Abstract
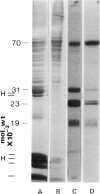
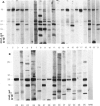
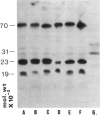
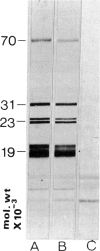
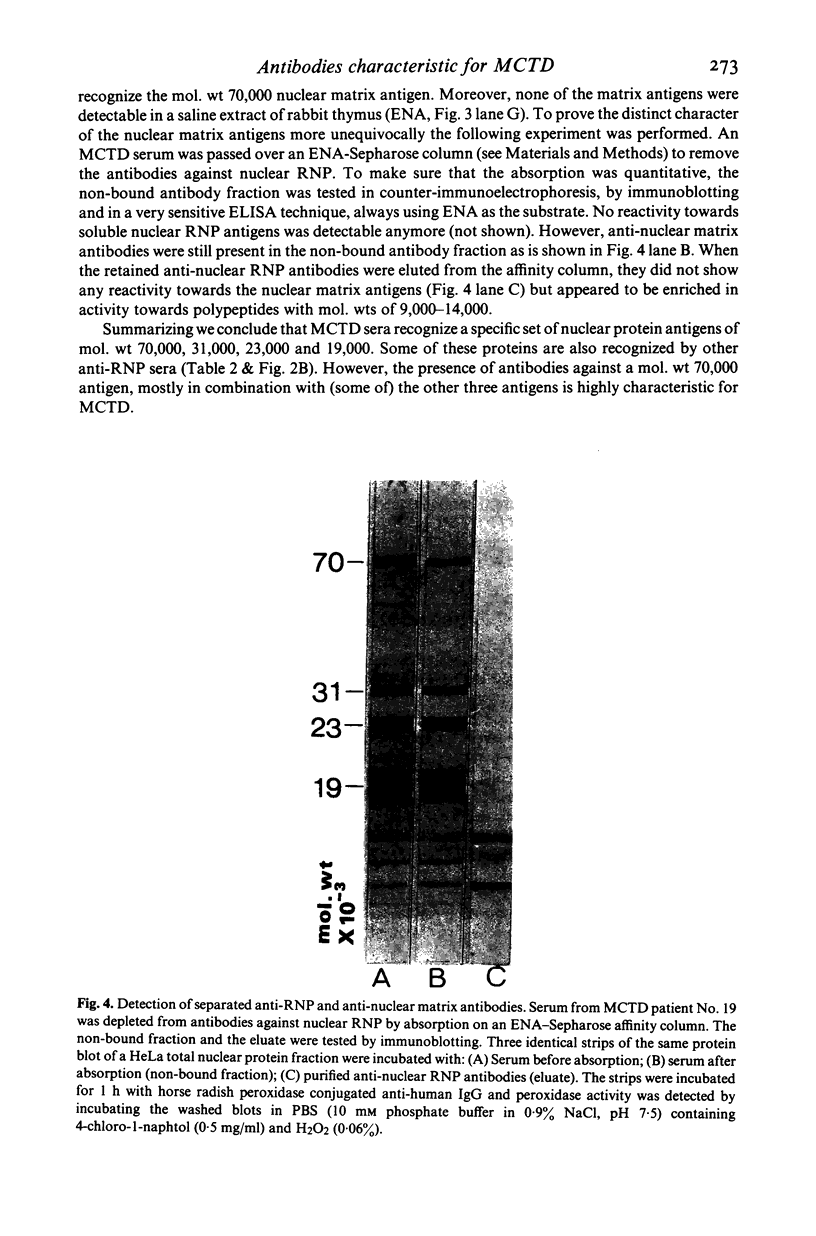
Specific nuclear proteins, separated according to their molecular weight (mol. wt) by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and subsequently transferred to nitrocellulose sheets, are able to bind antibodies in sera from patients suffering from different types of connective tissue diseases. Antibodies against a characteristic set of nuclear protein antigens are found in sera from patients with mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD). Screening of 21 MCTD sera revealed a typical immunoblot pattern with major protein antigens of mol. wt 70,000 (20/21) (not identical with the Scl-70 antigen characteristic for scleroderma), mol. wt 31,000 (17/21), two proteins around mol. wt 23,000 (15/21) and two around mol. wt 19,000 (10/21). The 70,000, 23,000 and 19,000 antigens appeared to be rather insoluble nuclear proteins (i.e. components of the nuclear matrix). On behalf of their structural character they were present in nuclei from several types of cells but only in low amounts detectable in salt extracts of thymus acetone powder. The presence of antibodies directed against the mol. wt 70,000 antigen correlated strongly with the diagnosis of MCTD. This 70,000 antigen is not identical with the RNP antigen, a soluble ribonuclease sensitive ribonucleoprotein, since antibodies against nuclear RNP can be separated from anti-nuclear matrix antibodies by affinity chromatography using immobilized thymus salt extract. The distinct character of soluble nuclear RNP and structural nuclear matrix antigens is further supported by the fact that from 14 other anti-RNP sera obtained from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), only three contained antibodies against the mol. wt 70,000 protein. Since the immunoblot pattern obtained with MCTD sera mostly was clearly distinguishable from the patterns obtained with sera from patients with related connective tissue diseases our results suggest that the immunoblotting technique might be useful as a diagnostic tool and support the concept of MCTD as a distinct entity.
