Abstract
The relative contribution of different lymphoid tissues to the anti-CII antibody response was studied in rats with arthritis produced as a result of immunizing them with collagen type II (CII). Antibody production was measured by maintaining lymphoid cells in short-term culture in collagen-coated microculture wells: the antibody they secreted was determined directly by a modified ELISA. Systemic sensitization to CII was established within a week of immunization, and a stronger response in the local draining lymph nodes relative to the spleen was associated with the development of clinical disease. From experiments involving splenectomy and adoptive cell transfer, the spleen was ascribed a suppressive role in controlling both arthritis and total antibody production. The bone marrow was found to be an important site of antibody production and the greater production of antibody by cells from tibial marrow in limbs with arthritis, compared with healthy limbs, argues for a local immune response to degrading joint antigens that may have systemic suppressive or protective properties. It is concluded that local immunity reflects the state of disease and that the antibodies produced by different lymphoid tissues may be made in response to different stimuli, and that the antibodies in turn may have different pathological effects.
Full text
PDF

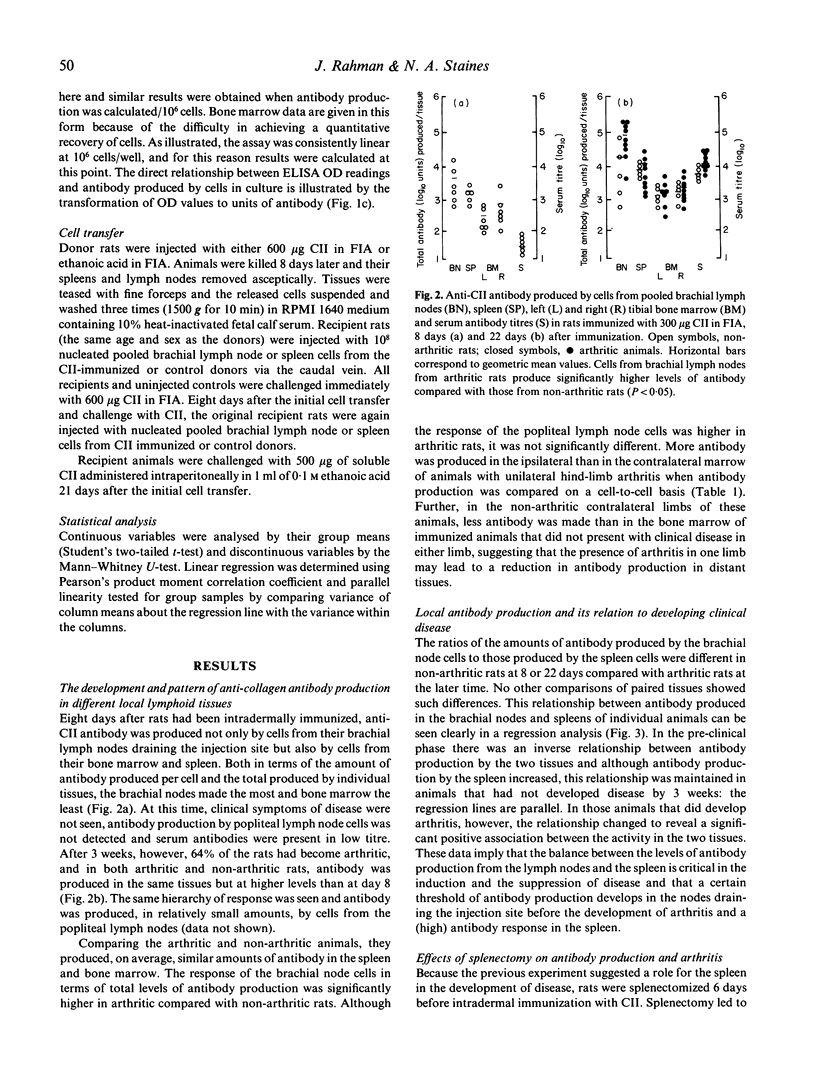
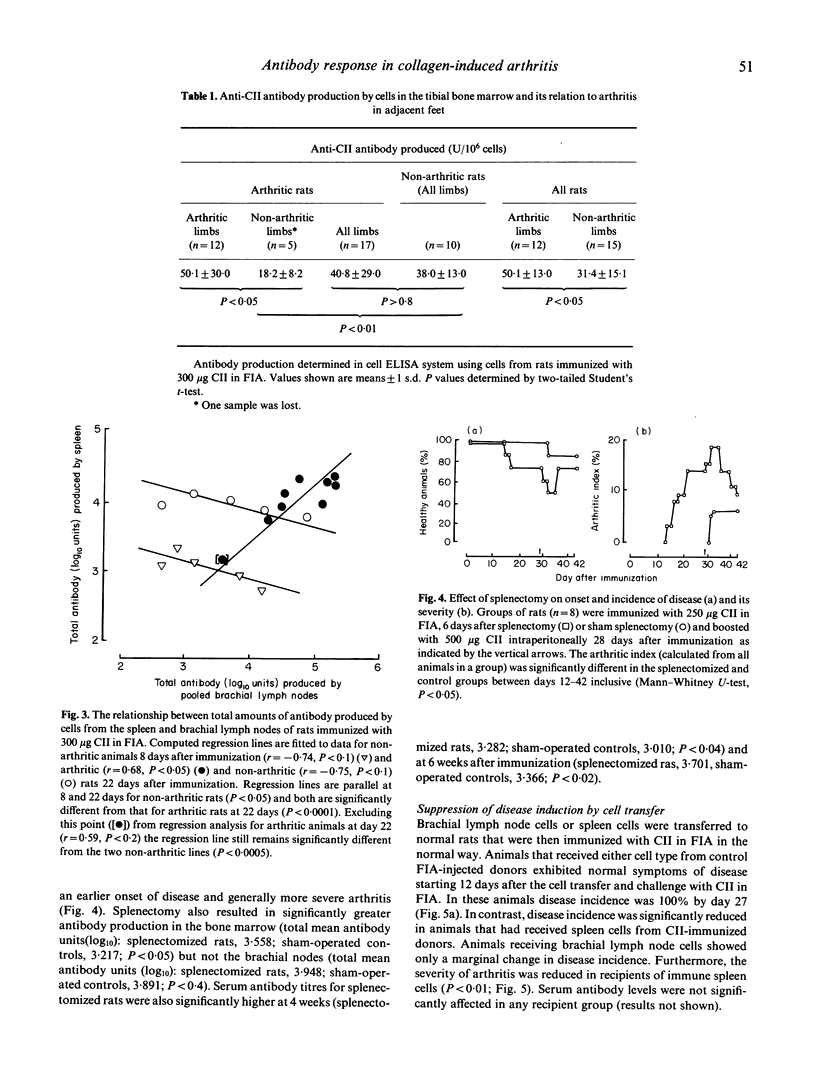
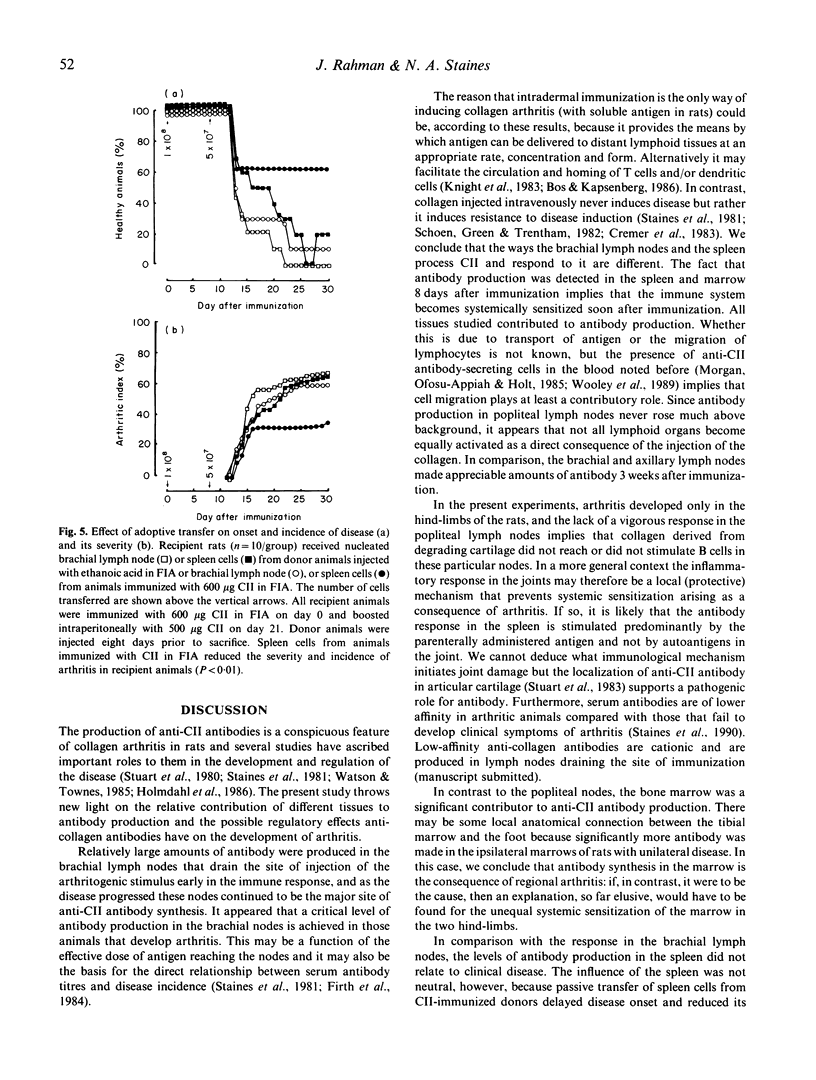


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arita C., Kaibara N., Jingushi S., Takagishi K., Hotokebuchi T., Arai K. Suppression of collagen arthritis in rats by heterologous anti-idiotypic antisera against anticollagen antibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jun;43(3):374–381. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrai I., Henderson B., Knight S. C., Staines N. A. Suppression of collagen type II-induced arthritis by transfer of lymphoid cells from rats immunized with collagen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Aug;61(2):368–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. O., Finlay-Jones J. J. Impaired regulation of erythrocyte autoantibody production after splenectomy. Br J Exp Pathol. 1979 Oct;60(5):466–470. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer M. A., Hernandez A. D., Townes A. S., Stuart J. M., Kang A. H. Collagen-induced arthritis in rats: antigen-specific suppression of arthritis and immunity by intravenously injected native type II collagen. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2995–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englert M., McReynolds R. A., Landes M. J., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Pretreatment of rats with anticollagen IgG renders them resistant to active type II collagen arthritis. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jan;90(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firth S. A., Morgan K., Evans H. B., Holt P. J. IgG subclasses in collagen-induced arthritis in the rat. Immunol Lett. 1984;7(5):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(84)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Rubin K., Klareskog L., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Characterization of the antibody response in mice with type II collagen-induced arthritis, using monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):400–410. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly B. S., Levy J. G., Sikora L. The use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection and quantification of specific antibody from cell cultures. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):45–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Holmdahl R., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Role of T lymphocytes in collagen II induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jan;51(1):117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. C., Mertin J., Stackpoole A., Clark J. Induction of immune responses in vivo with small numbers of veiled (dendritic) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6032–6035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresina T. F., Finegan C. K. Restricted expression of anti-type II collagen antibody isotypes in mice suppressed for collagen-induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jan;45(1):60–66. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresina T. F., Moskowitz R. W. Adoptive transfer of suppression of arthritis in the mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis. Evidence for a type II collagen-specific suppressor T cell. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1990–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI111917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K., Ofosu-Appiah W. A., Holt P. J. Collagen-induced arthritis--use of the direct and indirect haemolytic plaque-assay to study the humoral response to collagen. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Jul-Sep;3(3):229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., Bober L. A., Robinson M. E., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Suppression of type II collagen-induced arthritis by intragastric administration of soluble type II collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7443–7446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubinian J. R., Papoian R., Pillarisetty R., Sawada S., Talal N. Immunological regulation of spontaneous antibodies to DNA and RNA. III. Early effects of neonatal thymectomy and splenectomy. Immunology. 