Abstract
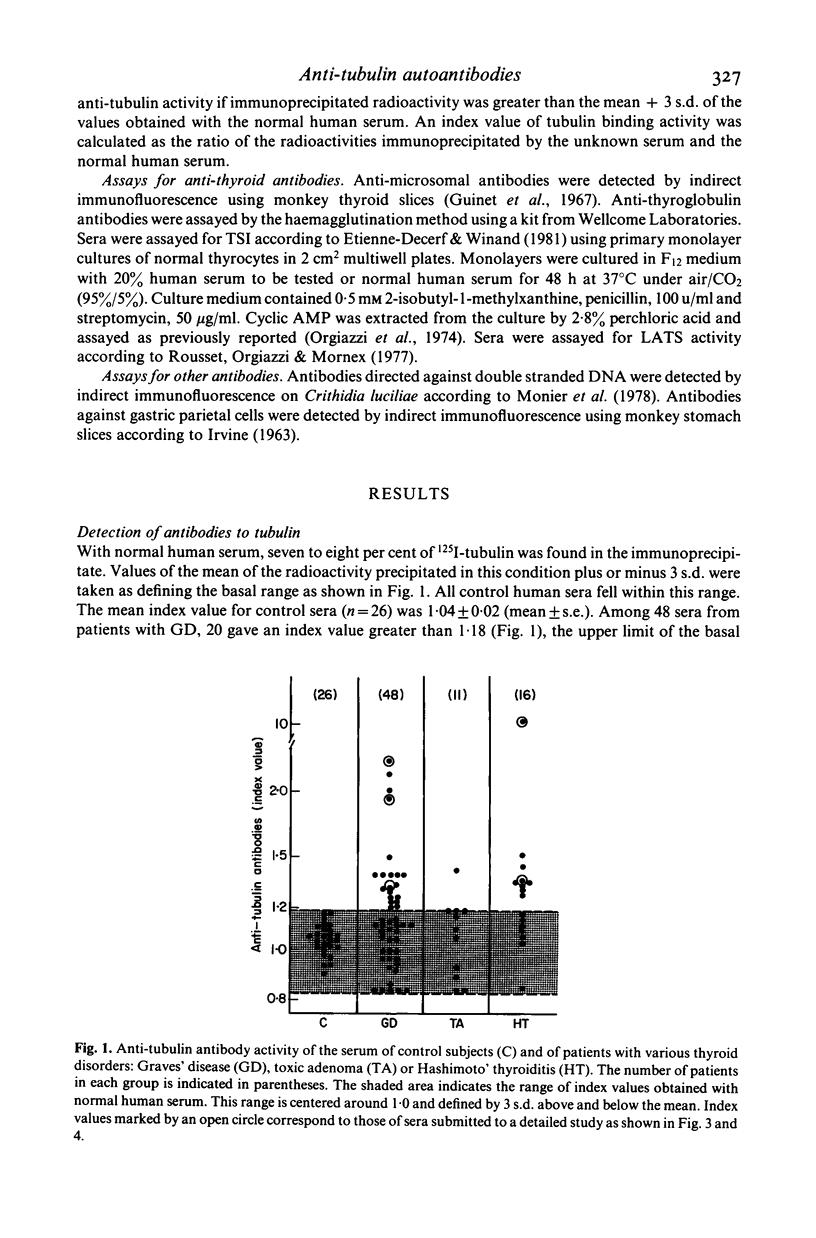
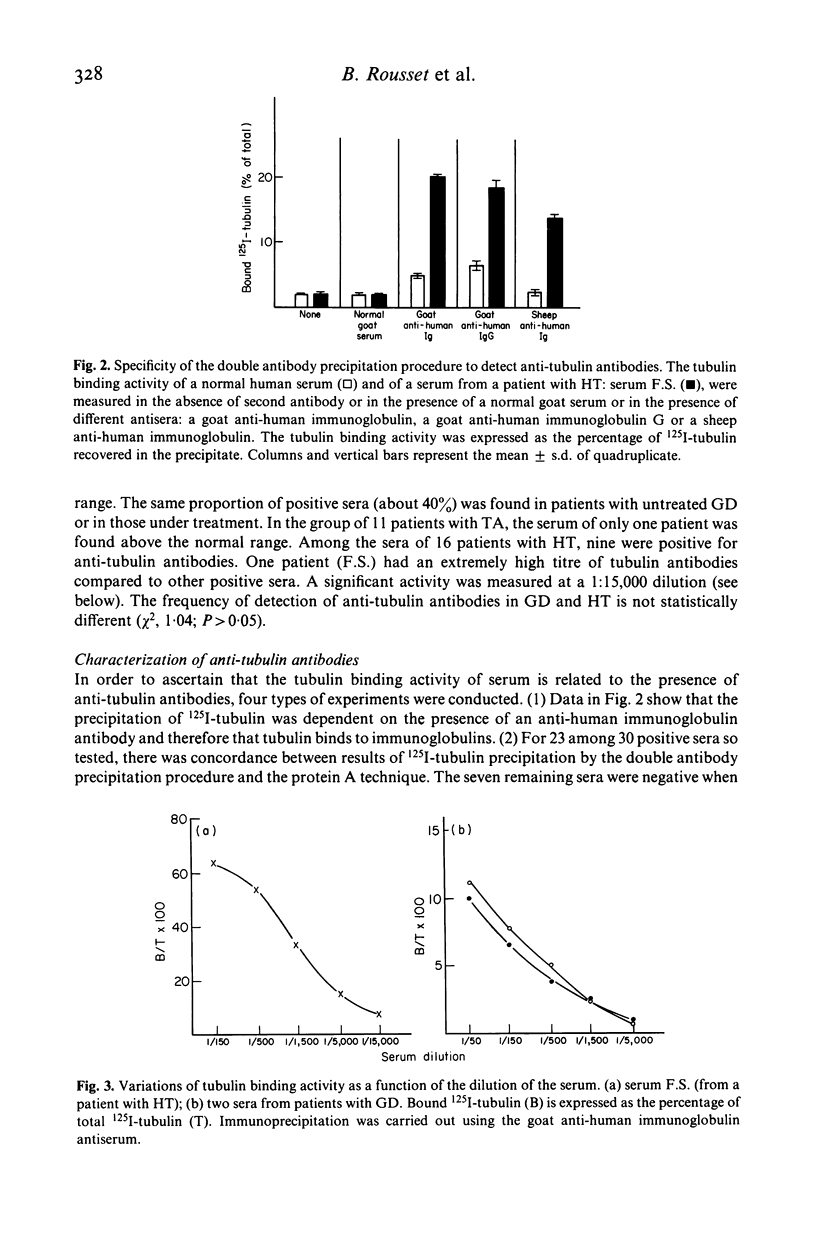
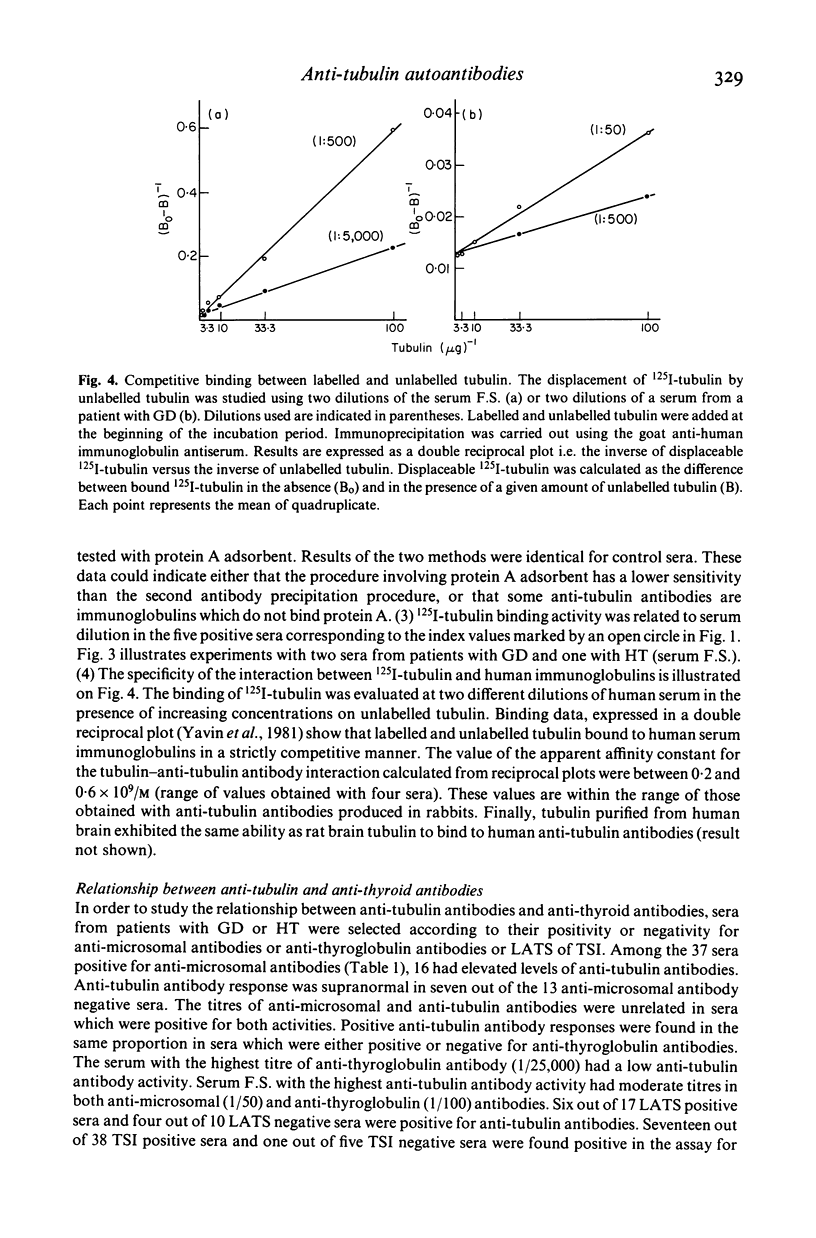
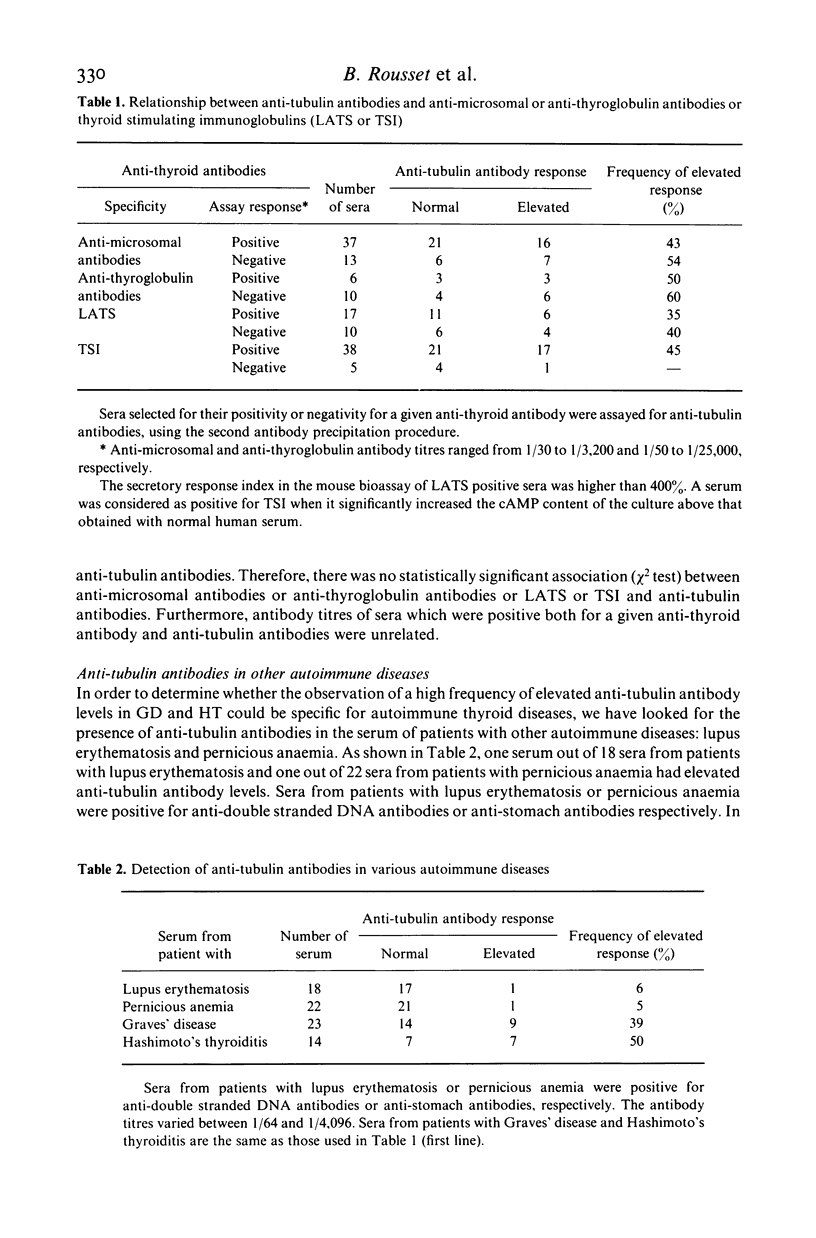
The presence of circulating antibodies directed against a cytoskeletal element, microtubules, in patients with autoimmune thyroid disorders, has been studied using pure brain tubulin as antigen. Immune complexes were immunoprecipitated using a goat anti-human immunoglobulin antibody. Twenty sera among 48 (41%) from patients with Graves' disease and nine sera among 16 (56%) from patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis had increased levels of anti-tubulin antibodies as compared to that of 26 sera from control subjects. Only one serum among 11 from patients with toxic adenoma was positive. Very similar results were obtained using protein A adsorbent to collect immune complexes. Specificity of the tubulin binding activity was ascertained by dilution of the sera and displacement of tracer tubulin by unlabelled pure tubulin from rat or human brain. Anti-tubulin antibody titres were