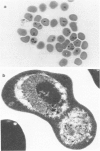
Abstract
Intravenous injection of t-butyl hydroperoxide rapidly killed Plasmodium vinckei in mice, and caused haemolysis. The same dose seemed harmless to unparasitized mice. Many parasites disintegrated inside circulating erythrocytes, so parasite death was not simply a passive consequence of haemolysis. Injection of desferrioxamine, which removes the traces of free iron that promote the dissociation of t-butyl hydroperoxide into radical species, prevented both parasite death and haemolysis. Lipid peroxidation, as measured by accumulation of malonyldialdehyde over 2 h in vitro, occurred in erythrocytes exposed to t-butyl hydroperoxide, and was particularly marked in erythrocytes from parasitized mice. These erythrocytes accumulated appreciable malonyldialdehyde even without exposure to t-butyl hydroperoxide. Desferrioxamine inhibited the accumulation of malonyldialdehyde, but did not prevent depletion of reduced glutathione by t-butyl hydroperoxide. This suggests that t-butyl hydroperoxide damaged parasites and erythrocytes by dissociating into radical species, rather than by decreasing intraerythrocyte anti-oxidant capacity. In earlier experiments we suggested that intraerythrocytic parasite death and haemolysis caused by alloxan were mediated by radical species, and these experiments with t-butyl hydroperoxide add weight to this interpretation. We regard both of these systems as models for macrophage-induced parasite death and host pathology in acute malaria.
Full text
PDF

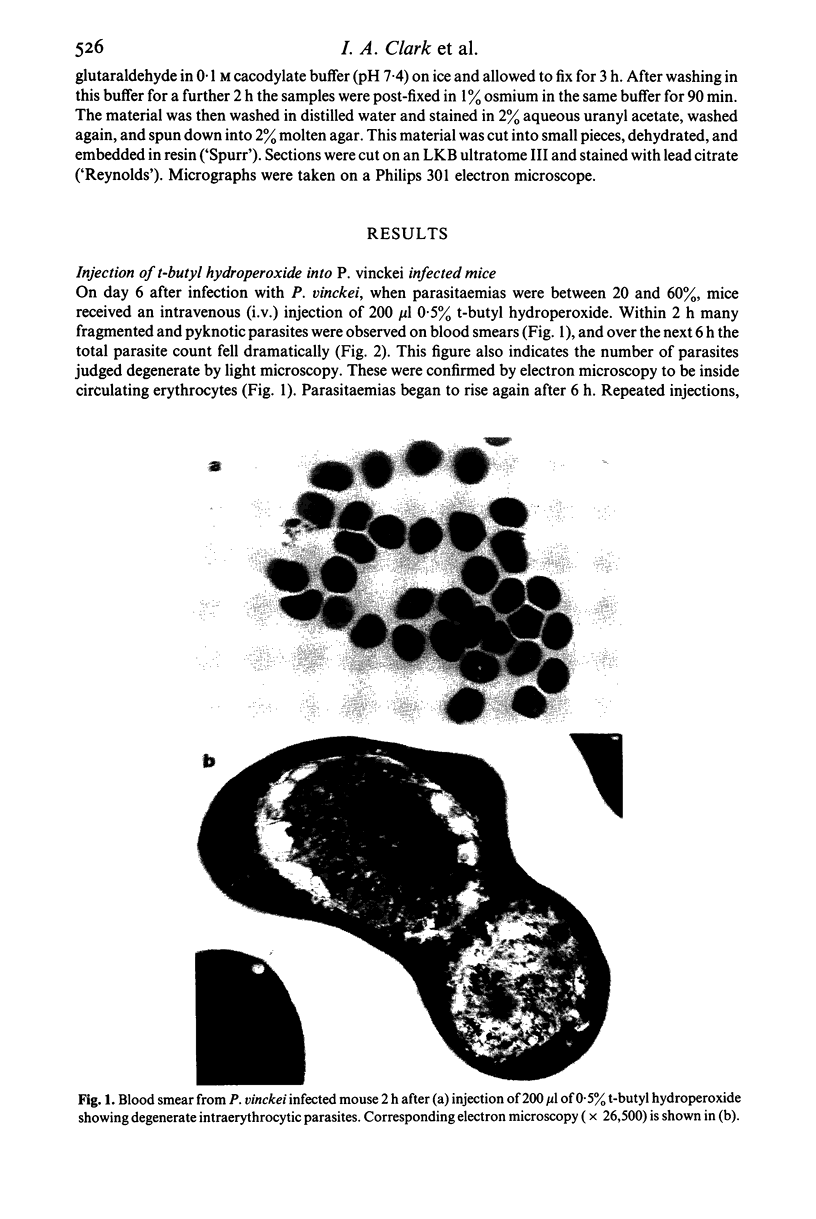
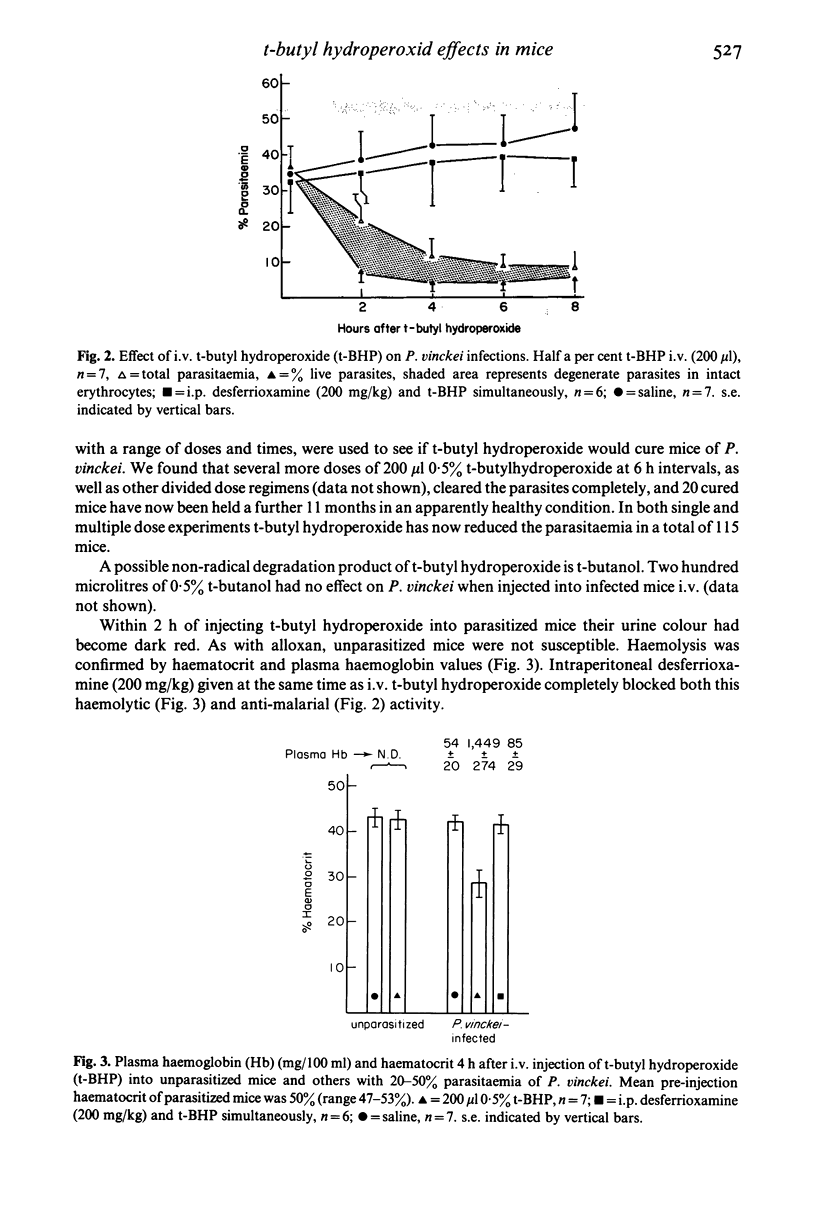
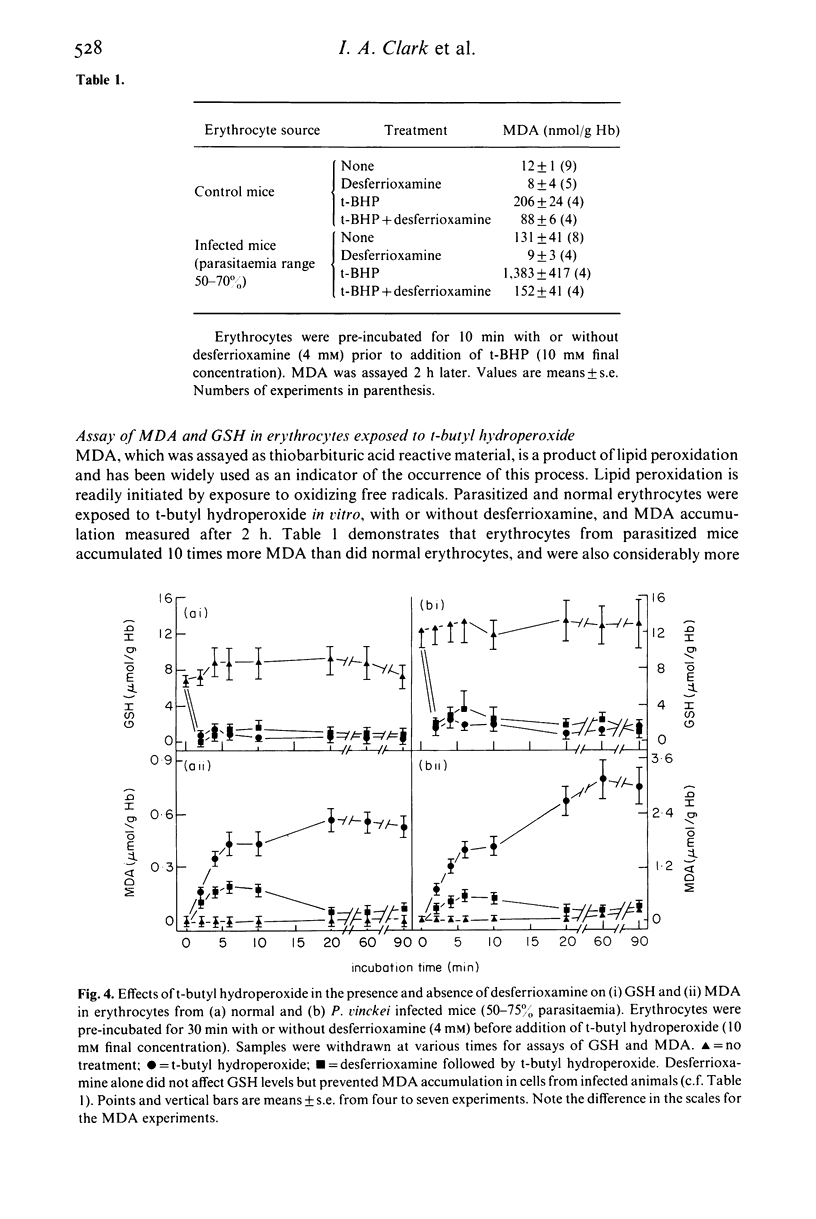


