Abstract
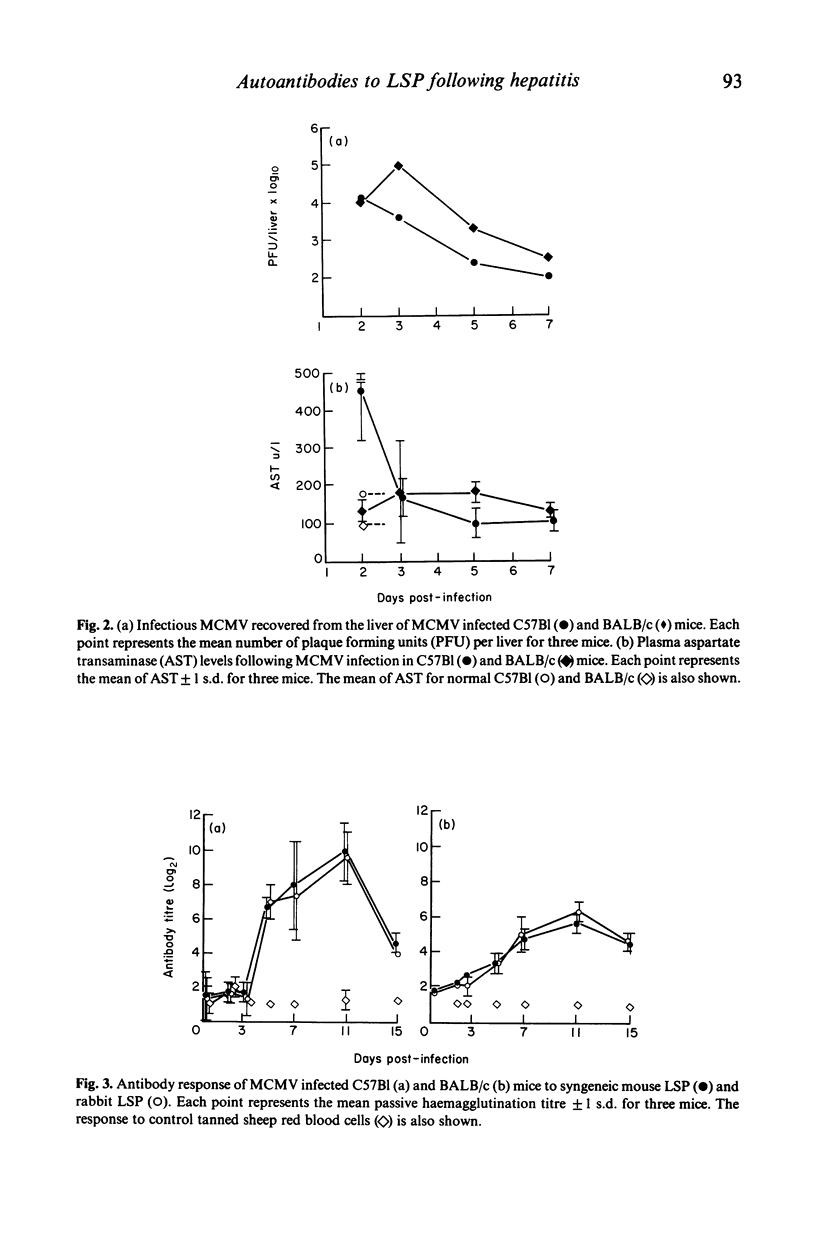
Autoantibodies to liver specific lipoprotein (LSP) are produced following acute non-fatal hepatitis in murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infected mice. Both C57B1 and BALB/c mice produced a transient LSP autoantibody response demonstrated by passive haemagglutination and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. C57Bl mice produced both IgM and IgG LSP autoantibody and BALB/c mice produced only IgM autoantibody. The autoantibody was species non-specific, reacting with both mouse and rabbit LSP. Plasma containing LSP autoantibody reacted with the surface of normal mouse hepatocytes by immunofluorescence. This model provides an opportunity for study of LSP autoantibody production during viral hepatitis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. E., Shellam G. R., Grundy J. E. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus infection on mitogen responses in genetically resistant and susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.235-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Andersen H. K. Smooth-muscle antibodies and other tissue antibodies in cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):22–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomaeus W. N., Reed W. D., Joske R. A., Shilkin K. B. Autoantibody responses to liver-specific lipoprotein in mice. Immunology. 1981 Jun;43(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixler G. S., Jr, Booss J. Adherent spleen cells from mice acutely infected with cytomegalovirus suppress the primary antibody response in vitro. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1294–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmer J. E., Mackenzie J. S., Stanley N. F. Resistance to murine cytomegalovirus linked to the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):107–114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales C., Cochrane A. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Mechanisms responsible for antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Gut. 1979 May;20(5):385–388. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.5.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., Mackenzie J. S., Stanley N. F. Influence of H-2 and non-H-2 genes on resistance to murine cytomegalovirus infection. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):277–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.277-286.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D., Smith R. D., Gehrke J. Non-fatal mouse cytomegalovirus hepatitis. Combined morphologic, virologic and immunologic observations. Am J Pathol. 1966 Nov;49(5):871–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Arnold W. Detection of a liver-membrane autoantibody in HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 11;294(11):578–582. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603112941103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Miller J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. II. Cell-mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. I. Humoral immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):109–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen D. M., McFarlane I. G., Portmann B. S., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Detection of antibodies directed against a liver-specific membrane lipoprotein in patients with acute and chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 6;299(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807062990101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Murine cytomegalovirus-induced immunosuppression. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.89-95.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manns M., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hess G. Autoantibodies against liver-specific membrane lipoprotein in acute and chronic liver diseases: studies on organ-, species-, and disease-specificity. Gut. 1980 Nov;21(11):955–961. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.11.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane I. G., Wojcicka B. M., Zucker G. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Purification and characterization of human liver-specific membrane lipoprotein (LSP). Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):381–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Kingsbury D. T., Oldstone M. B. Pathogenesis of cytomegalovirus infection. Distribution of viral products, immune complexes and autoimmunity during latent murine infection. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):267–280. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. I., Cooksley W. G., Powell L. W. Cell-mediated immunity to liver antigen in toxic liver injury. I. Occurrence and specificity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Mar;39(3):607–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinghitella T. J., Booss J. Enhanced immune response late in primary cytomegalovirus infection of mice. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2442–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wager O., Räsänen J. A., Hagman A., Klemola E. Mixed cryoimmunoglobulinaemia in infectious mononucleois and Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(4):345–361. doi: 10.1159/000230129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



