Abstract
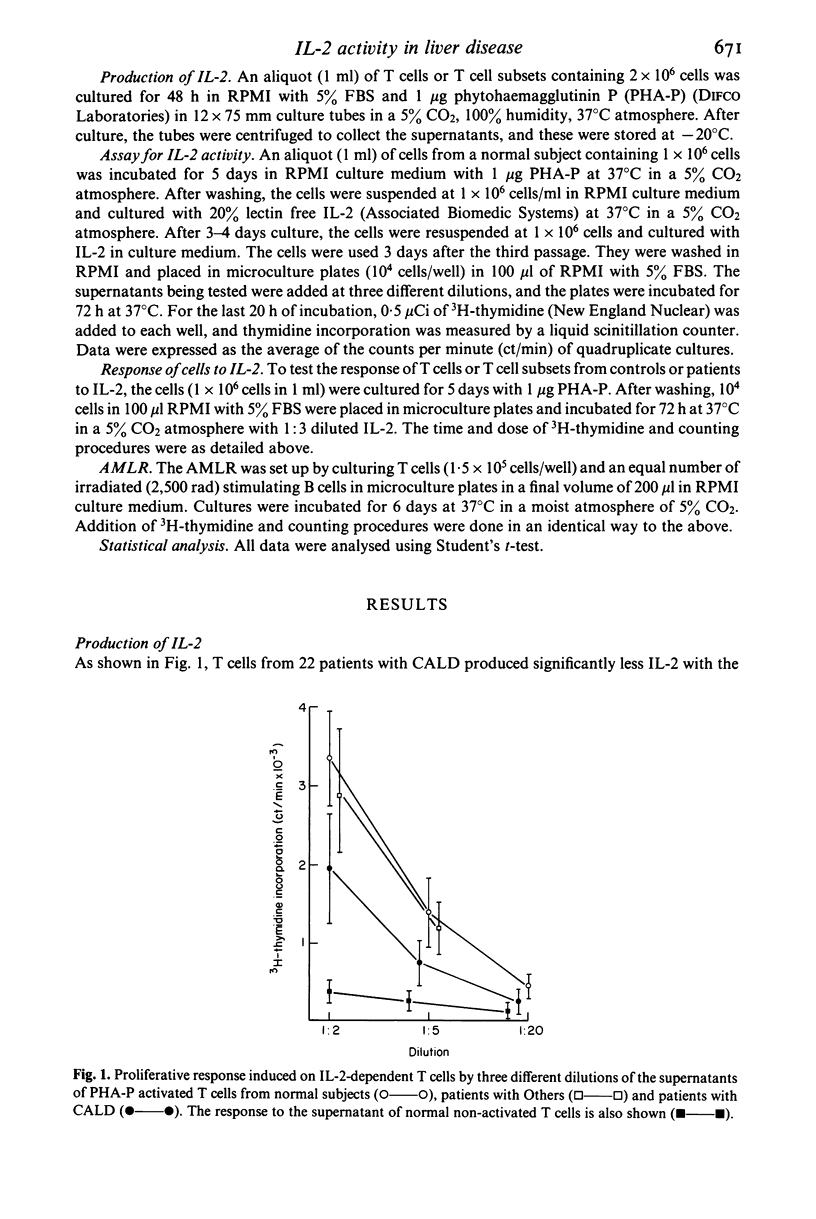
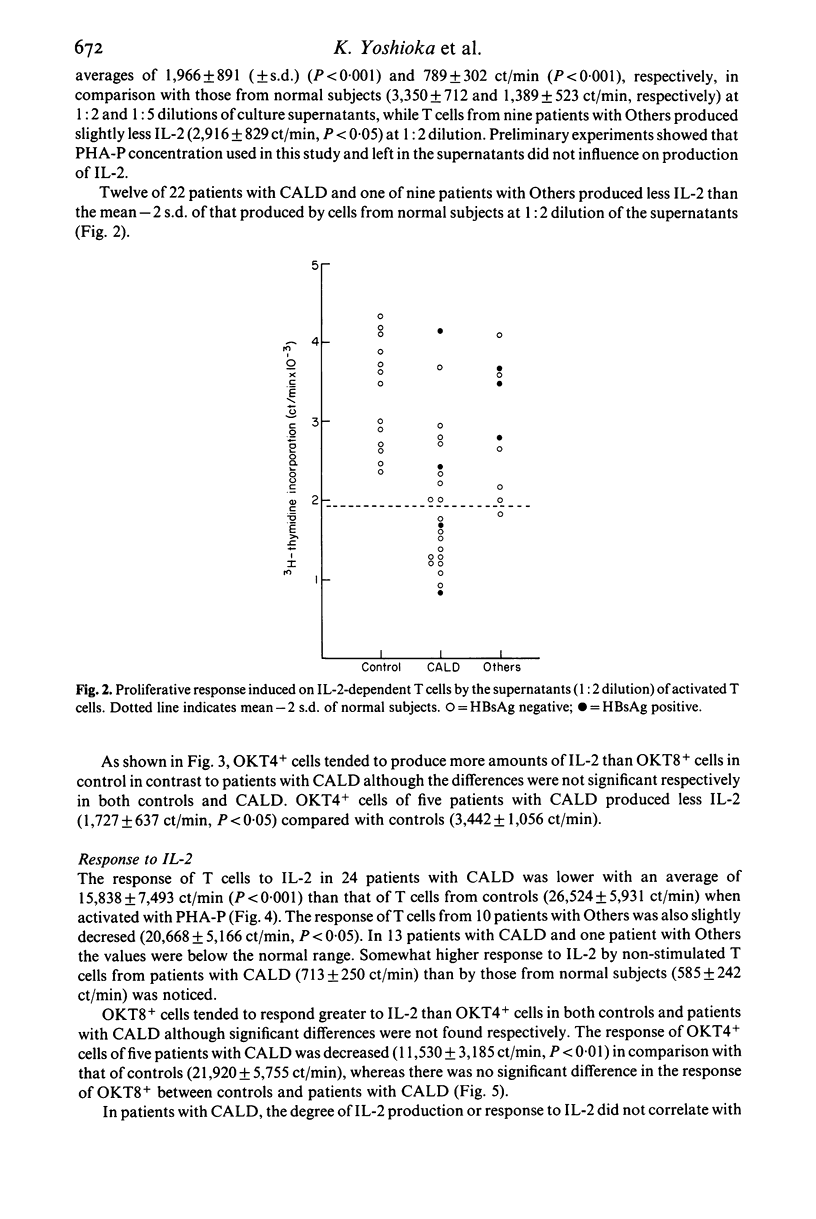
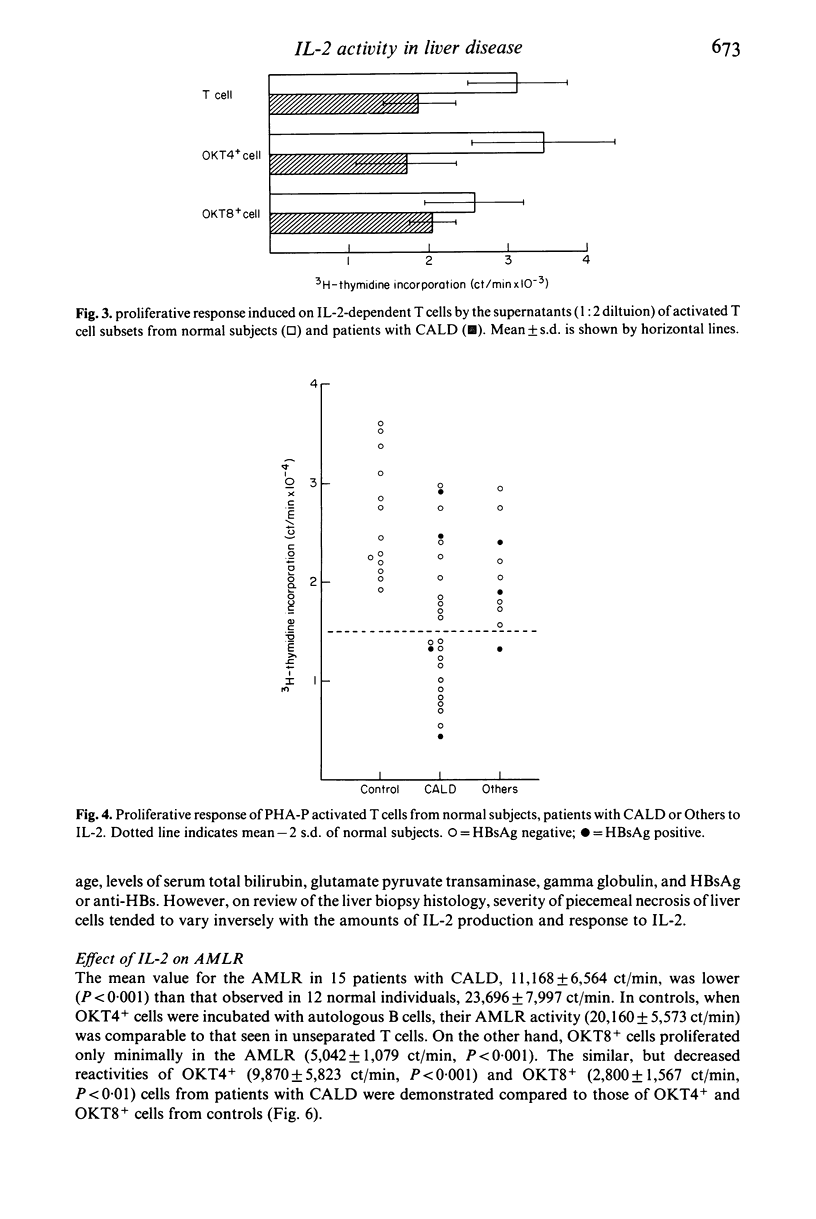
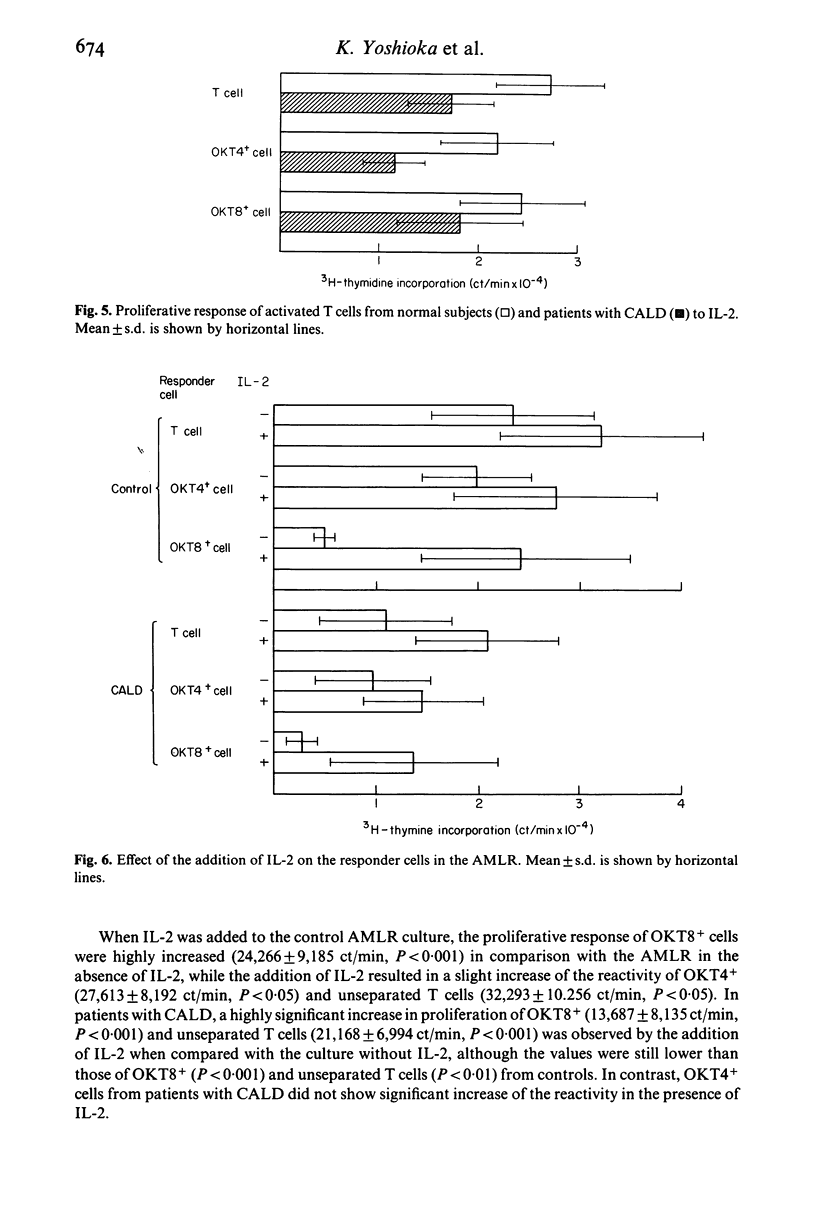
The T cell growth factor, interleukin-2 (IL-2), is a lymphokine which supports the immunoregulatory function of T cells. We measured the production of and response to IL-2 of peripheral blood T cell subsets from patients with chronic active liver diseases (CALD) and other liver diseases (Others) by the proliferative response of the cells activated with phytohaemogglutin P. Both production of and response to IL-2 of T cells from 24 patients with CALD were markedly decreased (P less than 0.001) in comparison with 13 controls. T cells from 10 patients with Others yielded low IL-2 titre (P less than 0.05) and responded to IL-2 in a depressed manner (P less than 0.05). OKT4+ and OKT8+ cells from five CALD patients as well as five controls equally produced IL-2 and responded to it. However, IL-2 production (P less than 0.05) and response to IL-2 (P less than 0.01) of OKT4+ cells from CALD patients were decreased in contrast to those of OKT8+ cells. We also examined the effect of IL-2 on the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. A highly significant increase (P less than 0.001) in the proliferative response of OKT8+ cells and unseparated T cells from 15 patients with CALD occurred with the addition of IL-2 although the values were still lower (P less than 0.01) than those