Abstract
IgG subclasses of antibodies to rubella were determined in indirect enzyme linked immunoassay (ELISA) with monoclonal antibodies specific for human IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4. Eleven sera from women with long past history of rubella, two hyperimmune and five non-hyperimmune immunoglobulin preparations were tested. Light chain types of the antibodies were tested in ELISA with polyclonal specific antibodies to kappa and lambda chains. Antibodies to rubella in the sera as well as in the immunoglobulin preparations were found in the IgG1 subclass only. Both light chain types were present in the antibodies.
Full text
PDF

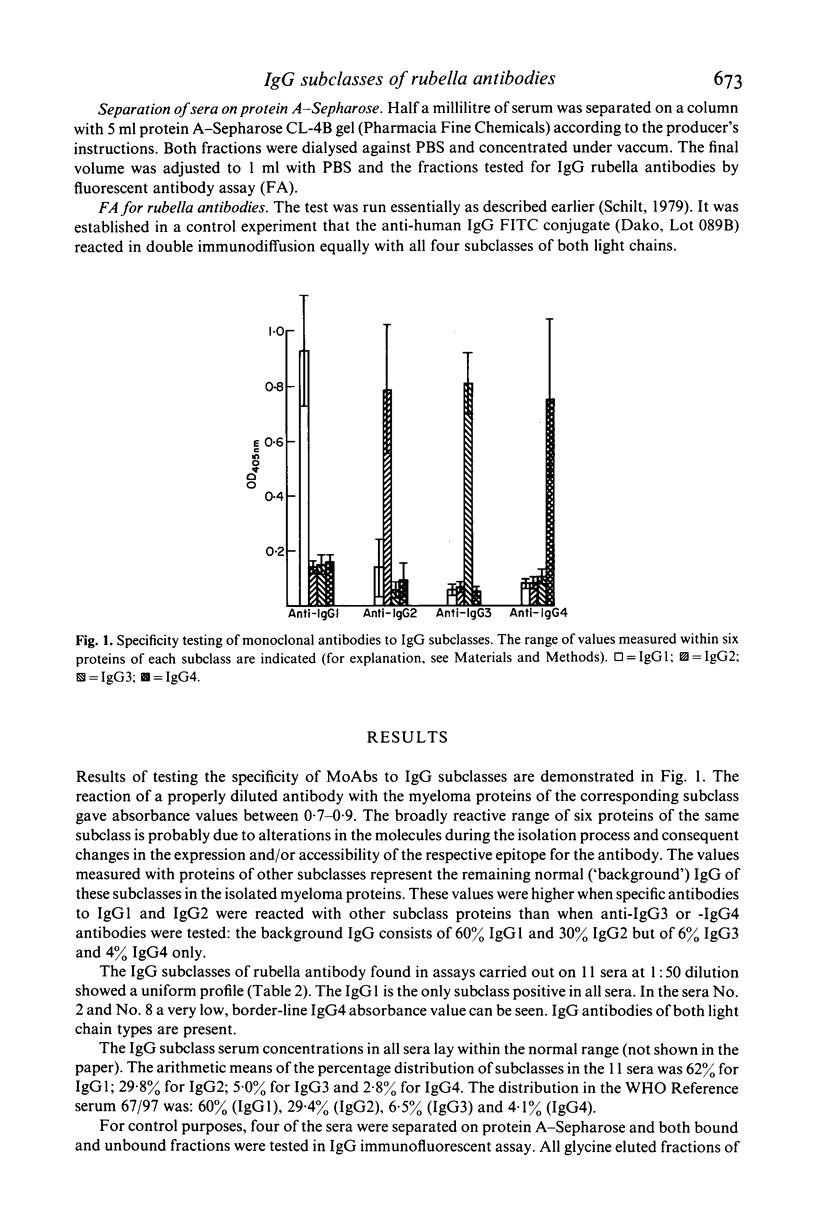
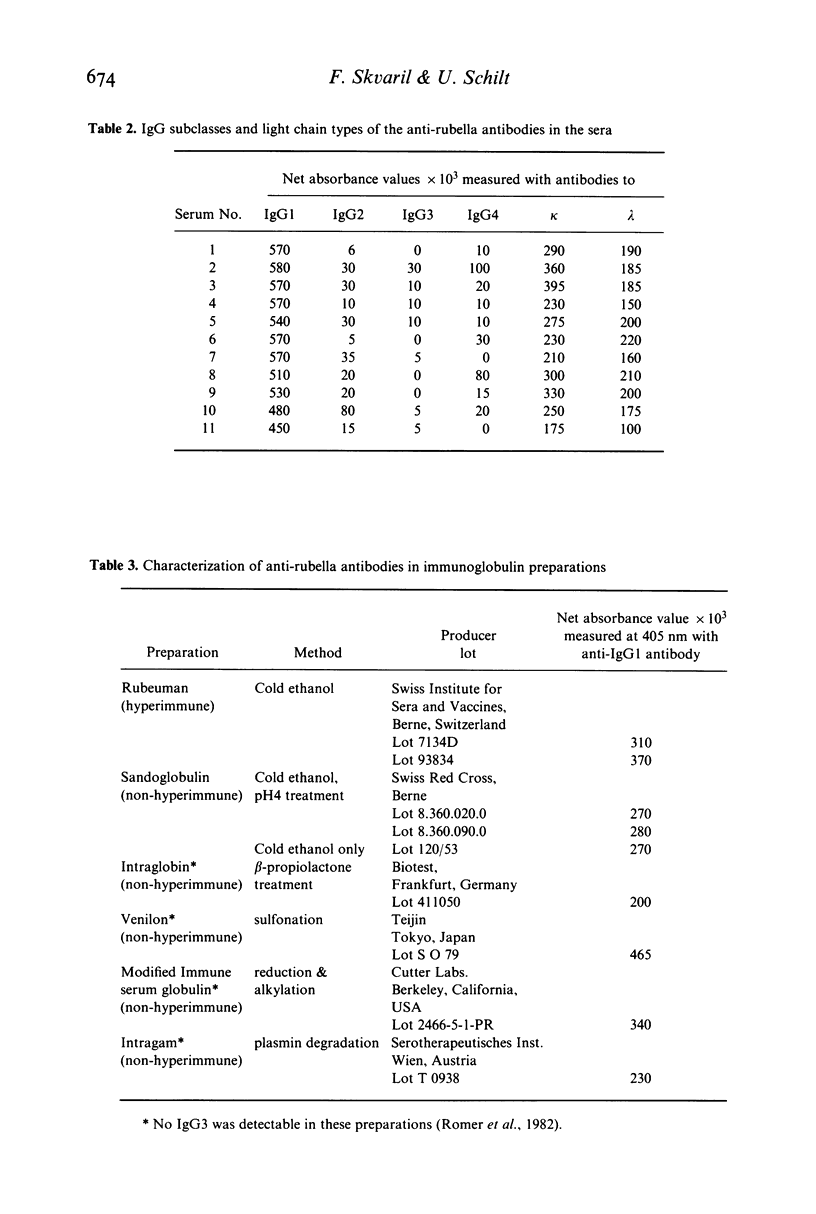


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck O. E. Distribution of virus antibody activity among human IgG subclasses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):626–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesen W. F., Skvaril F., Braun D. G. Natural infection of man with group A streptococci. Levels; restriction in class, subclass, and type; and clonal appearance of polysaccharide-group-specific antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer J., Morgenthaler J. J., Scherz R., Skvaril F. Characterization of various immunoglobulin preparations for intravenous application. I. Protein composition and antibody content. Vox Sang. 1982 Feb;42(2):62–73. doi: 10.1159/000460850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilt U. Rötelnimmunität. Immunfluoreszenztest als rascher und zuverlässiger Alternativtest zum Hämagglutinationshemmungstest. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1979 Jan 5;104(1):22–24. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1103836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H. Human gamma-g subclasses. Prog Clin Immunol. 1972;1:71–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R. Human IgG subclasses in health and disease. (A review). Part II. Ric Clin Lab. 1980 Oct-Dec;10(4):561–580. doi: 10.1007/BF02906696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F., Barandun S. A simple method for the simultaneous detection of human immunoglobulins of both light chain types. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Oct;3(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F., Roth-Wicky B., Barandun S. IgG subclasses in human gamma-globulin preparations for intravenous use and their reactivity with staphylococcus protein A. Vox Sang. 1980;38(3):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. A simple method for detecting antibodies to rubella. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Aug;56(4):338–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


