Abstract
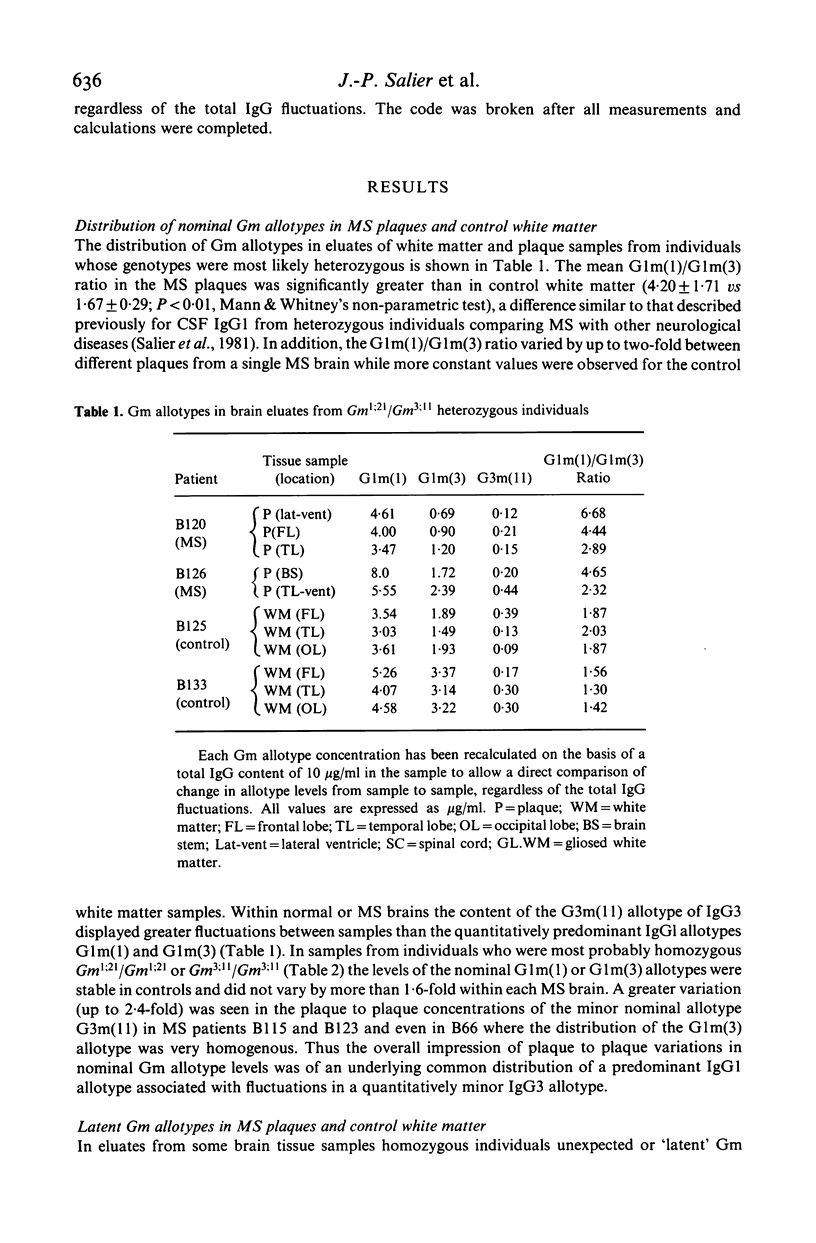
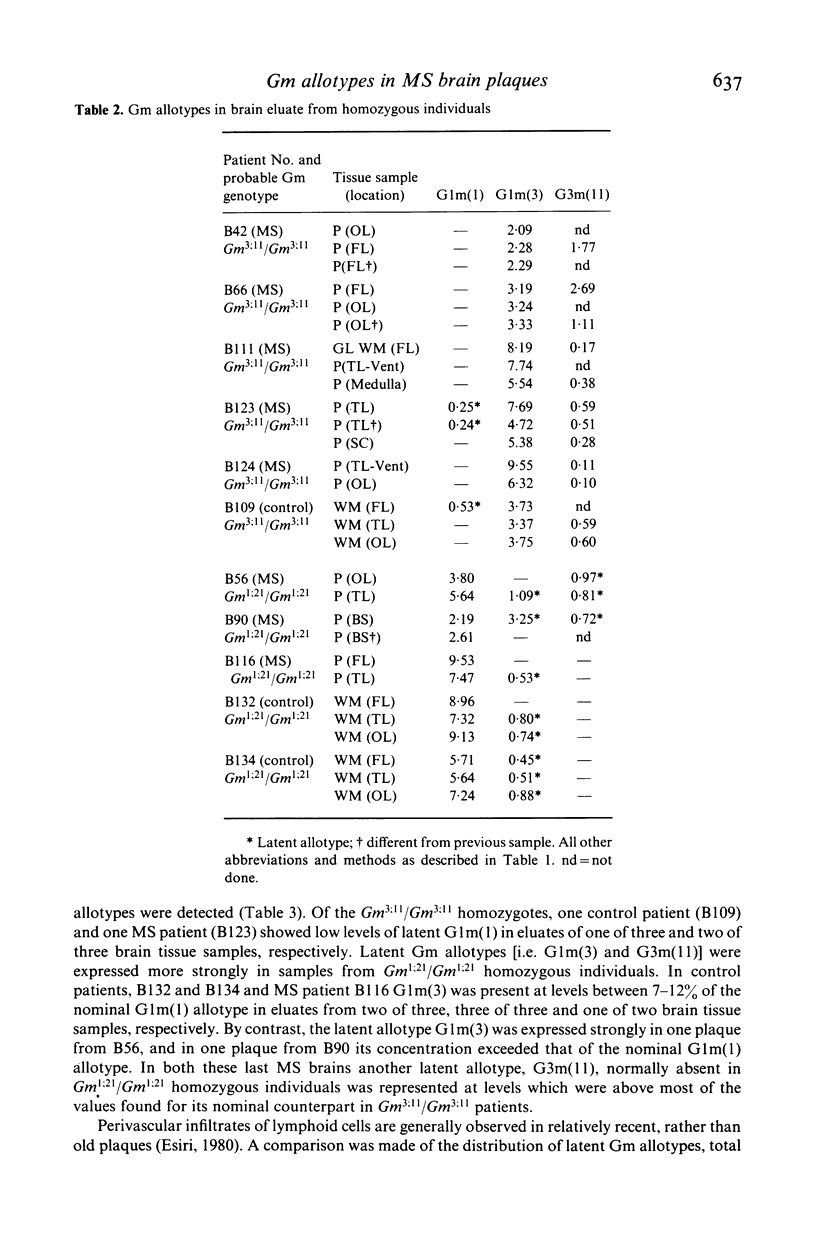
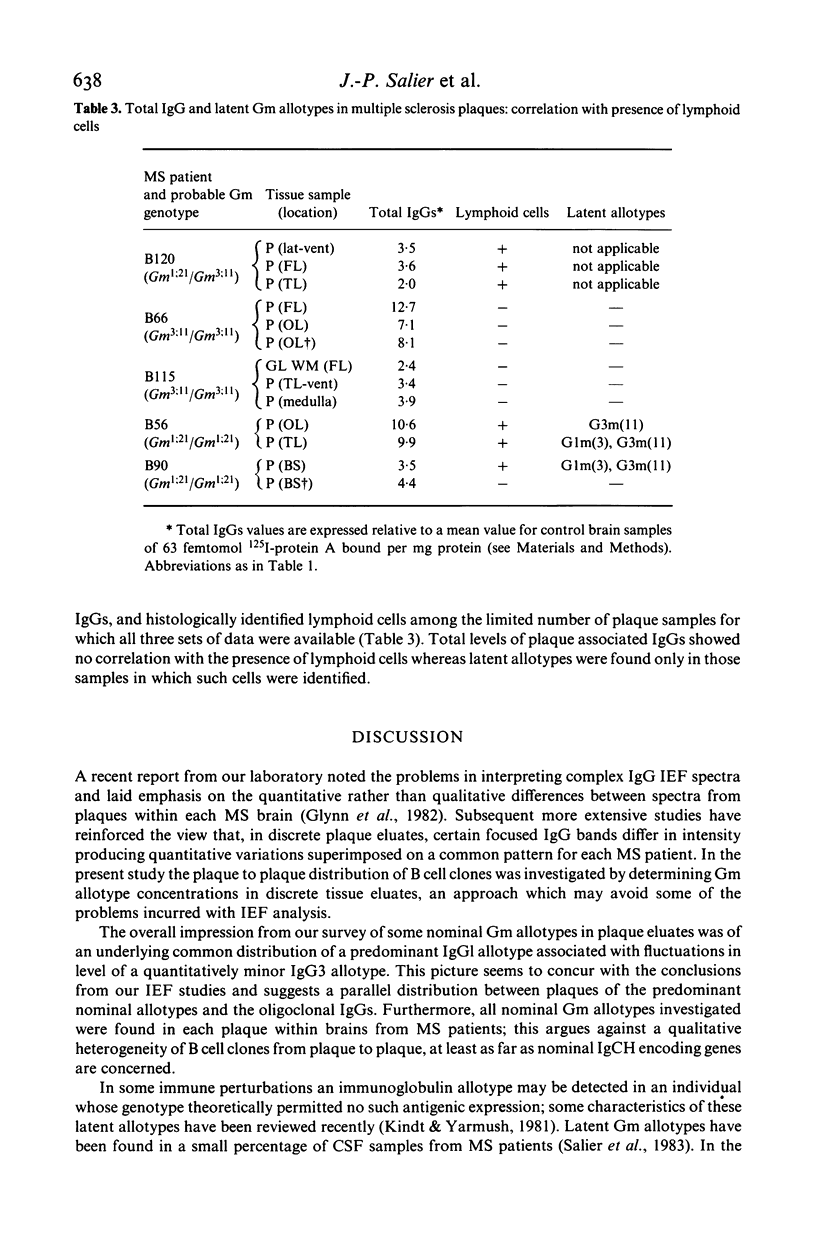
Concentrations of IgG allotypes G1m(1), G1m(3) and G3m(11) in neutral pH eluates from discrete plaques of multiple sclerosis (MS) brain and from white matter of control brain were determined to obtain information about distribution of B cell clones among MS lesions. Within each MS brain a predominant nominal IgG1 allotype was distributed rather homogeneously in all plaques while quantitatively minor allotypes showed some fluctuation. Latent IgG1 allotypes were detected (7-12% of the corresponding nominal allotype level) in some tissue eluates from both MS and control brains, which were homozygous for either G1m(1) or G1m(3). By contrast, the expression of a latent IgG3 allotype, namely G3m(11), was apparently MS restricted. Large amounts of latent allotypes were detected only in recent plaques with lymphoid cells whereas the distribution of total plaque associated IgGs did not correlate with the presence of lymphoid cells. Latent allotypes in recent MS lesions may mark a transient immunological activity which coincides with the infiltration of lymphoid cells and precedes the appearance in these plaques of oligoclonal IgGs, the distribution of which may parallel that of the predominant nominal allotypes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Esiri M. M. Multiple sclerosis: a quantitative and qualitative study of immunoglobulin-containing cells in the central nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1980 