variable; one serum was positive at dilution higher than 1:15,000, a titre similar to those obtained in animals experimentally immunized against tubulin. Binding of labelled and unlabelled tubulin to immunoglobulins from positive sera was strictly competitive. The apparent affinity constant for the binding of tubulin to human anti-tubulin autoantibodies determined on four sera was 0.2-0.6 X 10(9)/M. There was no significant association between anti-tubulin antibodies and anti-microsomal antibodies or anti-thyroglobulin antibodies or thyroid stimulating antibodies. In contrast, only five to six per cent of sera from patients with other autoimmune diseases: lupus erythematosis or pernicious anaemia, had increased levels of anti-tubulin antibodies. In conclusion, tubulin represents a new autoantigen which is expressed rather specifically in autoimmune thyroid disorders and probably independently from the classical thyroid antigens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernier-Valentin F., Rousset B. Interaction of tubulin with rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7092–7099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne-Decerf J., Winand R. J. A sensitive technique for determination of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) in unfractionated serum. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Jan;14(1):83–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinet P., Mornex R., Pousset U. G., Monier J. C., Thivolet J. Utilisation de la technique d'immunofluorescence pour la recherche des anticorps antithyroïdiens. Lyon Med. 1967 Dec 10;218(50):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRVINE W. J. GASTRIC ANTIBODIES STUDIED BY FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1963 Oct;48:427–438. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1963.sp001685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Guilbert B., Bornens M., Avrameas S. Antibodies to tubulin in normal nonimmunized animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. M., Cowin P., Whitehouse J. M. Antitubulin antibody in healthy adults and patients with infectious mononucleosis and its relationship to smooth muscle antibody (SMA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):328–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier J. C., Perraud M., Picard F., Gioud M. Comparison of three techniques for the detection of antibodies to double-stranded DNA: immunofluorescence on Trypanosoma gambiense, immunofluorescence on Crithidia luciliae and radioimmunoassay using the Farr technique. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1978 Apr-Jun;129 100(4):463–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset B., Orgiazzi J., Mornex R. Perchlorate ion enhances mouse thyroid responsiveness to thyrotropin, human chorionic gonadotropin and long acting thyroid stimulator. Endocrinology. 1977 Jun;100(6):1628–1635. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-6-1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset B., Wolff J. Purification of brain tubulin by affinity chromatography on immobilized lactoperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11677–11681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