Full text
PDF



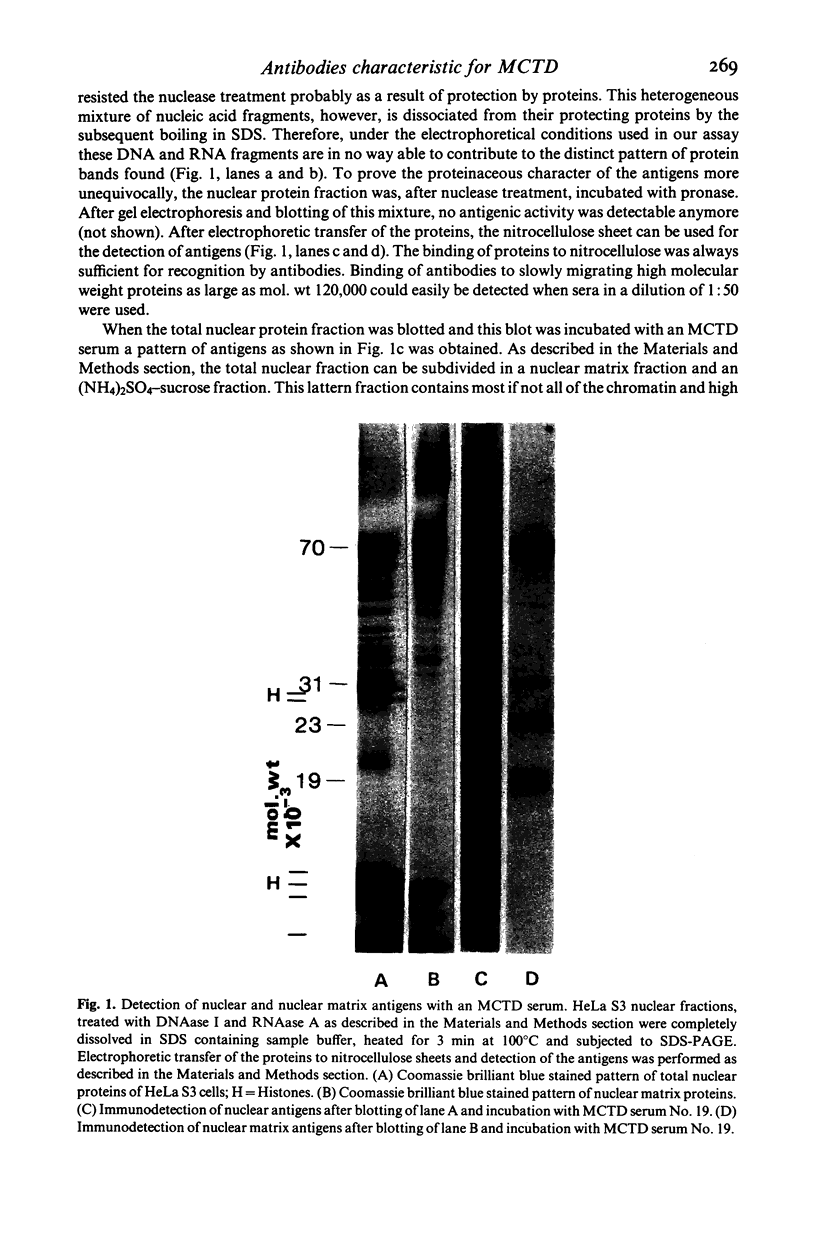
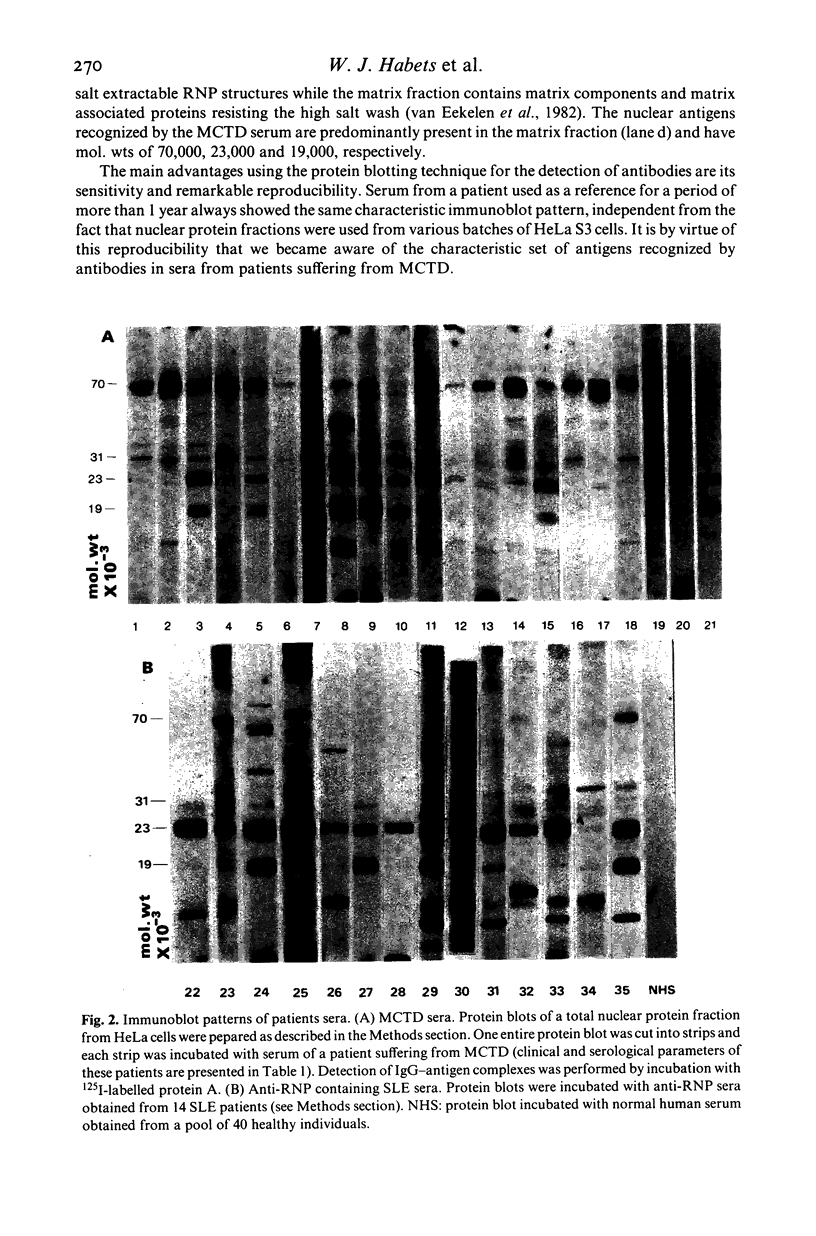
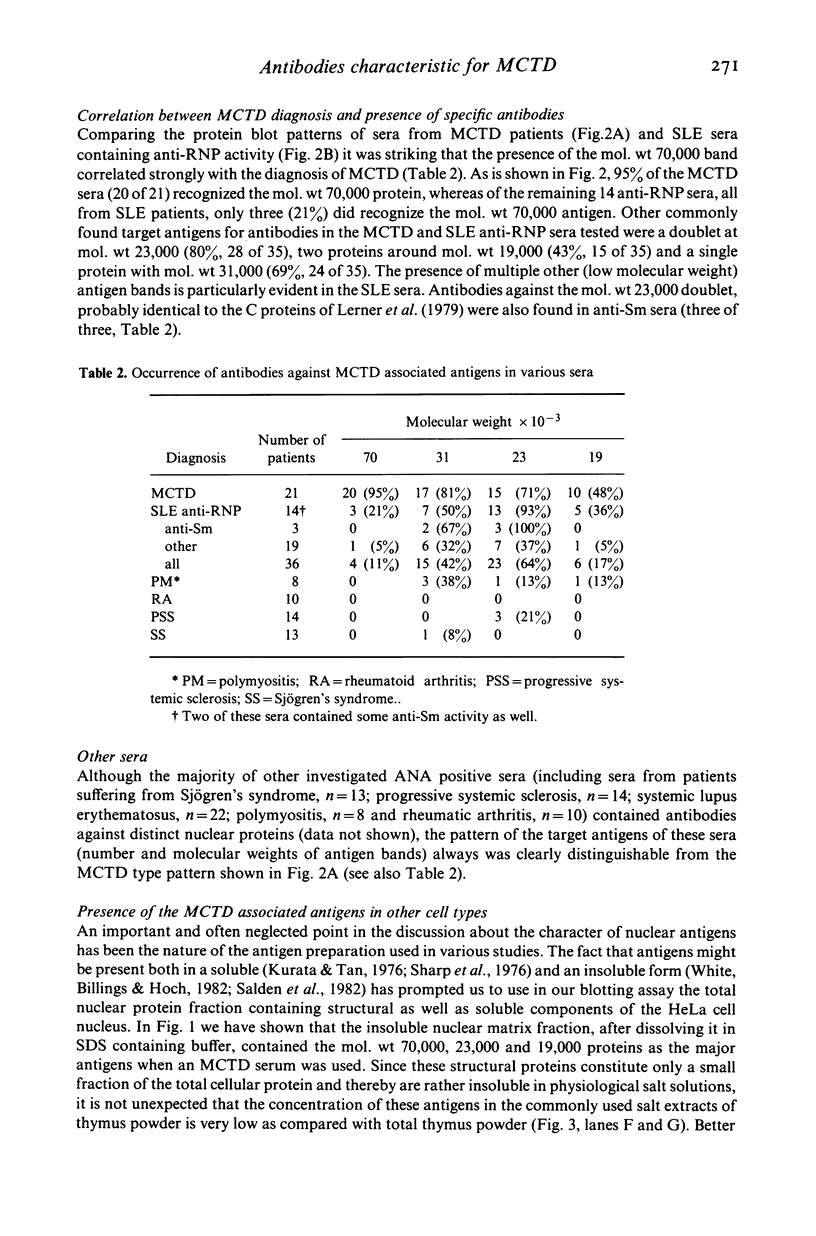
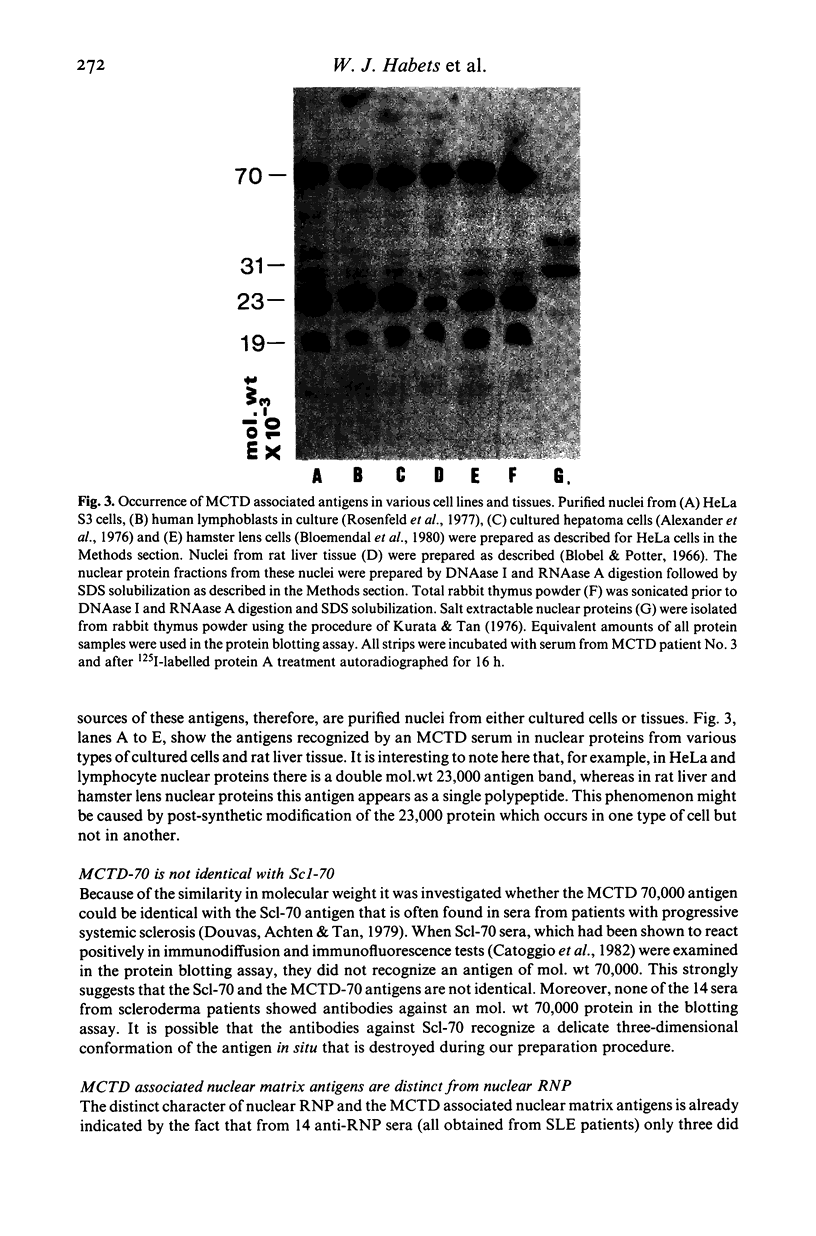



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., de Groot E. R., Feltkamp T. E. Immunology of DNA. III. Crithidia luciliae, a simple substrate for the determination of anti-dsDNA with the immunofluorescence technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. J., Bey E. M., Geddes E. W., Lecatsas G. Establishment of a continuously growing cell line from primary carcinoma of the liver. S Afr Med J. 1976 Dec 18;50(54):2124–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H., Lenstra J. A., Dodemont H., Ramaekers F. C., Groeneveld A. A., Dunia I., Benedetti E. L. SV40-transformed hamster lens epithelial cells: a novel system for the isolation of cytoskeletal messenger RNAs and their translation products. Exp Eye Res. 1980 Nov;31(5):513–525. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(80)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohan A., Peter J. B., Bowman R. L., Pearson C. M. Computer-assisted analysis of 153 patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Jul;56(4):255–286. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197707000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cats A., Klein F. Quantitative aspects of the latex-fixation and Whaaler-Rose tests. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Nov;29(6):663–672. