Abstract
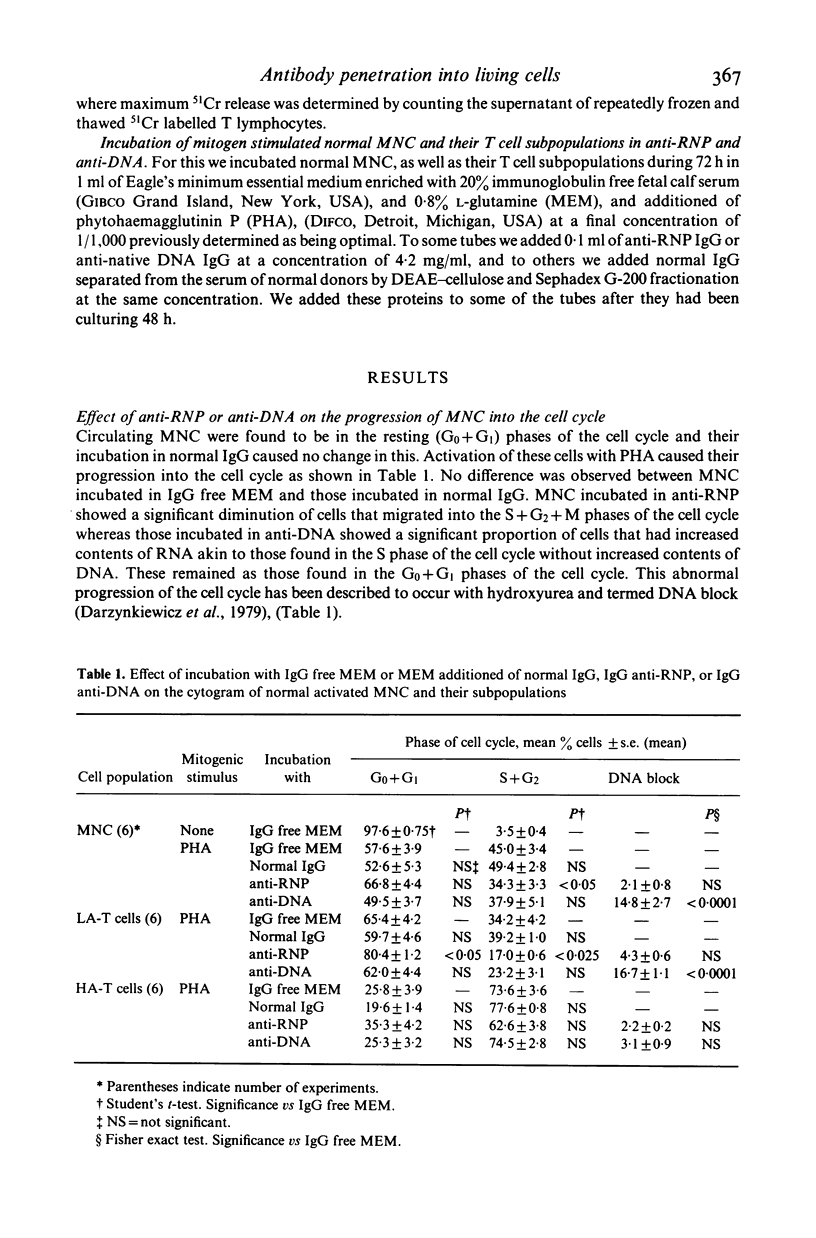
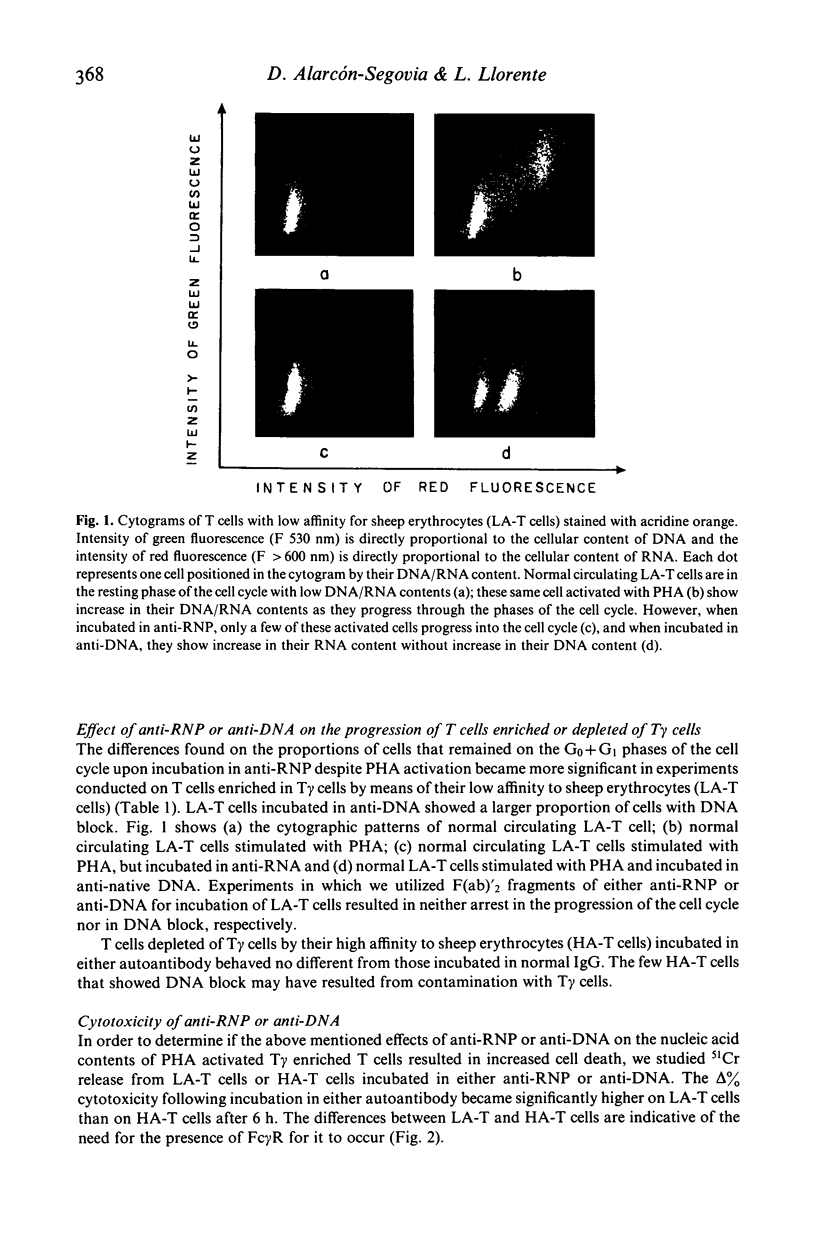
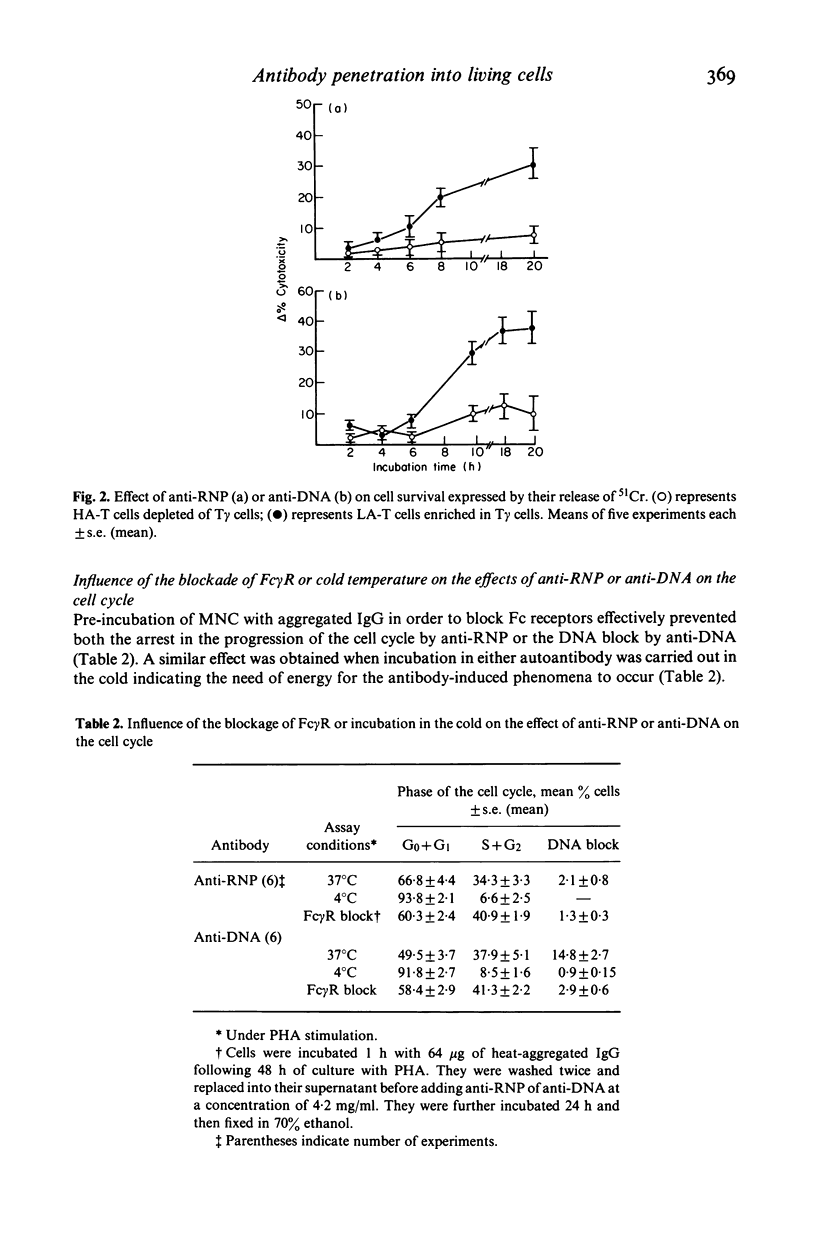
Normal T cells bearing receptors for the Fc portion of IgG that were incubated in anti-RNP or anti-DNA at the time of activation with phytohaemagglutinin showed different effects on this activation as determined by flow cytometric analysis of acridine orange stained cells. Incubation in anti-RNP caused an arrest in the progression from the G0 + G1 to the S + G2 phases of the cell cycle. Incubation in anti-native DNA caused activated cells to have an increase in their RNA content without a concomitant increase in their DNA content (DNA block). These effects were not seen in T cells that were depleted of T gamma cells by means of their property of forming rosettes with high affinity for sheep erythrocytes. Use of F(ab')2 fragments of either autoantibody, pre-incubation with aggregated IgG, or incubation with the respective autoantibodies in the cold effectively prevented their effect on the nucleic acid content of T gamma cells. Despite their different effect on the cell cycle both antibodies caused similar increase of 51Cr release of low affinity T cells 6 h after incubation in them. Our findings show that different anti-nuclear antibodies seem to cause different effects upon the cells they penetrate. These differences may have pathogenetic significance in the diseases where these antibodies occur.