitt D. B., Sharma D. L., Mackay I. R. Stress deficiency of the T-lymphocyte system exemplified by Down syndrome. Lancet. 1977 Jan 22;1(8004):163–166. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91763-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


