Abstract
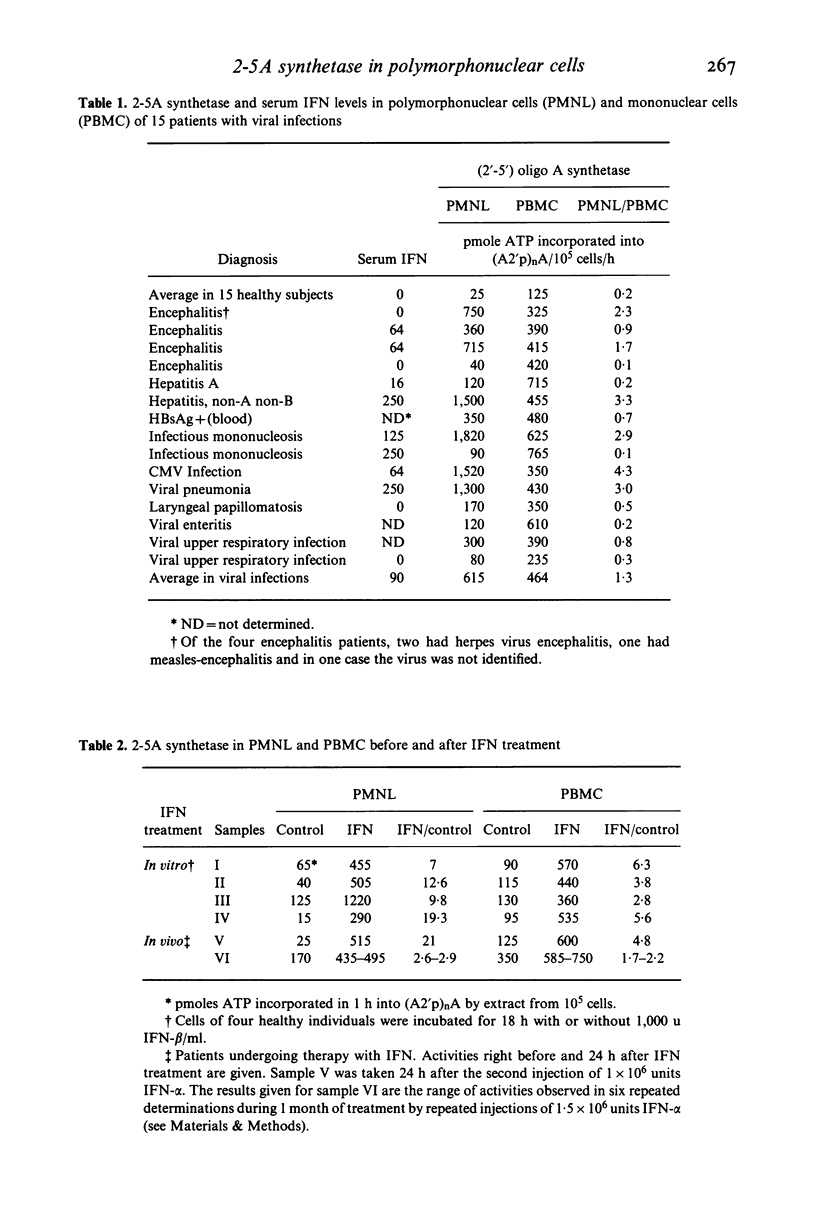
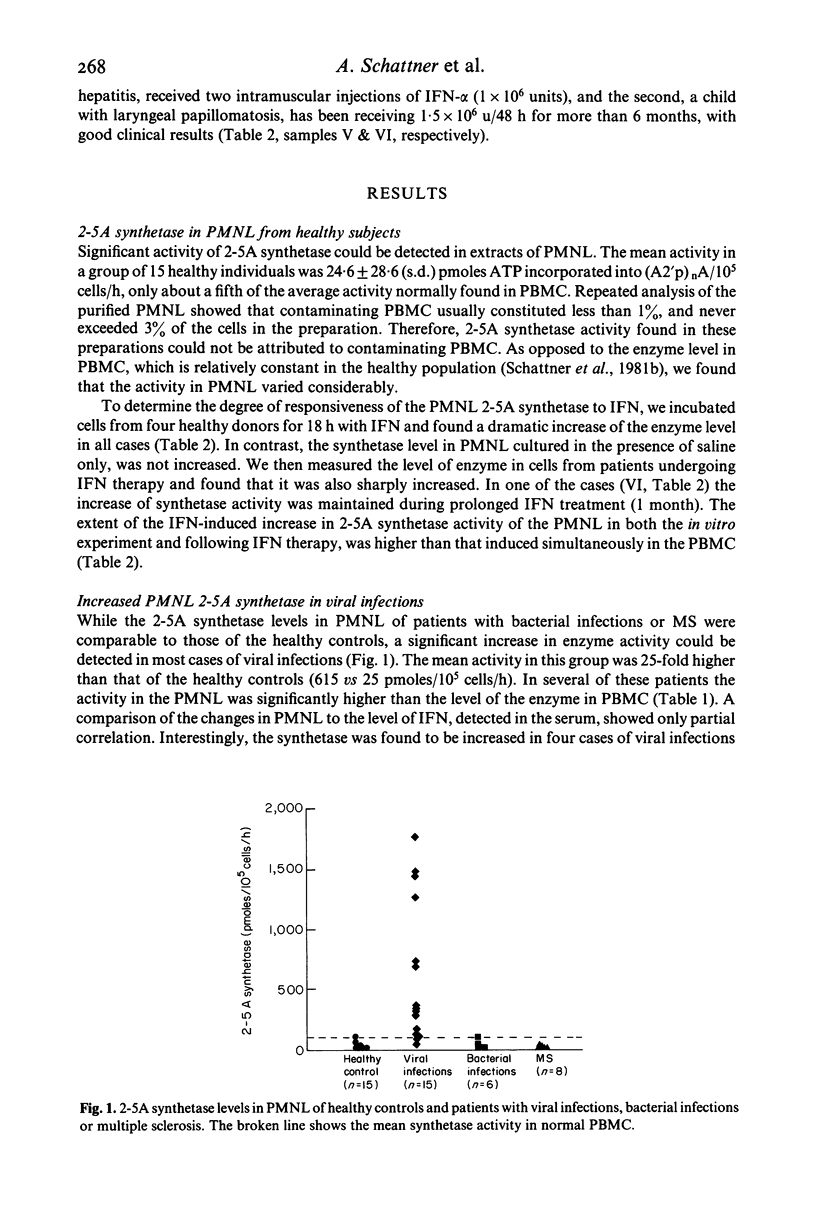
The interferon (IFN)-induced enzyme 2-5A synthetase was found in human peripheral blood polymorphonuclear cells (PMNL). The average enzyme activity in a group of 15 patients with various viral infections was significantly higher (25-fold) than in healthy individuals. Eight patients with multiple sclerosis and six patients with bacterial infections were found to have normal 2-5A synthetase levels in the PMNL. Relationship of PMNL 2-5A synthetase levels to IFN was confirmed by finding enzyme increases in PMNL incubated in vitro with IFN, as well as in patients undergoing IFN therapy. These findings suggest that in PMNL, as in other cells, the level of 2-5A synthetase can be regulated by IFN and can be increased as a result of IFN information in diseases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Interactions of antibodies, complement components and various cell types in immunity against viruses and pyogenic bacteria. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):3–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland P., Berg K. Interferon enhances the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1585–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Brown R. E., Kerr I. M. Synthesis of low molecular weight inhibitor of protein synthesis with enzyme from interferon-treated cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):537–540. doi: 10.1038/268537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M., Cayley P. J., Silverman R. H., Wreschner D. H., Gilbert C. S., Brown R. E., Kerr I. M. Radioimmune, radiobinding and HPLC analysis of 2-5A and related oligonucleotides from intact cells. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):189–192. doi: 10.1038/288189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan I., Baglioni C. 2'5' oligo(A) polymerase activity in serum of mice infected with EMC virus or treated with interferon. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):485–488. doi: 10.1038/285485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSorley J., Shapiro L., Brownstein M. H., Hsu K. C. Herpes simplex and varicella-zoster: comparative histopathology of 77 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1974 Mar-Apr;13(2):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1974.tb01769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin G., Revel M., Wallach D. The interferon-induced enzyme oligo-isoadenylate synthetase: rapid determination of its in vitro products. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Rothko K., Klippel J. H., Friedman R. M., Johnston M. I. Interferon-induced 2'-5' adenylate synthetase in vivo and interferon production in vitro by lymphocytes from systemic lupus erythematosus patients with and without circulating interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2140–2146. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A., Henson P. M. Neutrophils in antiviral immunity: inhibition of virus replication by a mediator produced by bovine neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):223–232. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A., Mukkur T. K. The role of neutrophils in antiviral defense--in vitro studies on the mechanism of antiviral inhibition. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1957–1961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Merlin G., Shapira A., Revel M., Wallach D. Comparison of (2'-5') oligo-adenylate synthetase and interferon blood-levels in mice early after viral infection. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(2):285–289. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Merlin G., Wallach D., Rosenberg H., Bino T., Hahn T., Levin S., Revel M. Monitoring of interferon therapy by assay of (2'--5') oligo-isoadenylate synthetase in human peripheral white blood cells. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(4):587–594. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A., Wallach D., Merlin G., Hahn T., Levin S., Revel M. Assay of an interferon-induced enzyme in white blood cells as a diagnostic aid in viral diseases. Lancet. 1981 Sep 5;2(8245):497–500. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90883-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokawa Y., Ando T., Ishihara Y. Induction of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and interferon in mouse trigeminal ganglia infected with herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):719–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.719-723.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szigeti R., Masucci M. G., Masucci G., Klein E., Klein G. Interferon suppresses antigen- and mitogen-induced leukocyte migration inhibition. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):594–596. doi: 10.1038/288594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


