Abstract
Lymphocytotoxic activity has been found by previous investigators in multiple sclerosis (MS) sera. We confirmed the presence of this activity in MS sera using techniques designed to eliminate possible sources of erroneous conclusion not considered in previous studies. We further characterized this activity and found it to be non-dialysable and complement dependent, and, therefore, presumably to be an antibody. This lymphocytotoxic antibody (LCA) is found in those patients with active or progressive disease, and appears to be preferentially directed against the suppressor subset of T cells, as defined by monoclonal antibodies. The LCA may play a role in the pathogenesis of acute exacerbation of MS.
Full text
PDF

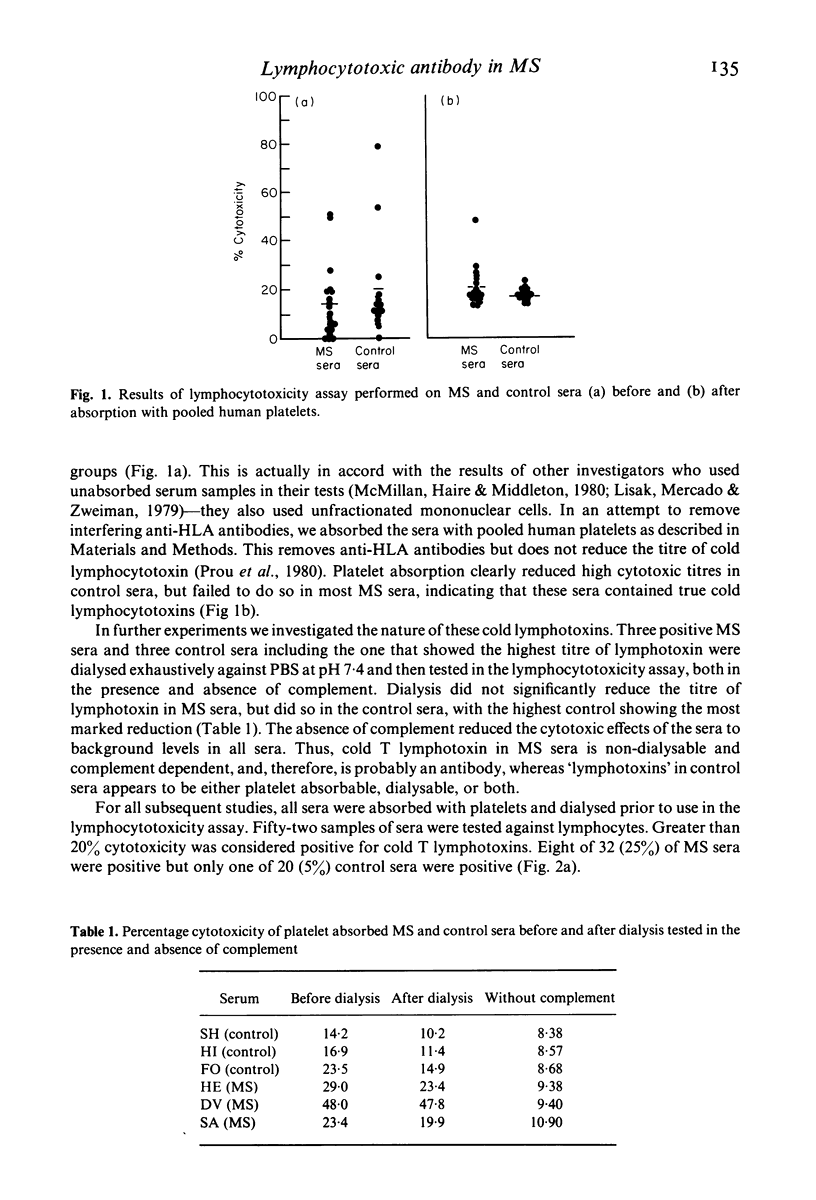
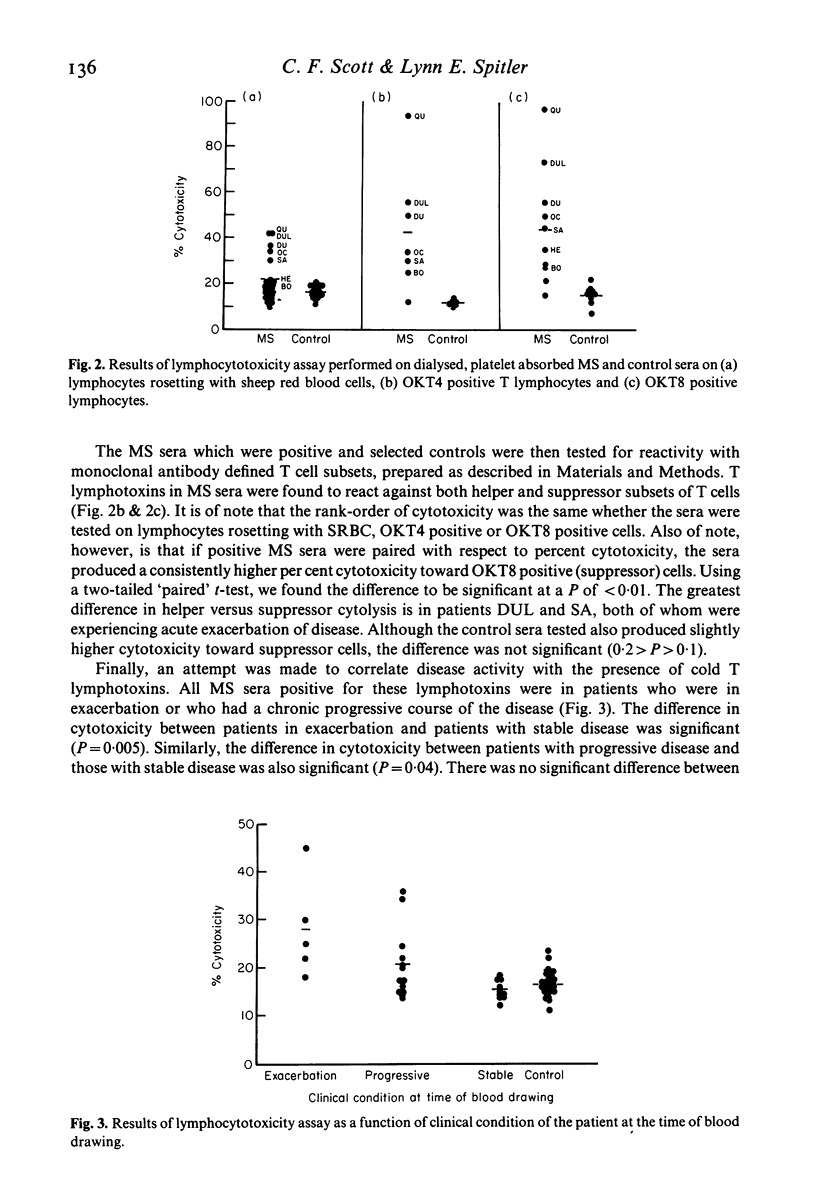



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramsky O., Lisak R. P., Silberberg D. H., Pleasure D. E. Antibodies to oligodendroglia in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1207–1211. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antel J. P., Richman D. P., Medof M. E., Arnason B. G. Lymphocyte function and the role of regulator cells in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1978 Sep;28(9 Pt 2):106–110. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.9_part_2.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. A., Phan-Dinh-Tuy F., Tournier E., Chatenoud L., Bach J. F., Martin C., Degos J. D. Deficit of suppressor T cells in active multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1980 Dec 6;2(8206):1221–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHoratius R. J., Tung K. S., Pincus T. Reduced T-lymphocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: effects of immune complexes and lymphocytotoxic antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Oct;17(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deicher H., Meyer zu Schwabedissen H., Baruth B., Patzold U., Haller P. Cerebrospinal fluid immune complexes in multiple sclerosis. Experientia. 1979 Sep 15;35(9):1249–1250. doi: 10.1007/BF01963318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haire M. Significance of virus antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Br Med Bull. 1977 Jan;33(1):40–44. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huddlestone J. R., Oldstone M. B. T suppressor (TG) lymphocytes fluctuate in parallel with changes in the clinical course of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1615–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Kobayashi S., Yoshiki T., Itoh T., Shirai T. Differential sensitivity of functional subsets of T cells to the cytotoxicity of natural T-lymphocytotoxic autoantibody of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;22(2):123–129. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwert E., Bertrams J. Leukocyte iso- and autoantibodies in multiple sclerosis (MS) with special regard to complement-dependent cold-reacting auto-lymphocytotoxins (CoCoCy). Eur Neurol. 1972;7(1):65–73. doi: 10.1159/000114413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. M., Pegrum G. D. Anti-lymphocyte antibody levels in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Acta Haematol. 1979;62(4):229–235. doi: 10.1159/000207577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Mercado F., Zweiman B. Cold reactive antilymphocyte antibodies in neurological diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Nov;42(11):1054–1057. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.11.