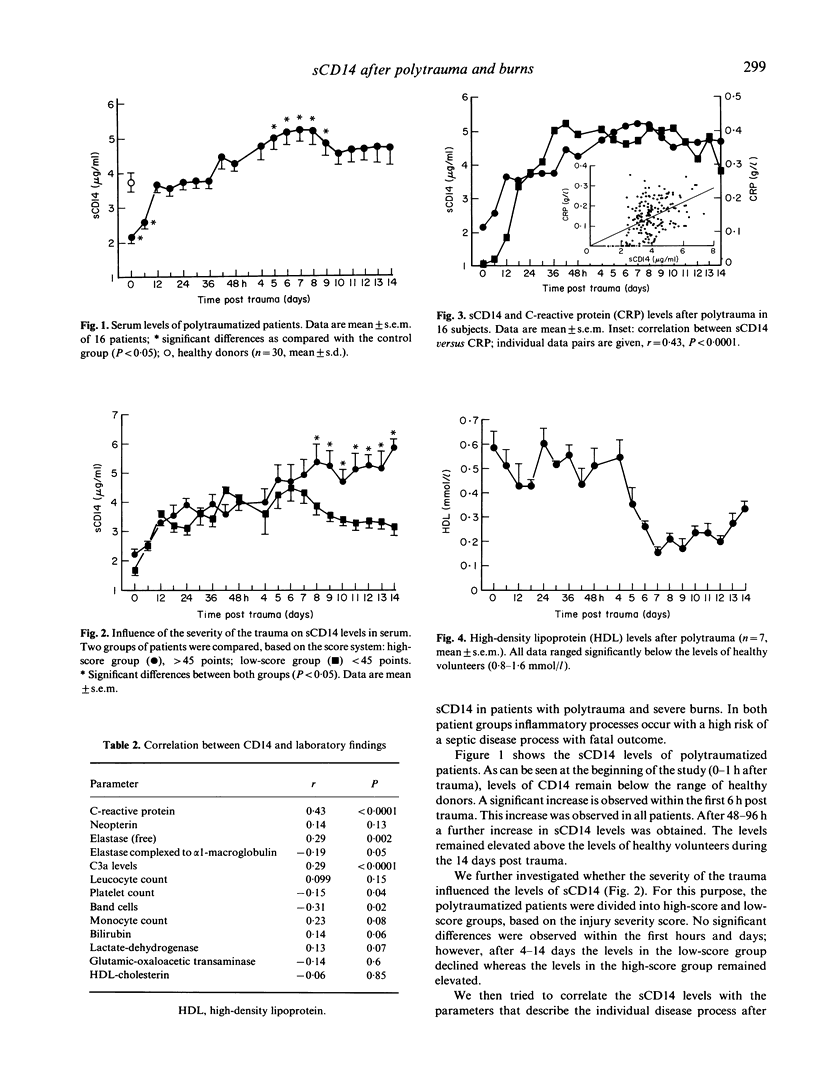
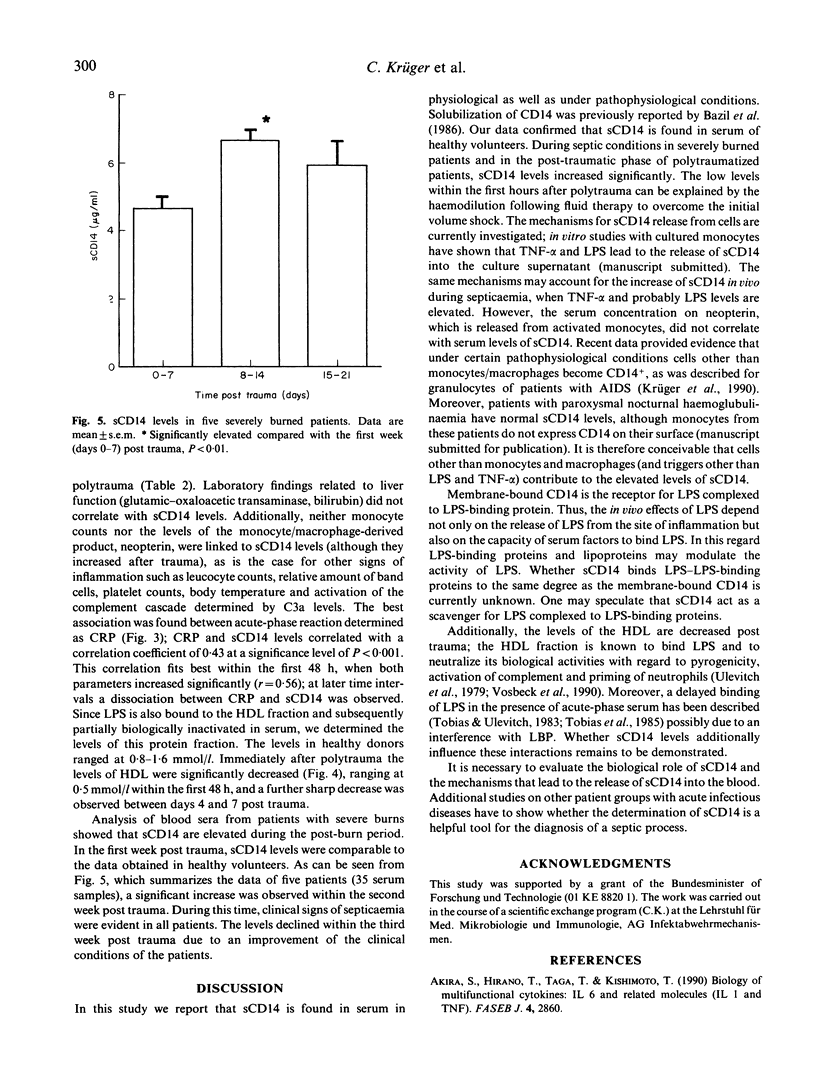
Abstract
Recently it has been demonstrated that the CD14 molecule which is expressed on monocytes and macrophages serves as a receptor for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) bound to LPS-binding protein (LBP) and thus mediates LPS-induced tumour necrosis factor (TNF) production. Here we report that CD14 is found as a soluble (s) molecule in serum. In healthy volunteers sCD14 levels (mean +/- s.e.m.) were 3.7 +/- 0.05 micrograms/ml (n = 30, 25-50 years of age) as determined by ELISA (detection limit 20 ng/ml serum) using two monoclonal antibodies in a sandwich technique. In polytraumatized patients (n = 16) significantly decreased levels (1.7 +/- 0.3) were detected immediately after the trauma, which increased to 4.9 +/- 0.3 micrograms/ml within the first 6 days post trauma. sCD14 remained elevated during the first 14 days post trauma in patients with the most severe injuries (injury severity score greater than 45 points), whereas a return to normal levels was observed in patients with an injury score of less than 45 points. In addition, the levels of the high-density lipoproteins that partially inactivate free endotoxin are significantly decreased post trauma. No correlation between parameters of inflammation (C3a and neopterin levels, leucocyte counts, amount of band cells), liver function and sCD14 levels was established. Comparable to polytraumatized patients, increased sCD14 serum levels were observed in five patients with burn trauma (burned area greater than 35%) within the second week post trauma when clinical signs of septicaemia were evident.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arturson G. Neutrophil granulocyte functions in severely burned patients. Burns Incl Therm Inj. 1985 Jun;11(5):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0305-4179(85)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. P., O'Neill B., Haddon W., Jr, Long W. B. The injury severity score: a method for describing patients with multiple injuries and evaluating emergency care. J Trauma. 1974 Mar;14(3):187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Horejsí V., Baudys M., Kristofová H., Strominger J. L., Kostka W., Hilgert I. Biochemical characterization of a soluble form of the 53-kDa monocyte surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCamp M. M., Demling R. H. Posttraumatic multisystem organ failure. JAMA. 1988 Jul 22;260(4):530–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. R., Faist E. Trauma and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Sep;9(9):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91300-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köller M., König W., Brom J., Erbs G., Müller F. E. Studies on the mechanisms of granulocyte dysfunctions in severely burned patients--evidence for altered leukotriene generation. J Trauma. 1989 Apr;29(4):435–445. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198904000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Marks C. B., Luce J. M., Montgomery A. B., Turner J., Metz C. A., Murray J. F. Plasma tumor necrosis factor in patients with septic shock. Mortality rate, incidence of adult respiratory distress syndrome, and effects of methylprednisolone administration. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Jan;141(1):94–97. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Cybulsky M. I., Colditz I. G., Chan M. K., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation in gram-negative infection: endotoxin, interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and neutrophils. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld W., Kasimir S., Köller M., Erbs G., Müller F. E., König W. Metabolism of platelet activating factor (PAF) and lyso-PAF in polymorphonuclear granulocytes from severely burned patients. J Trauma. 1990 Dec;30(12):1554–1561. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199012000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütt C., Ringel B., Nausch M., Bazil V., Horejsí V., Neels P., Walzel H., Jonas L., Siegl E., Friemel H. Human monocyte activation induced by an anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody. Immunol Lett. 1988 Dec;19(4):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. S., Richards S. J., Master P. S., Kendall J., Limbert H. J., Roberts B. E. Flow cytometric analysis of membrane CD11b, CD11c and CD14 expression in acute myeloid leukaemia: relationships with monocytic subtypes and the concept of relative antigen expression. Eur J Haematol. 1990 Jan;44(1):24–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1990.tb00342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., McAdam K. P., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Control of lipopolysaccharide-high-density lipoprotein interactions by an acute-phase reactant in human serum. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):73–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.73-76.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Identification of a lipid A binding site in the acute phase reactant lipopolysaccharide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10867–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Their participation in intravascular reactions of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI109610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosbeck K., Tobias P., Mueller H., Allen R. A., Arfors K. E., Ulevitch R. J., Sklar L. A. Priming of polymorphonuclear granulocytes by lipopolysaccharides and its complexes with lipopolysaccharide binding protein and high density lipoprotein. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Feb;47(2):97–104. doi: 10.1002/jlb.47.2.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal O. Bacterial endotoxins. The second Carl Prausnitz Memorial Lecture. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(1-2):1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