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcon-Segovia D., Llorente L., Ruiz-Arguelles A. Antibody penetration into living cells. III. Effect of antiribonucleoprotein IgG on the cell cycle of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Apr;23(1):22–33. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcon-Segovia D., Ruiz-Arguelles A., Fishbein E. Antibody to nuclear ribonucleoprotein penetrates live human mononuclear cells through Fc receptors. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):67–69. doi: 10.1038/271067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcon-Segovia D., Ruiz-Arguelles A., Llorente L. Antibody penetration into living cells. II. Anti-ribonucleoprotein IgG penetrates into Tgamma lymphocytes causing their deletion and the abrogation of suppressor function. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1855–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Ruíz-Argüelles A., Fishbein E. Antibody penetration into living cells. I. Intranuclear immunoglobulin in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in mixed connective tissue disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Mar;35(3):364–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Evenson D., Staiano-Coico L., Sharpless T., Melamed M. R. Relationship between RNA content and progression of lymphocytes through S phase of cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):358–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Traganos F., Sharpless T., Melamed M. R. Interphase and metaphase chromatin. Different stainability of DNA with acridine orange after treatment at low pH. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Nov;110(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Jouanen E., Rivero S. J., Llorente L., Alarcón-Segovia D. Receptor and non-receptor-bearing lymphocytes in untreated systemic lupus erythematosus. Variations with disease activity. Rev Invest Clin. 1977 Oct-Dec;29(4):265–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried J., Perez A. G., Clarkson B. D. Flow cytofluorometric analysis of cell cycle distributions using propidium iodide. Properties of the method and mathematical analysis of the data. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):172–181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivero S. J., Llorente L., Díaz-Jouanen E., Alarcón-Segovia D. T-lymphocyte subpopulation in untreated SLE. Variations with disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1169–1173. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Payne S. M., Weese J. L., Herberman R. B. Human T lymphocyte subpopulations: correlation between E-rosette-forming affinity and expression of the Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):548–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


