Abstract
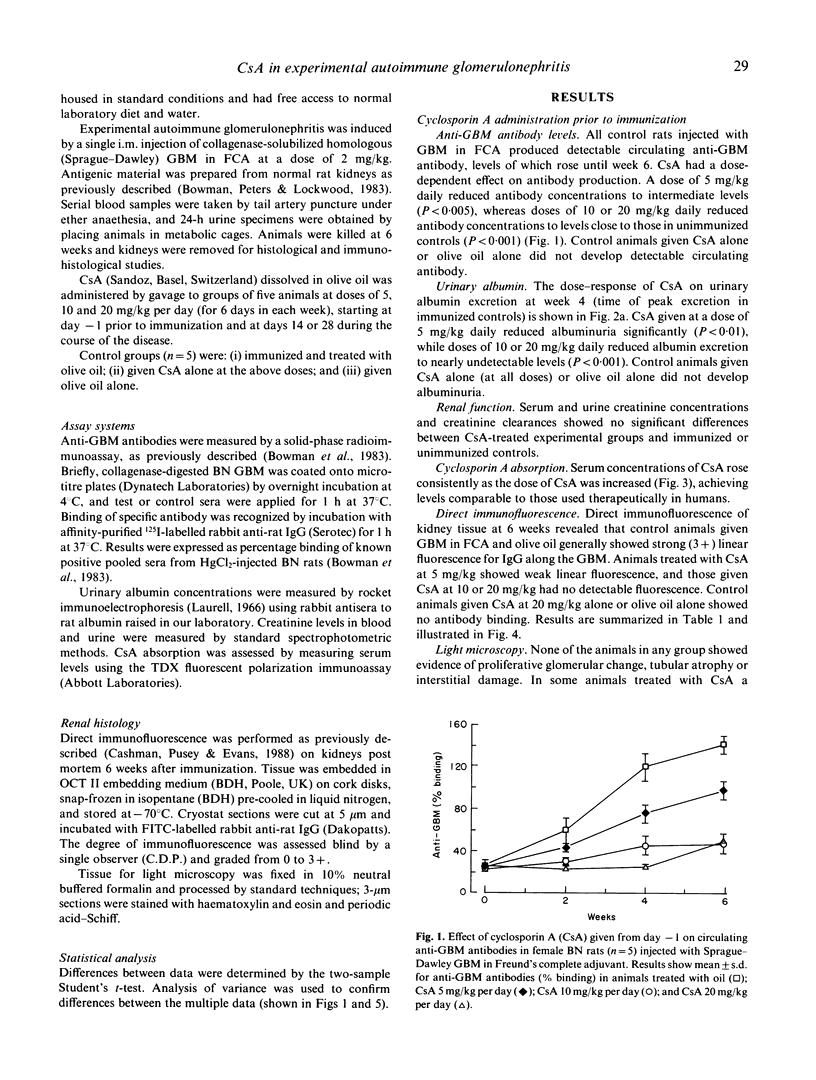
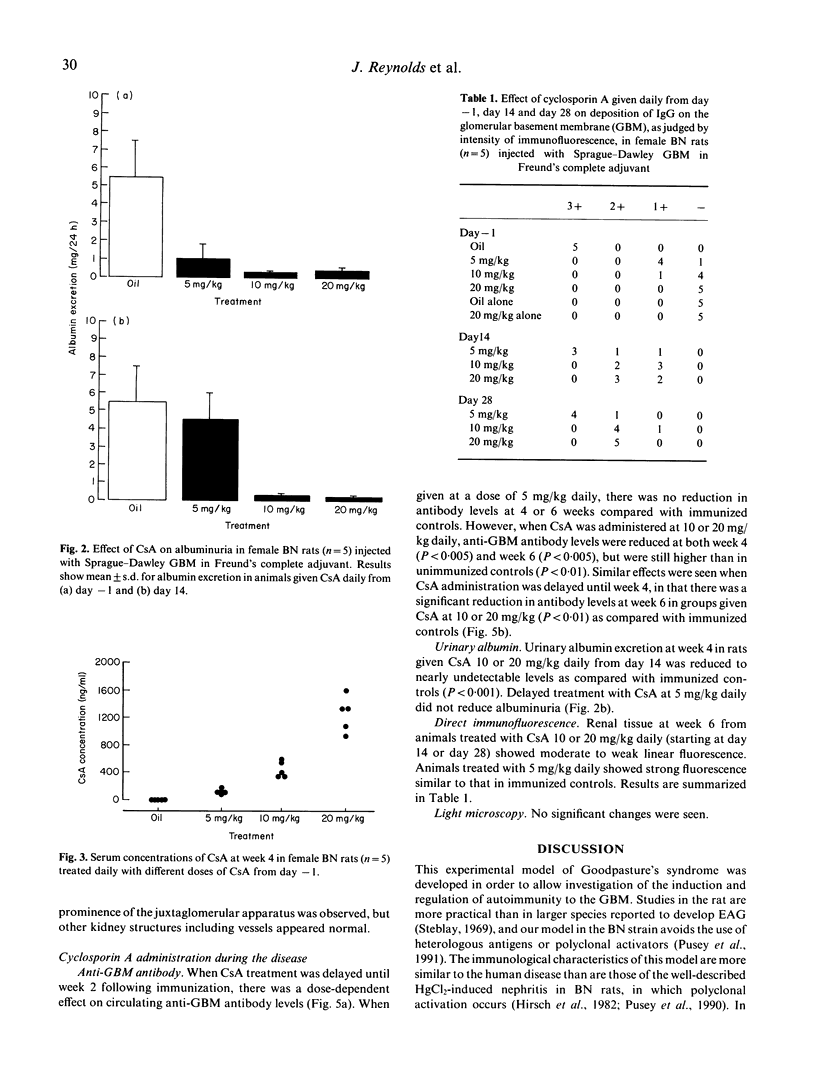
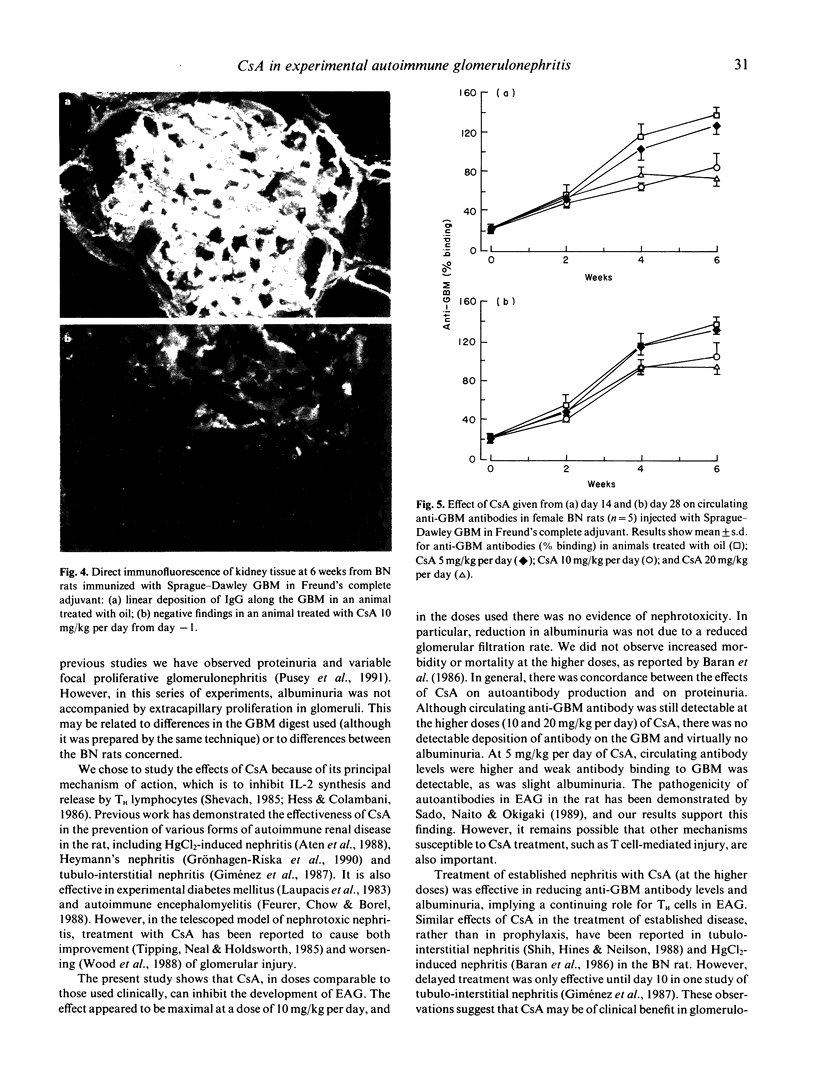
Experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis (EAG) was induced in brown Norway (BN) rats by a single i.m. injection of collagenase-solubilized homologous glomerular basement membrane (GBM) in Freund's complete adjuvant. This model of anti-GBM disease is characterized by the development, over several weeks, of circulating and deposited anti-GBM antibodies, accompanied by albuminuria. We examined the effects of treatment with oral cyclosporin A (CsA) at different doses, starting at the time of immunization and during the course of the disease. Pretreatment with CsA 5 mg kg daily produced a moderate reduction in circulating anti-GBM antibody levels, reduced deposition of antibody on the GBM and decreased albuminuria. Doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg CsA produced a marked reduction in circulating antibody, absence of detectable deposited antibody and virtual absence of albuminuria. Renal function remained normal in CsA-treated and control animals. When CsA treatment was introduced at 2 or 4 weeks after immunization, there were significant effects on the subsequent autoimmune response and albuminuria at 10 and 20 mg/kg daily. These studies demonstrate that CsA in conventional doses has a therapeutic effect in this model of anti-GBM disease, and suggest a role for T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of EAG.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aten J., Bosman C. B., De Heer E., Hoedemaeker P. J., Weening J. J. Cyclosporin A induces long-term unresponsiveness in mercuric chloride-induced autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Aug;73(2):307–311. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C., Peters D. K., Lockwood C. M. Anti-glomerular basement membrane autoantibodies in the Brown Norway rat: detection by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman S. J., Pusey C. D., Evans D. J. Extraglomerular distribution of immunoreactive Goodpasture antigen. J Pathol. 1988 May;155(1):61–70. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feurer C., Chow L. H., Borel J. F. Preventive and therapeutic effects of cyclosporin and valine2-dihydro-cyclosporin in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):219–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giménez A., Leyva-Cobián F., Fierro C., Río M., Bricio T., Mampaso F. Effect of cyclosporin A on autoimmune tubulointerstitial nephritis in the brown Norway rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):550–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönhagen-Riska C., von Willebrand E., Tikkanen T., Honkanen E., Miettinen A., Holthöfer H., Törnroth T. The effect of cyclosporin A on the interstitial mononuclear cell infiltration and the induction of Heymann's nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):266–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. D., Colombani P. M. Cyclosporin. Mechanism of action: in vitro studies. Prog Allergy. 1986;38:198–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch F., Couderc J., Sapin C., Fournie G., Druet P. Polyclonal effect of HgCl2 in the rat, its possible role in an experimental autoimmune disease. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jul;12(7):620–625. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laupacis A., Stiller C. R., Gardell C., Keown P., Dupre J., Wallace A. C., Thibert P. Cyclosporin prevents diabetes in BB Wistar rats. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. The role of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody in the pathogenesis of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):989–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallamaci F., Zoccali C., Ciccarelli M., Briggs J. D. Autonomic function in uremic patients treated by hemodialysis or CAPD and in transplant patients. Clin Nephrol. 1986 Apr;25(4):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Rees A. J., Lockwood C. M., Pusey C. D. Treatment and prognosis in antibasement membrane antibody-mediated nephritis. Transplant Proc. 1982 Sep;14(3):513–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey C. D., Bowman C., Morgan A., Weetman A. P., Hartley B., Lockwood C. M. Kinetics and pathogenicity of autoantibodies induced by mercuric chloride in the brown Norway rat. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):76–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEBLAY R. W. Glomerulonephritis induced in sheep by injections of heterologous glomerular basement membrane and Freund's complete adjuvant. J Exp Med. 1962 Aug 1;116:253–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sado Y., Naito I. Experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis in rats by soluble isologous or homologous antigens from glomerular and tubular basement membranes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Oct;68(5):695–704. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sado Y., Naito I., Okigaki T. Transfer of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis in inbred rats with isologous antibodies from the urine of nephritic rats. J Pathol. 1989 Aug;158(4):325–332. doi: 10.1002/path.1711580410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M. The effects of cyclosporin A on the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:397–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih W., Hines W. H., Neilson E. G. Effects of cyclosporin A on the development of immune-mediated interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 1988 Jun;33(6):1113–1118. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping P. G., Neale T. J., Holdsworth S. R. T lymphocyte participation in antibody-induced experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1985 Mar;27(3):530–537. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1973 Feb;3(2):74–89. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A., Adu D., Birtwistle R. J., Brewer D. B., Michael J. Cyclosporin A and anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody glomerulonephritis in rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Apr;69(2):189–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L., Acha-Orbea H. T cell recognition as the target for immune intervention in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90786-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


