Abstract
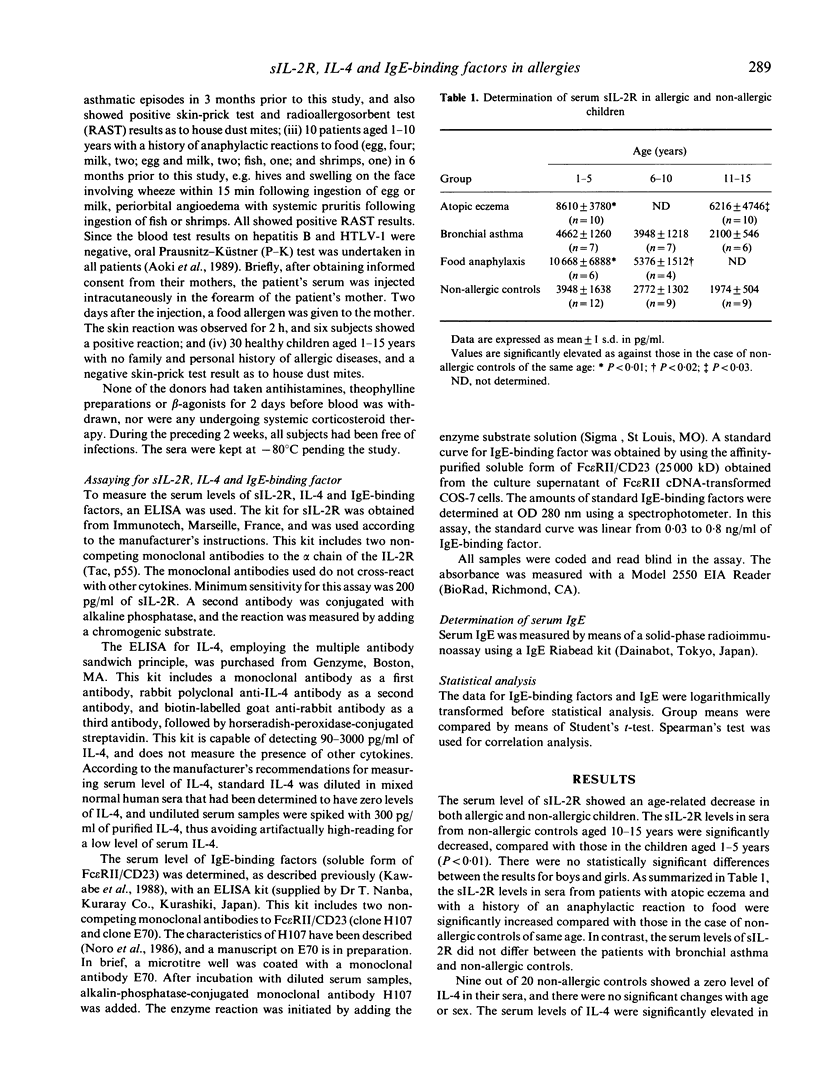
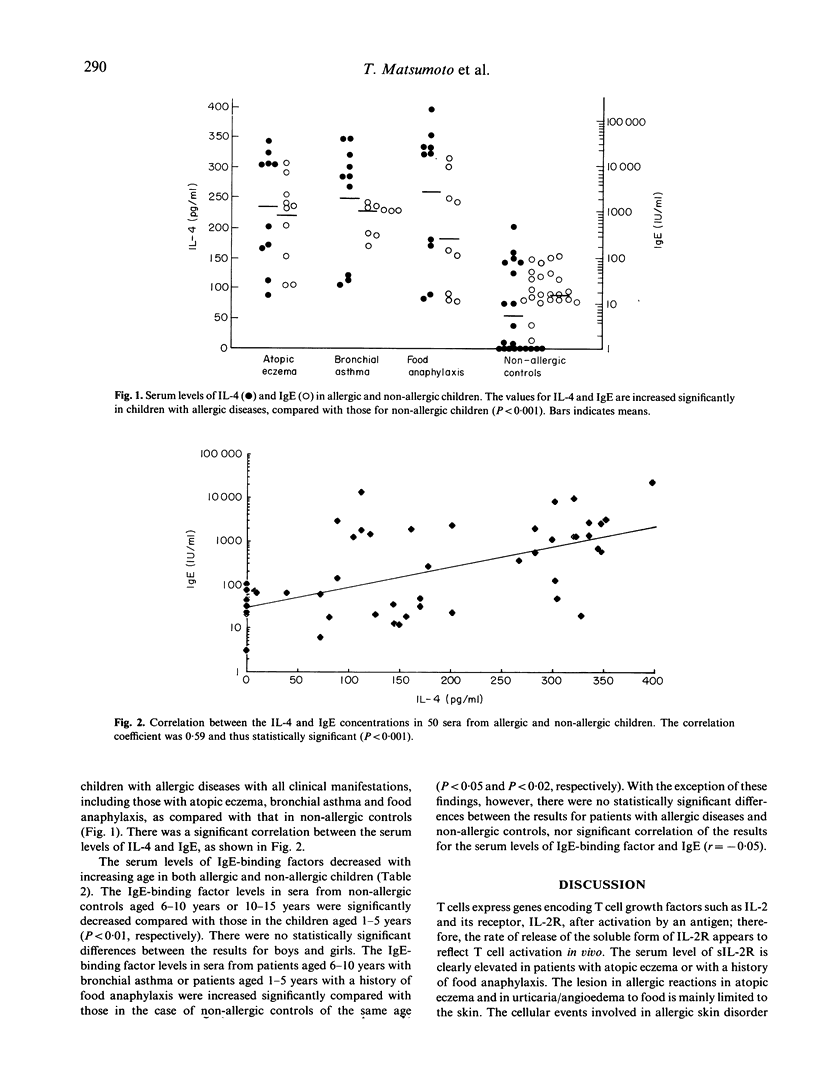
The serum levels of soluble IL-2 receptor (sIL-2R), IL-4 and IgE-binding factors were examined in children with allergic diseases, and compared with those in non-allergic controls of the same age and sex. The results showed age-related decreases in the serum levels of sIL-2R and IgE-binding factors, but not in that of IL-4 in both allergic and non-allergic individuals. Significant elevation of sIL-2R was observed in sera from children with atopic eczema or history of an anaphylactic reaction to food, as compared with that in non-allergic controls. The serum concentration of IL-4 was elevated in all allergic groups, including cases of atopic eczema, bronchial asthma and anaphylaxis to food, compared with non-allergic controls, and was correlated significantly with the serum level of IgE (r = 0.59). The IgE-binding factor levels in sera from patients aged 6-10 years with bronchial asthma, or patients aged 1-5 years with a history of food anaphylaxis were elevated as compared with those in non-allergic controls of same age. There was no significant correlation between the serum levels of IgE-binding factors and IgE. Since sIL-2R is released by activated T cells, the present study is in favour of T cell activation causing allergic skin disorders. The serum levels of IL-4 as well as IgE did not differ among allergic patients of different clinical categories. The role of IgE in atopic eczema and other allergic diseases is not clearly established; however, it seems likely that IL-4 is deeply involved in the increased production of IgE seen in allergic individuals. The possible involvement of IgE-binding factors in the age-related changes of clinical manifestations in childhood allergic diseases was also discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T., Funai T., Kojima M., Adachi J. Absorption of egg antigens by the gut observed by oral Prausnitz-Küstner (Walzer) reaction in atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1989;144:100–104. doi: 10.2340/00015555144100104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra R. K., Baker M. Numerical and functional deficiency of suppressor T cells precedes development of atopic eczema. Lancet. 1983 Dec 17;2(8364):1393–1394. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90924-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claassen J. L., Levine A. D., Buckley R. H. Recombinant human IL-4 induces IgE and IgG synthesis by normal and atopic donor mononuclear cells. Similar dose response, time course, requirement for T cells, and effect of pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2123–2130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Flores-Romo L., Cairns J. A., Millsum M. J., Lane P. J., Johnson G. D., MacLennan I. C. CD23: a multi-functional receptor/lymphokine? Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemady Z., Gellis S., Chambers M., Rocklin R. E. Abnormal regulation of in vitro IgE synthesis by T cells obtained from patients with atopic dermatitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 May;35(2):156–168. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Takami M., Hosoda M., Maeda Y., Sato S., Mayumi M., Mikawa H., Arai K., Yodoi J. Regulation of Fc epsilon R2/CD23 gene expression by cytokines and specific ligands (IgE and anti-Fc epsilon R2 monoclonal antibody). Variable regulation depending on the cell types. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1376–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi E., Del Prete G. F., Parronchi P., Tiri A., Macchia D., Biswas P., Simonelli C., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Role for T cells, IL-2 and IL-6 in the IL-4-dependent in vitro human IgE synthesis. Immunology. 1989 Nov;68(3):300–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Miike T., Mizoguchi K., Yamaguchi K., Takatsuki K., Hosoda M., Kawabe T., Yodoi J. Decreased serum levels of IgE and IgE-binding factors in individuals infected with HTLV-I. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):207–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Takahashi H., Miike T. Increase of T cells bearing Fc epsilon R-associated antigen in patients with atopic asthma. Ann Allergy. 1987 Apr;58(4):261–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noro N., Yoshioka A., Adachi M., Yasuda K., Masuda T., Yodoi J. Monoclonal antibody (H107) inhibiting IgE binding to Fc epsilon R(+) human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1258–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H. Serum interleukin-2 receptor: clinical and biological implications. Leukemia. 1989 May;3(5):323–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Wideman J., Bonnefoy J. Y., De Vries J. E. Interleukin 5 enhances interleukin 4-induced IgE production by normal human B cells. The role of soluble CD23 antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):929–935. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Bron D., Lagneaux L., Fonteyn C., Frost H., Delespesse G. Elevation of IgE-binding factors in serum of patients with B cell-derived chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Rector E., Wong K., Rubio-Trujillo M., Sehon A. H., Delespesse G. In vitro synthesis of IgE by human lymphocytes. II. Enhancement of the spontaneous IgE synthesis by IgE-binding factors secreted by RPMI 8866 lymphoblastoid B cells. Immunology. 1984 Oct;53(2):197–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Geha R. S., Maksad K. N., Leung D. Y. Characterization of human T cell-derived IgE-potentiating factor. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Aug;16(8):985–991. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