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Eugui E. M. A radical interpretation of immunity to malaria parasites. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1431–1433. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTLER E., DURON O., KELLY B. M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 May;61:882–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Cowden W. B., Butcher G. A. Free oxygen radical generators as antimalarial drugs. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):234–234. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Cowden W. B., Butcher G. A., Hunt N. H. Free oxygen radicals in malaria. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):359–360. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91664-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Cox F. E., Allison A. C. Protection of mice against Babesia spp. and Plasmodium spp. with killed Corynebacterium parvum. Parasitology. 1977 Feb;74(1):9–18. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004748x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Hunt N. H. Evidence for reactive oxygen intermediates causing hemolysis and parasite death in malaria. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.1-6.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockrell H. M., Playfair J. H. Killing of blood-stage murine malaria parasites by hydrogen peroxide. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):456–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.456-459.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grankvist K., Marklund S., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Superoxide dismutase, catalase and scavengers of hydroxyl radical protect against the toxic action of alloxan on pancreatic islet cells in vitro. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):17–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1820017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Mitchell G. F. Accelerated clearance of uninfected red cells from Plasmodium berghei-infected mouse blood in normal mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Oct;57(5):455–457. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Mohandas N., Clark M. R., Shohet S. B. The effect of malonyldialdehyde, a product of lipid peroxidation, on the deformability, dehydration and 51Cr-survival of erythrocytes. Br J Haematol. 1983 Feb;53(2):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. V., Ambrus J. L., DeSouza J. M., Lee R. V. Diminished red blood cell deformability in uncomplicated human malaria. A preliminary report. J Med. 1982;13(5-6):479–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Usami S., Chien S. Alteration in the rheologic properties of Plasmodium knowlesi--infected red cells. A possible mechanism for capillary obstruction. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1451–1455. doi: 10.1172/JCI106629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfafferott C., Meiselman H. J., Hochstein P. The effect of malonyldialdehyde on erythrocyte deformability. Blood. 1982 Jan;59(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocks J., Offerman E. L., Modell C. B., Dormandy T. L. The susceptibility to autoxidation of human red cell lipids in health and disease. Br J Haematol. 1972 Dec;23(6):713–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]