Jan-Feb;6(1):9–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1980.tb00199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn P., Gilbert H. M., Newcombe J., Cuzner M. L. Analysis of immunoglobulin G in multiple sclerosis brain: quantitative and isoelectric focusing studies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):102–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goust J. M., Hogan E. L., Arnaud P. Abnormal regulation of IgG production in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1982 Mar;32(3):228–234. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.3.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson D. H., Roos R. P., Arnason B. G. Isoelectric focusing of IgG eluted from multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis brains. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):335–337. doi: 10.1038/287335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson D. H., Roos R. P., Arnason B. G. Oligoclonal IgG in multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis brains. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Jun;2(3-4):261–276. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe J., Glynn P., Cuzner M. L. Analysis by transfer electrophoresis of reactivity of IgG with brain proteins in multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):1192–1194. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Goust J. M., Salier J. P., Fudenberg H. H. Immunoglobulin G heavy chain (Gm) allotypes in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1797–1800. doi: 10.1172/JCI110220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roström B. Antibodies against viruses and structural brain components in oligoclonal IgG obtained from multiple sclerosis brain. J Neurol. 1982;226(4):255–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00313398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Goust J. M., Pandey J. P., Fudenberg H. H. Preferential synthesis of the G1m(1) allotype of IgG1 in the central nervous system of multiple sclerosis patients. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1400–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.6973823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Sarvas H., Reisner H. M., Wang A. C., Fudenberg H. H. Quantitative studies of Gm allotypes--III. Some effects of IgG aggregation in radioimmunoassays using human IgM and rabbit IgG anti-Gm antibodies. Mol Immunol. 1979 Apr;16(4):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavolato B. F. Immunoglobulin G distribution in multiple sclerosis brain. An immunofluorescence study. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Jan;24(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartdal F., Vandvik B. Multiple sclerosis. Electrofocused "bands" of oligoclonal CSF IgG do not carry antibody activity against measles, varicella-zoster or rotaviruses. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Apr;54(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartdal F., Vandvik B., Norrby E. Viral and bacterial antibody responses in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1980 Sep;8(3):248–255. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