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.6.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A. S., Achten M., Tan E. M. Identification of a nuclear protein (Scl-70) as a unique target of human antinuclear antibodies in scleroderma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10514–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlaw C. S., Dusing-Swartz S. K., Berget S. M. Human U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins contain common and unique polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1159–1166. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata N., Tan E. M. Identification of antibodies to nuclear acidic antigens by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19(3):574–580. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenk R. P., Maizel J. V., Jr, Crouch R. J. Expression of two late adenovirus genes is altered by introducing antibodies against ribonucleoprotein into living HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(3):475–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter L., Schopfer K., Wilhelm J. A., Nyffenegger T., Parisot R. F., De Robertis E. M. Molecular characterization of ribonucleoprotein antigens bound by antinuclear antibodies. A diagnostic evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1278–1283. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notman D. D., Kurata N., Tan E. M. Profiles of antinuclear antibodies in systemic rheumatic diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Oct;83(4):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-4-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld C., Goutner A., Choquet C., Venuat A. M., Kayibanda B., Pico J. L., Greaves M. F. Phenotypic characterisation of a unique non-T, non-B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):841–843. doi: 10.1038/267841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salden M. H., Van Eekelen C. A., Habets W. J., Vierwinden G., Van de Putte L. B., Van Venrooy W. J. Anti-nuclear matrix antibodies in mixed connective tissue disease. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Sep;12(9):783–786. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., May C. M., Holman H. R., McDuffie F. C., Hess E. V., Schmid F. R. Association of antibodies to ribonucleoprotein and Sm antigens with mixed connective-tissue disease, systematic lupus erythematosus and other rheumatic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 18;295(21):1149–1154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611182952101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sri-Widada J., Assens C., Liautard J. P., Jeanteur P., Brunel C. Isolation of a pure U1 snRNP from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90659-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Agris P. F., Sharp G. C. Purification and biochemical characterization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigen using purified antibody from serum of a patient with mixed connective tissue disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1449–1456. doi: 10.1172/JCI109809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Golden S. S., Sharp G. C., Agris P. F. Molecular relationships between two nuclear antigens, ribonucleoprotein and Sm: purification of active antigens and their biochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5929–5936. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Billings P. B., Hoch S. O. Assays for the Sm and RNP autoantigens: the requirement for RNA and influence of the tissue source. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2751–2756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Gardner W. D., Hoch S. O. Identification of the immunogenically active components of the Sm and RNP antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):626–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Hoch S. O. Definition of the antigenic polypeptides in the Sm and RNP ribonucleoprotein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91530-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C. A., Salden M. H., Habets W. J., van de Putte L. B., van Venrooij W. J. On the existence of an internal nuclear protein structure in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C. A., van Venrooij W. J. hnRNA and its attachment to a nuclear protein matrix. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):554–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]