Abstract
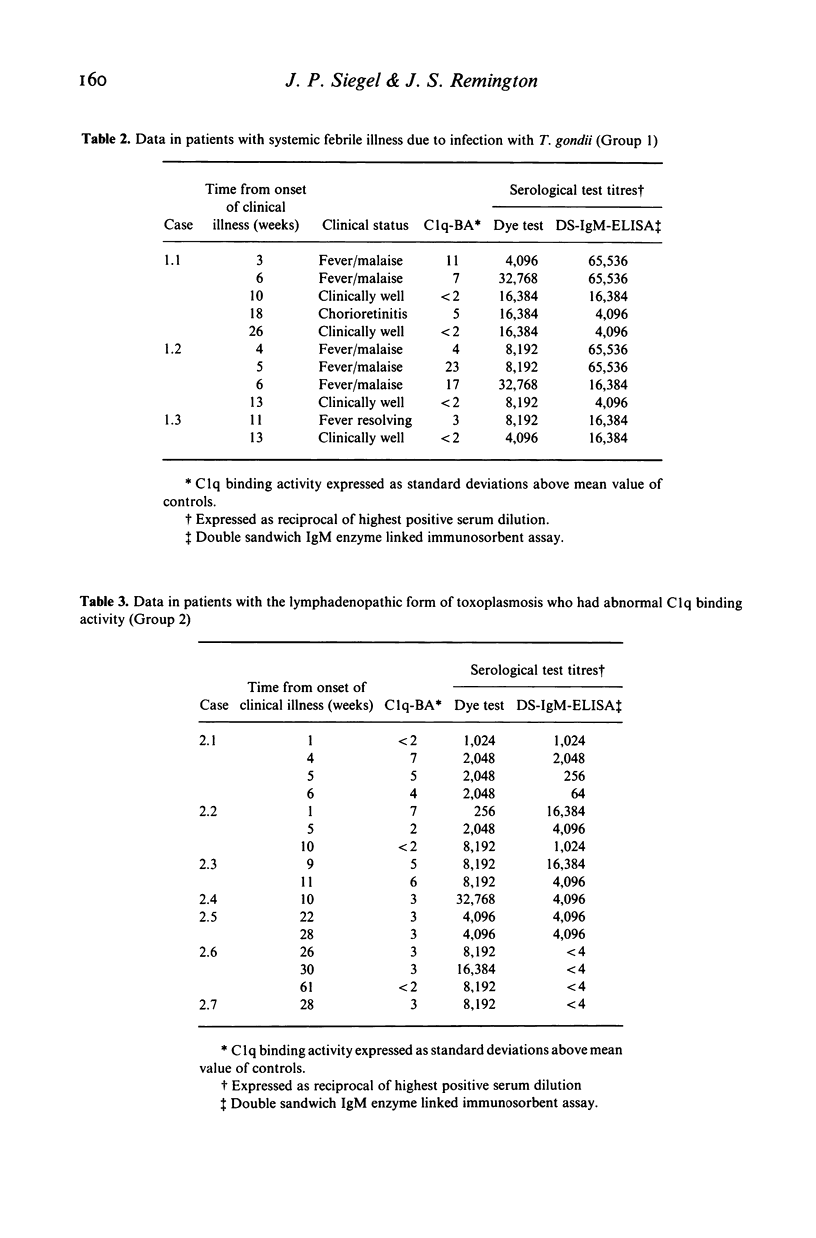
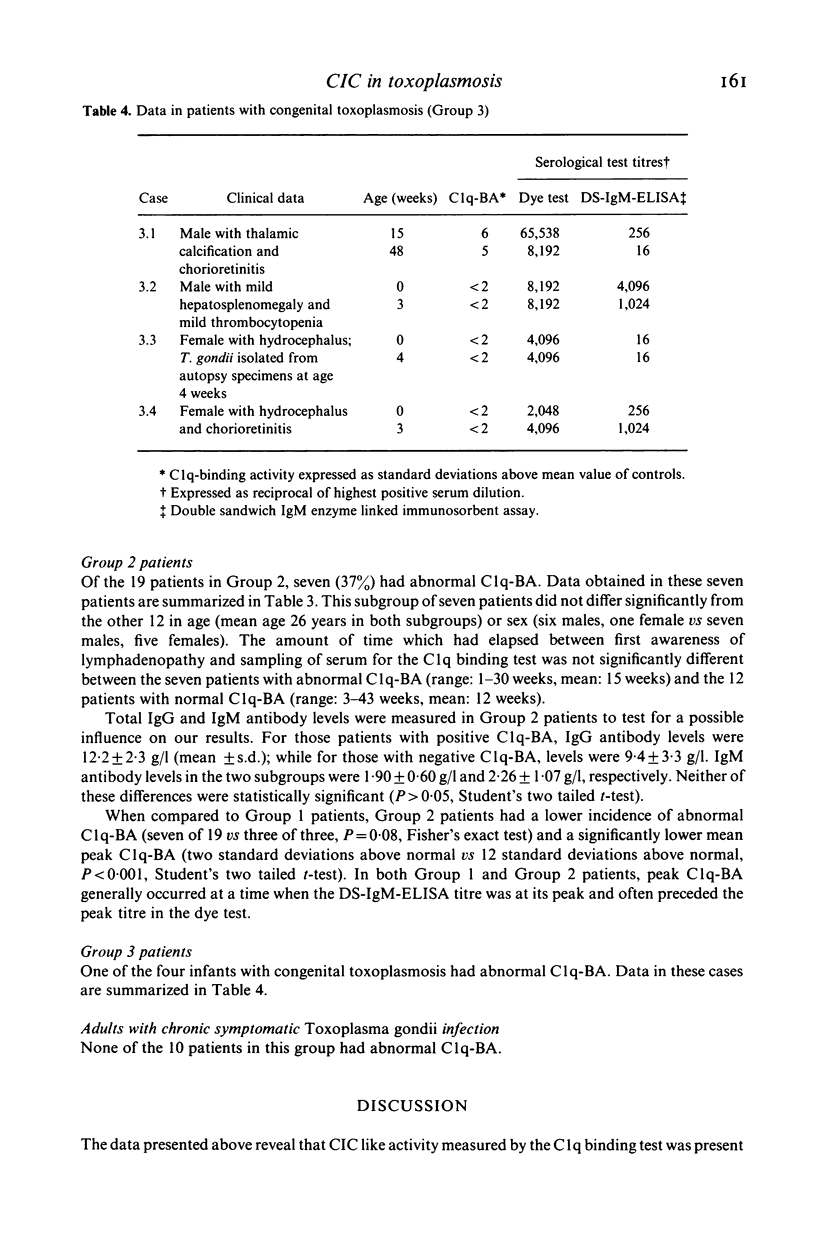
The 125I-C1q binding test was employed to detect circulating immune complexes in serum of 27 subjects with acute toxoplasmosis. The subjects had no known underlying disease. Elevated C1q binding activity (C1q-BA) was found in the serum of each of three adults with the systemic febrile form of toxoplasmosis, seven of 19 patients with the lymphadenopathic form, and one of four infants with congenital infection. The patients with the systemic form of illness had significantly greater mean C1q-BA than did those with the lymphadenopathic form (P less than 0.001). In six episodes of symptomatic toxoplasmosis associated with elevated C1q-BA, follow-up sera were obtained after resolution of all signs and symptoms. Each of these sera showed normalization of C1q-BA. We conclude that immune complex like material is frequently present in the serum of patients with toxoplasmosis and parallels disease activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V. Immune complex assays: the first ten years. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):266–267. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman R. F., Remington J. S. Value of lymph-node biopsy in the diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 25;289(17):878–881. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310252891702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg B. E., Wasserman J., Huldt G., Bergstrand A. Case of glomerulonephritis associated with acute toxoplasmosis. Br Med J. 1974 Sep 14;3(5932):664–665. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5932.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahin B., Papadopoulou Z. L., Jenis E. H. Congenital nephrotic syndrome associated with congenital toxoplasmosis. J Pediatr. 1974 Sep;85(3):366–370. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teutsch S. M., Juranek D. D., Sulzer A., Dubey J. P., Sikes R. K. Epidemic toxoplasmosis associated with infected cats. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 29;300(13):695–699. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903293001302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. The biology and detection of immune complexes. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:89–220. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


