Abstract
A comparative study of human B lymphoma cells activation by monoclonal (murine hybridoma) antibodies to mu heavy chains (Ma-mu) as compared to polyclonal (rabbit) antibodies to mu heavy chains (Ra-mu) has been carried out. Early events related to calmodulin activation such as 86Rb influx and changes in cell volume at 4 h could be induced by Ma-mu. One antibody (AF6) approached Ra-mu with regard to the strength of response obtained. However, Ma-mus including AF6 were deficient in inducing DNA synthesis under conditions where this was achieved with Ra-mu. Studies in one lymphoma, where stimulation of re-expressed surface IgM could be studied, revealed that Ma-mu was deficient in stimulating re-expressed sIgM. These findings raise questions with regard to polyclonal antibody to surface Ig as a model for B cell triggering by antigen and suggest that antigen-induced B cell triggering may be more complex than indicated by previous studies with polyclonal antibody.
Full text
PDF

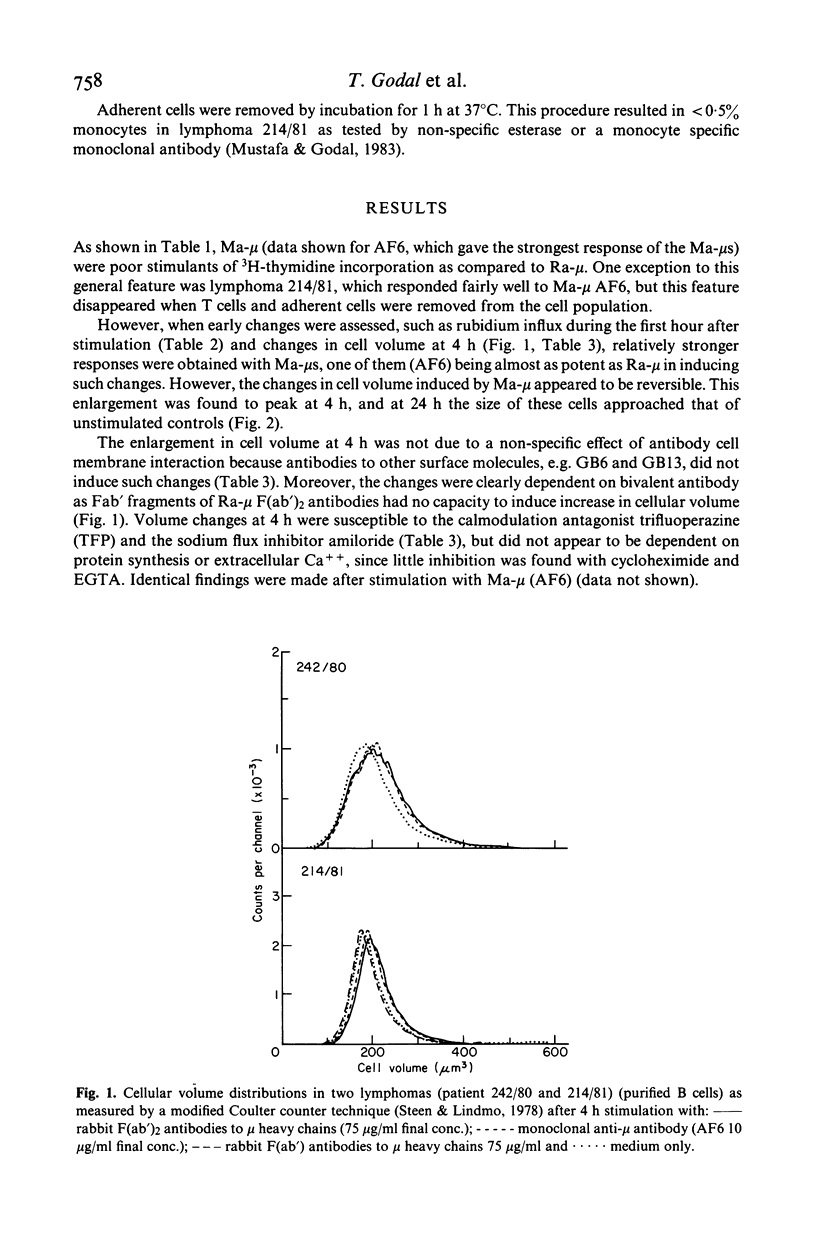
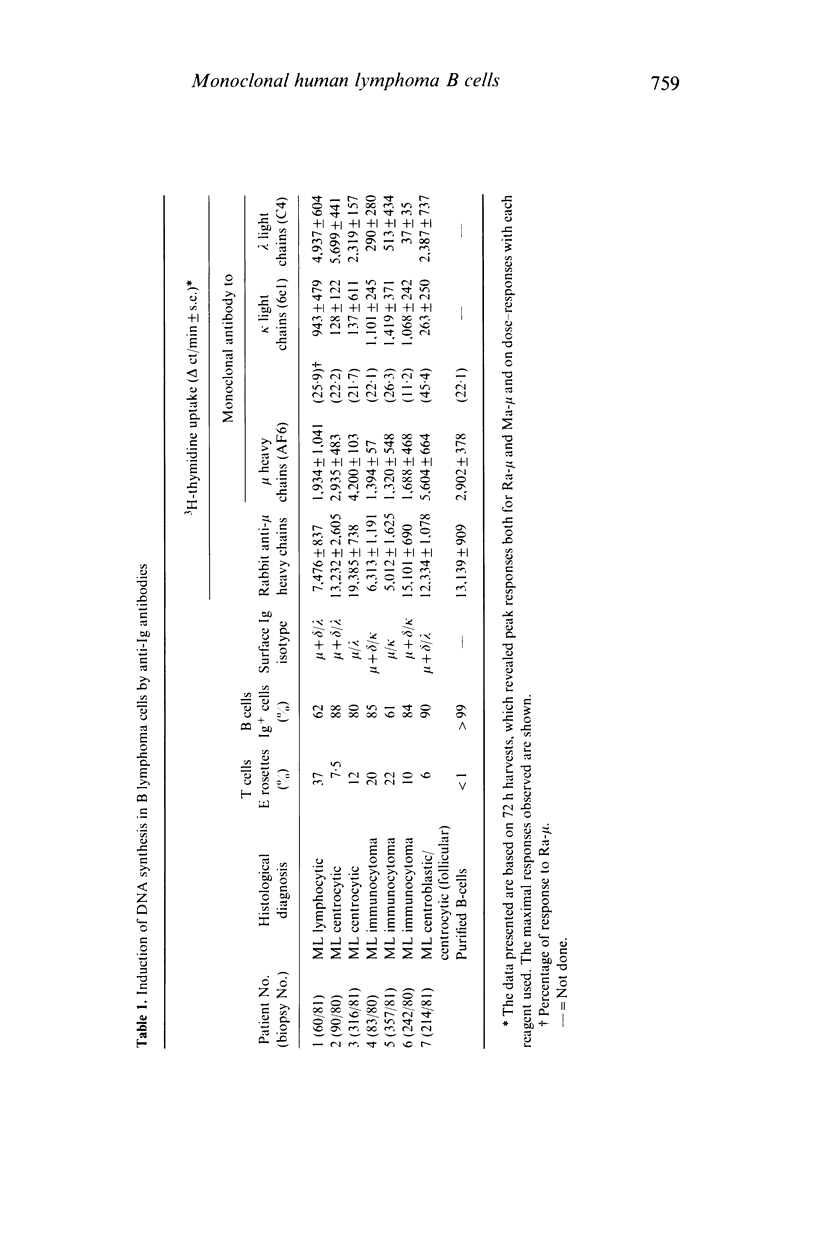
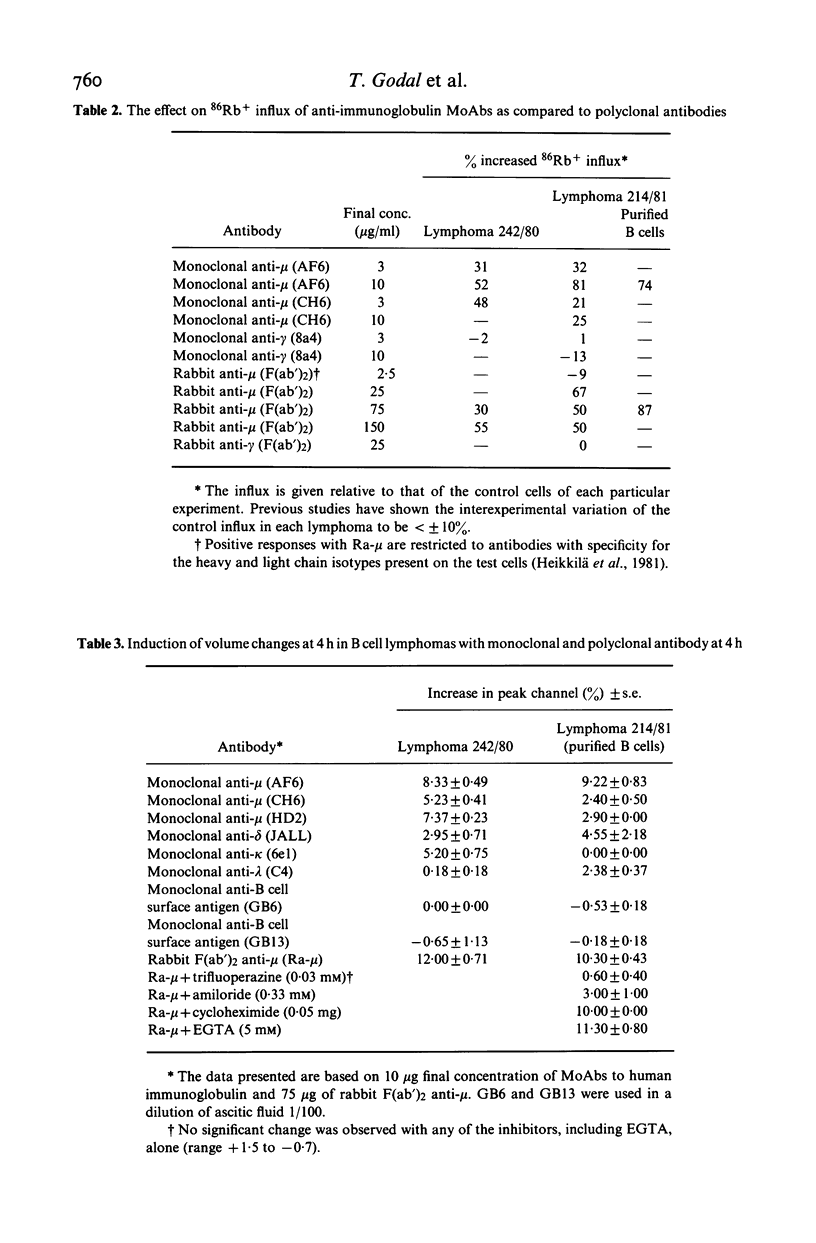
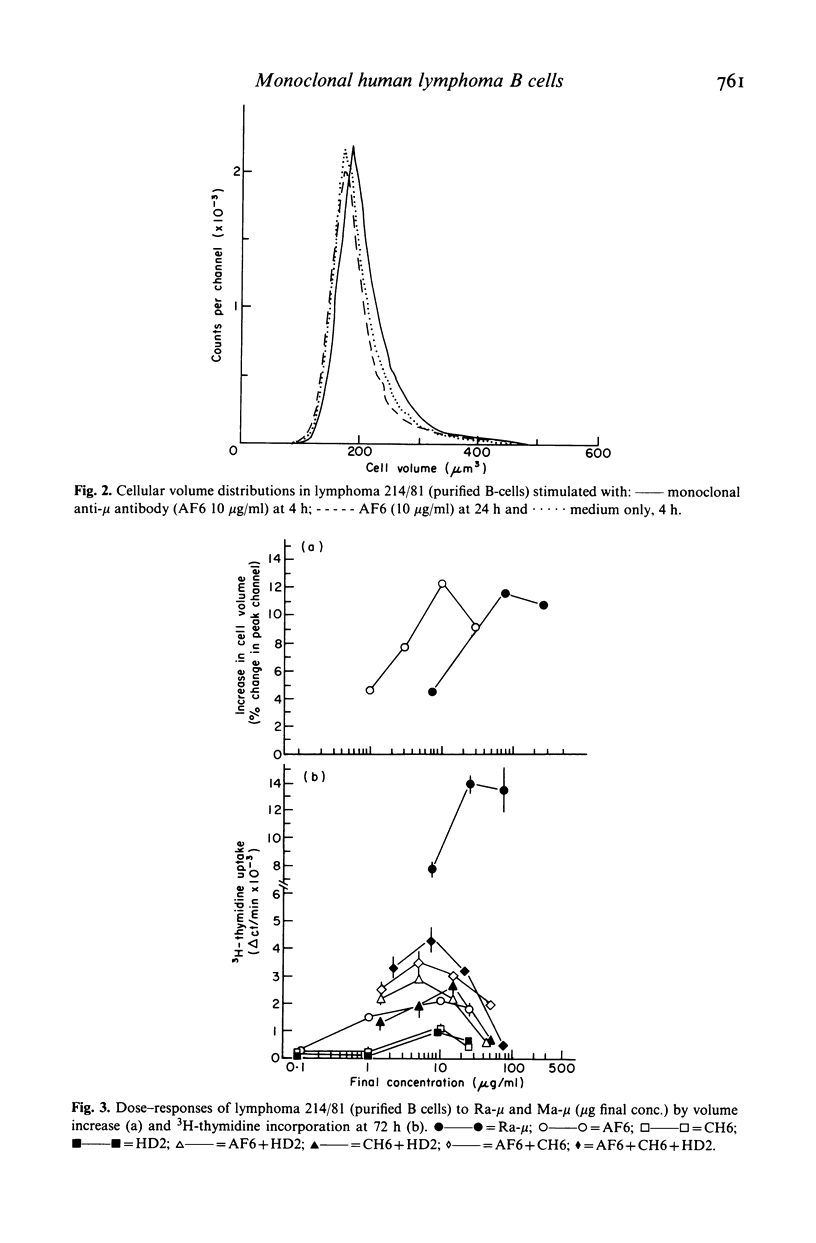


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Schreier M. H., Melchers F. T-cell-dependent B-cell stimulation is H-2 restricted and antigen dependent only at the resting B-cell level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Monroe J. G., Neale M. J. Definition of conditions that enable antigen-specific activation of the majority of isolated trinitrophenol-binding B cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1635–1649. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defranco A. L., Raveche E. S., Asofsky R., Paul W. E. Frequency of B lymphocytes responsive to anti-immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1523–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funderud S., Lindmo T., Ruud E., Marton P. F., Langholm R., Elgjo R. F., Vaage S., Lie S., Godal T. Delineation of subsets in human B-cell lymphomas by a set of monoclonal antibodies raised against B lymphoma cells. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Feb;17(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Funderud S. Human B-cell neoplasms in relation to normal B-cell differentiation and maturation processes. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;36:211–255. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Henriksen A., Ruud E., Michaelsen T. Monoclonal human B lymphoma cells respond to DNA synthesis to anti-immunoglobulins in the presence of the tumour promotor TPA. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Mar;15(3):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal T., Lindmo T., Marton P. F., Landaas T. O., Langholm R., Høie J., Foss Abrahamsen A. Immunological subsets in human B-cell lymphomas. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Nov;14(5):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkilä R., Godal T., Henriksen A., Iversen J. G. Anti-immunoglobulin-induced potassium flux in relation to capping and DNA synthesis. An analysis in monoclonal human B lymphoma cell populations. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Dec;136(2):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Farrar J., Hilfiker M., Johnson B., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Paul W. E. Identification of a T cell-derived b cell growth factor distinct from interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakson P. C., Puré E., Vitetta E. S., Krammer P. H. T cell-derived B cell differentiation factor(s). Effect on the isotype switch of murine B cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):734–748. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M., Ewald S., Douglas R., Sibley C., Raschke W., Fambrough D., Hood L. The immunoglobulin mu chains of membrane-bound and secreted IgM molecules differ in their C-terminal segments. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):393–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F. Plasma membrane and cell cortex interactions in lymphocyte functions. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:1–120. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Hardie D., Jefferis R., Ling N. R., Drysdale P., Richardson P., Raykundalia C., Catty D., Appleby P., Drew R. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to human immunoglobulin kappa and lambda chains. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):649–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen T. E., Natvig J. B. Three new fragments, F(ab) 2 , F(c) 2 , and Fab-c, obtained by papain proteolysis of normal human IgG. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(3):255–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Godal T. In vitro induction of human suppressor T cells by mycobacterial antigens. BCG activated OKT4+ cells mediate suppression of antigen induced T cell proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):29–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C. Separable helper factors support B cell proliferation and maturation to Ig secretion. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruud E., Steen H. B., Beiske K., Godal T. Different responses elicited in vitro by antibodies to IgM and IgD in cells from a surface IgM + D-positive human follicular lymphoma. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Feb;17(2):155–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen H. B., Lindmo T. Cellular and nuclear volume during the cell cycle of NHIK 3025 cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1978 Jan;11(1):69–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1978.tb00876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Bennich H. H., Natvig J. B. Pepsin digestion of human G-myeloma proteins of different subclasses. I. The characteristic features of pepsin cleavage as a function of time. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Nov;7(5):603–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki K., Nakagawa T., Kaieda T., Muraguchi A., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Induction of proliferation and Ig production in human B leukemic cells by anti-immunoglobulins and T cell factors. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1296–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


