Abstract
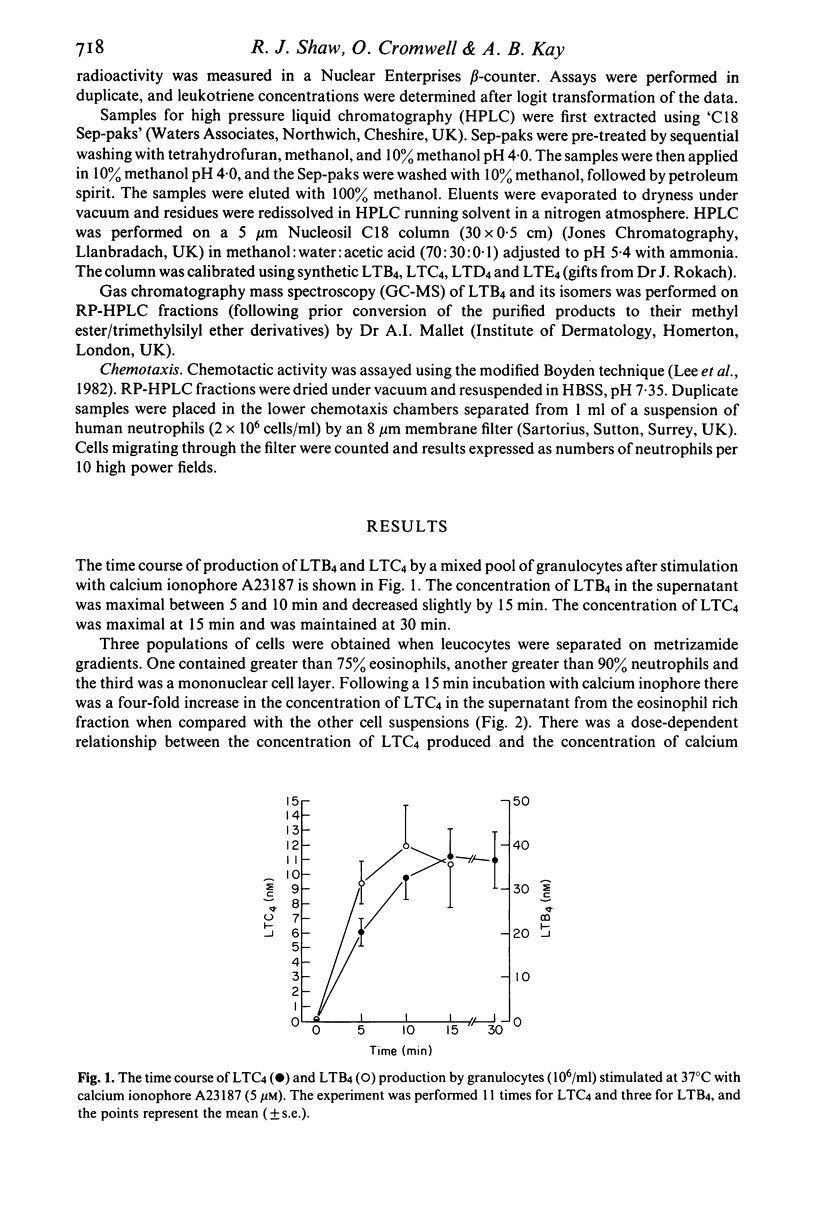
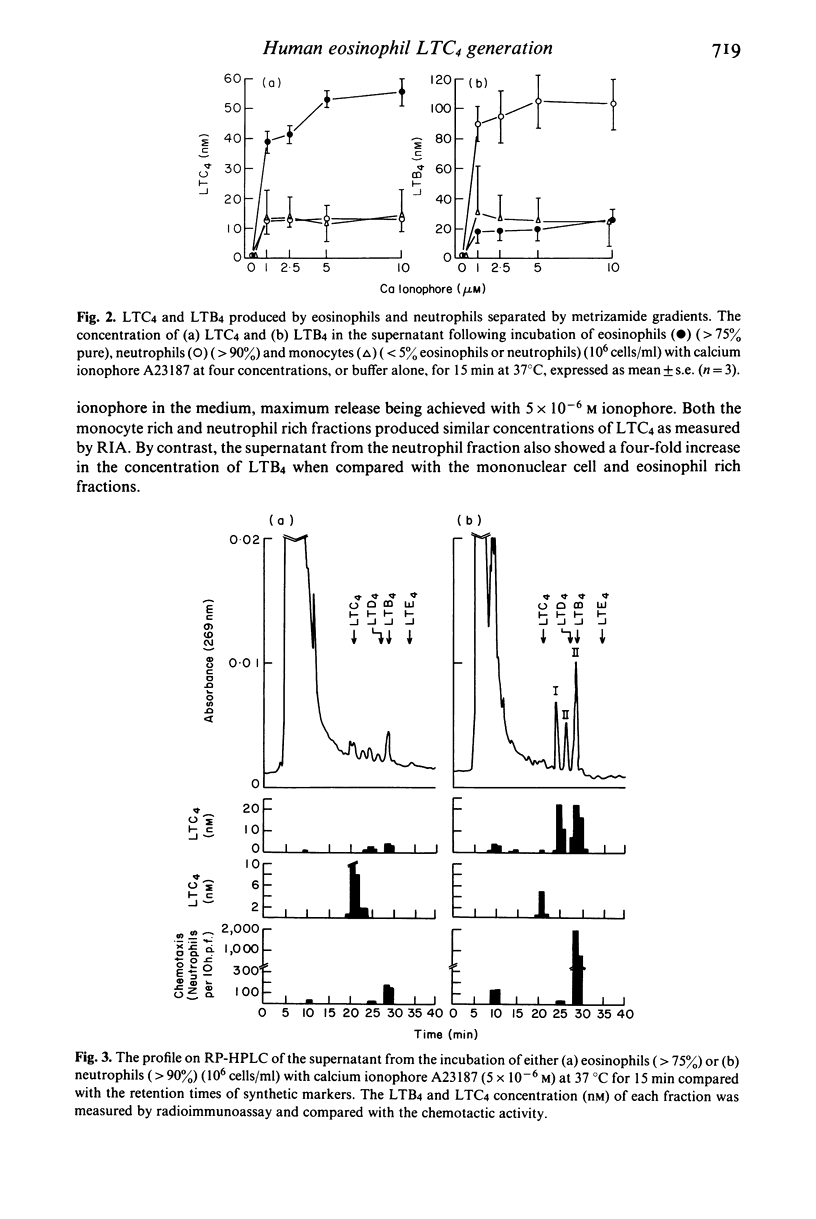
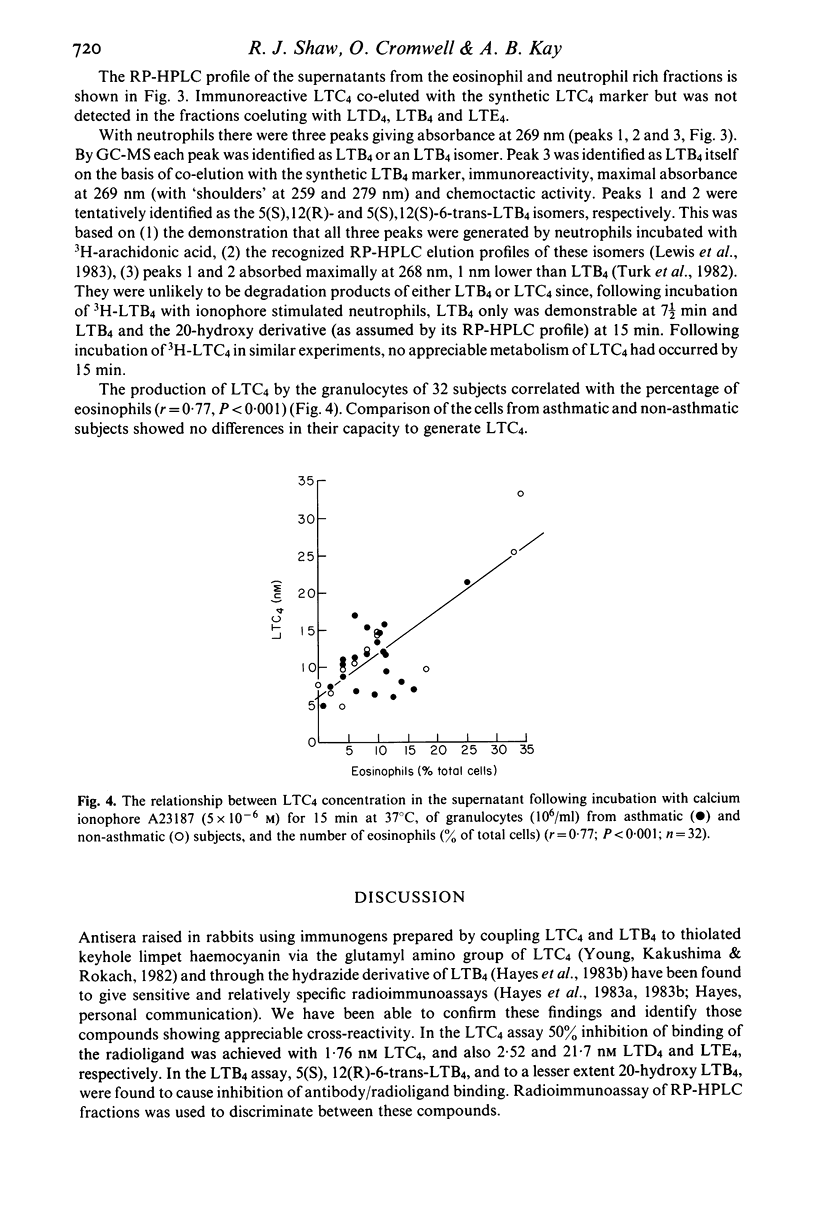
The leukotriene generating capacities of ionophore stimulated human eosinophils and neutrophils were compared using specific radioimmunoassays for LTB4 and LTC4. Mixed granulocyte preparations (neutrophils and eosinophils) produced both LTB4 and LTC4 in a time-dependent fashion which was maximal at 10 and 15 min, respectively. Following the separation of eosinophils (greater than 75%) and neutrophils (greater than 90%) by metrizamide gradients, LTC4 production was predominantly from eosinophils, whereas neutrophils were the principal source of LTB4. The concentrations of leukotrienes produced by the eosinophil and neutrophil rich cell preparations were directly proportional to the concentration of ionophore. Following purification of eosinophil derived products by RP-HPLC the LTC4 immunoreactivity corresponded to the elution profile of a synthetic LTC4 marker. Furthermore, in 32 atopic subjects (21 bronchial asthmatics and 11 non-asthmatics) the amounts of LTC4 produced by unseparated leucocytes were directly proportional to the percentage of eosinophils in the total cell suspension. Preferential generation of LTB4 by neutrophils was also demonstrated by immunoreactivity of ionophore stimulated supernatants subjected to RP-HPLC, as well as by its characteristic u.v. absorbance and GC-MS profile and the ability to promote directional neutrophil locomotion (chemotaxis). These experiments support the concept that eosinophils accumulate in tissues partly as a result of the response to neutrophil derived LTB4, and that these cells contribute to the production of sulphidopeptide leukotrienes with subsequent amplification of the acute allergic response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aehringhaus U., Wölbling R. H., König W., Patrono C., Peskar B. M., Peskar B. A. Release of leukotriene C4 from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as determined by radioimmunoassay. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80715-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp R. D., Coutts A. A., Greaves M. W., Kay A. B., Walport M. J. Responses of human skin to intradermal injection of leukotrienes C4, D4 and B4. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;80(3):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damon M., Chavis C., Godard P., Michel F. B., Crastes de Paulet A. Purification and mass spectrometry identification of leukotriene D4 synthesized by human alveolar macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):518–524. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):264–265. doi: 10.1038/286264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J. The conversion of leukotriene C4 to isomers of leukotriene B4 by human eosinophil peroxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):270–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M., Weiss J. W., Leitch A. G., McFadden E. R., Jr, Corey E. J., Austen K. F., Drazen J. M. Effects of leukotriene D on the airways in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):436–439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna C. J., Bach M. K., Pare P. D., Schellenberg R. R. Slow-reacting substances (leukotrienes) contract human airway and pulmonary vascular smooth muscle in vitro. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):343–344. doi: 10.1038/290343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. C., Lombardo D. L., Girard Y., Maycock A. L., Rokach J., Rosenthal A. S., Young R. N., Egan R. W., Zweerink H. J. Measuring leukotrienes of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis: development of a specific radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):429–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher T. Role of the eosinophil in the allergic reactions. I. EDI-an eosinophil-derived inhibitor of histamine release. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1379–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörg A., Henderson W. R., Murphy R. C., Klebanoff S. J. Leukotriene generation by eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):390–402. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Nagy L., Nagakura T., Walport M. J., Kay A. B. Identification and partial characterization of an exercise-induced neutrophil chemotactic factor in bronchial asthma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):889–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI110528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Lee C. W., Levine L., Morgan R. A., Weiss J. W., Drazen J. M., Oh H., Hoover D., Corey E. J., Austen K. F. Biology of the C-6-sulfidopeptide leukotrienes. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;11:15–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Schleimer R. P., Peters S. P., Schulman E. S., Adams G. K., 3rd, Newball H. H., Lichtenstein L. M. Generation of leukotrienes by purified human lung mast cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):747–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI110670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marom Z., Shelhamer J. H., Bach M. K., Morton D. R., Kaliner M. Slow-reacting substances, leukotrienes C4 and D4, increase the release of mucus from human airways in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;126(3):449–451. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy L., Lee T. H., Goetzl E. J., Pickett W. C., Kay A. B. Complement receptor enhancement and chemotaxis of human neutrophils and eosinophils by leukotrienes and other lipoxygenase products. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):541–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Salmon J. A. Release of leukotriene B4 from human neutrophils and its relationship to degranulation induced by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, serum-treated zymosan and the ionophore A23187. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):65–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Simmons P. M., Palmer R. M. Synthesis and metabolism of leukotriene B4 in human neutrophils measured by specific radioimmunoassay. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):18–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80696-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Maas R. L., Brash A. R., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Oates J. A. Arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase products from human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7068–7076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Inactivation of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis by human eosinophil arylsulfatase. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. W., Drazen J. M., Coles N., McFadden E. R., Jr, Weller P. F., Corey E. J., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Bronchoconstrictor effects of leukotriene C in humans. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):196–198. doi: 10.1126/science.7063880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. N., Kakushima M., Rokach J. Studies on the preparation of conjugates of leukotriene C4 with proteins for development of an immunoassay for SRS-A (1). Prostaglandins. 1982 Apr;23(4):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger R. S., Yurdin D. L., Colten H. R. Histamine metabolism. II. Cellular and subcellular localization of the catabolic enzymes, histaminase and histamine methyl transferase, in human leukocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Jul;58(1 Pt 2):172–179. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