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P. Multiple sclerosis: immunologic aspects. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;5(5):324–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan S. A., Haire M., Middleton D. Antibodies to lymphocytes and smooth muscle in the sera of patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jul;16(3):374–385. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C. Loss of suppressor T-lymphocyte function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):125–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Abe T., Homma M., Schlossman S. F. Characteristics of anti-T-cell antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for selective reactivity with normal suppressor cells defined by monoclonal antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Aug;16(4):474–484. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Borel Y., Mantzouranis E., Steinberg A. D., Schlossman S. F. Autoantibody to an immunoregulatory inducer population in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):753–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI110092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F., Schur P. H., Mills J. A., Steinberg A. D. Alterations in immunoregulatory T cell subsets in active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1171–1174. doi: 10.1172/JCI109948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies K. M., Brown J. C., Dubois E. L., Quismorio F. P., Friou G. J., Terasaki P. I. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens and lymphocytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):397–402. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Multiple sclerosis: an immunologic reassessment. J Chronic Dis. 1973 Mar;26(3):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(73)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prou O., Kaplan C., Muller J. Y. Freeze dried platelets for HLA alloantibodies absorption. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Jul;16(1):105–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quin J. W., Charlesworth J. A., Lee C. H., Macdonald G. J. Studies of lymphocytotoxins in infectious mononucleosis: reduced lymphocyte killing in the acute phase. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Mar;39(3):588–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L., Hauser S. L., Cohen J. A., Distaso J. A., Schlossman S. F. Loss of suppressor T cells in active multiple sclerosis. Analysis with monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 17;303(3):125–129. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007173030303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schocket A. L., Weiner H. L., Walker J., McIntosh K., Kohler P. F. Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Jan;7(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mottironi V. D., Barnett E. V. Cytotoxins in disease. Autocytotoxins in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):724–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. J. Laboratory diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: immunological and biochemical aspects. Br Med Bull. 1977 Jan;33(1):28–33. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Winchester R. J., Wernet P., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Nature of cold-reactive antibodies to lymphocyte surface determinants in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jan-Feb;18(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