1977 Sep;33(3):399–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoen R. T., Greene M. I., Trentham D. E. Antigen-specific suppression of type II collagen-induced arthritis by collagen-coupled spleen cells. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):717–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Ekong T. A., Thompson H. S., Isaacs A. B., Loryman B., Major P. J., Hobbs S. M., Devey M. E. Low affinity antibodies against collagen type II are associated with pathology in collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Autoimmun. 1990 Dec;3(6):643–657. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Hardingham T., Smith M., Henderson B. Collagen-induced arthritis in the rat: modification of immune and arthritic responses by free collagen and immune anti-collagen antiserum. Immunology. 1981 Dec;44(4):737–744. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Dixon F. J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):378–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. S., Henderson B., Spencer J. M., Hobbs S. M., Peppard J. V., Staines N. A. Tolerogenic activity of polymerized type II collagen in preventing collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Apr;72(1):20–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. S., Staines N. A. Gastric administration of type II collagen delays the onset and severity of collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):581–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., David J. R. Passive transfer by cells of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):359–366. doi: 10.1172/JCI109136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson W. C., Townes A. S. Genetic susceptibility to murine collagen II autoimmune arthritis. Proposed relationship to the IgG2 autoantibody subclass response, complement C5, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and non-MHC loci. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1878–1891. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., McGregor A. M., Hall R. A short-term-culture ELISA system to detect IgG and autoantibody synthesis by human lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Oct 15;54(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Whalen J. D., Warner L. M., Losten M. K., Chapdelaine J. M. Type II collagen induced arthritis in mice. V. The role of the spleen cell response in the immune and arthritogenic reaction to type II collagen. J Rheumatol. 1989 Sep;16(9):1192–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