of OKT8+ and unseparated T cells from 12 controls. Addition of IL-2 did not result in a significant increase of the reactivity of OKT4+ cells from patients with CALD. These results further delineate the nature of the immunoregulatory aberration in CALD.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcocer-Varela J., Alarcón-Segovia D. Decreased production of and response to interleukin-2 by cultured lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1388–1392. doi: 10.1172/JCI110579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdstock G., Ershler W. B., Krawitt E. L. Demonstration of non-specific B-cell stimulation in patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 1982 Sep;23(9):724–728. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.9.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Elson C. O., Waggoner J. G., Jones E. A., Strober W. Deficiency of the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1305–1310. doi: 10.1172/JCI109982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakumu S., Hara T., Goji H., Sakamoto N. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity against Chang liver cells in chronic active hepatitis. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 1;36(1):46–53. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakumu S., Yata K., Kashio T. Immunoregulatory T-cell function in acute and chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1980 Oct;79(4):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashio T., Hotta R., Kakumu S. Lymphocyte suppressor cell activity in acute and chronic liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):459–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D. E., Gillis S., Okada M., Henney C. S. The role of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in the differentiatin of cytotoxic T cells: the effect of monoclonal anti-IL-2 antibody and absorption with IL-2 dependent T cell lines. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1323–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Smolen J. S., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D., Oppenheim J. J. Human lymphocytes with either the OKT4 or OKT8 phenotype produce interleukin 2 in culture. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):470–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI110637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka N., Sauvezie B., Pierce D. A., Daniels T. E., Talal N. Decreased autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):928–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI109960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opelz G., Kiuchi M., Takasugi M., Terasaki P. I. Autologous stimulation of human lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1327–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetkau V., Shaw J., Mills G., Caplan B. Cellular origins and targets of costimulator (IL2). Immunol Rev. 1980;51:157–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Möller G. T cell growth factor abrogates concanavalin A-induced suppressor cell function. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1360–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2894–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Failure of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactions between T and non-T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Talal N. Significance of self-recognition and interleukin-2 for immunoregulation, autoimmunity and cancer. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Oct;16(4):269–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Luger T. A., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D. Responder cells in the human autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1601–1604. doi: 10.1172/JCI110416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnatz H., Rösch W., Gerlich W., Gutmann W. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and cell-mediated cytotoxicity (CMC) to HBsAg-coated target cells in patients with hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis (CAH). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jan;35(1):133–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Mochizuki D. Interleukin 2: a class of T cell growth factors. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:257–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


