Abstract
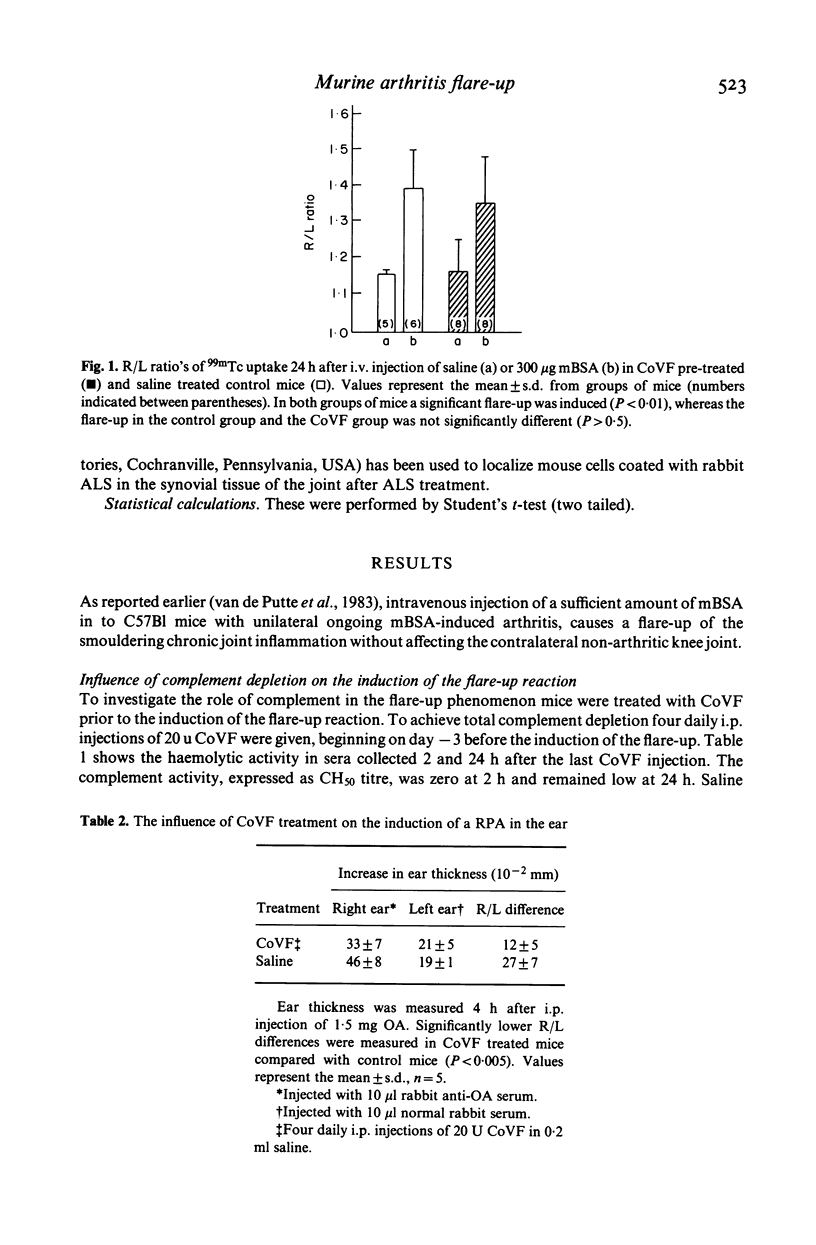
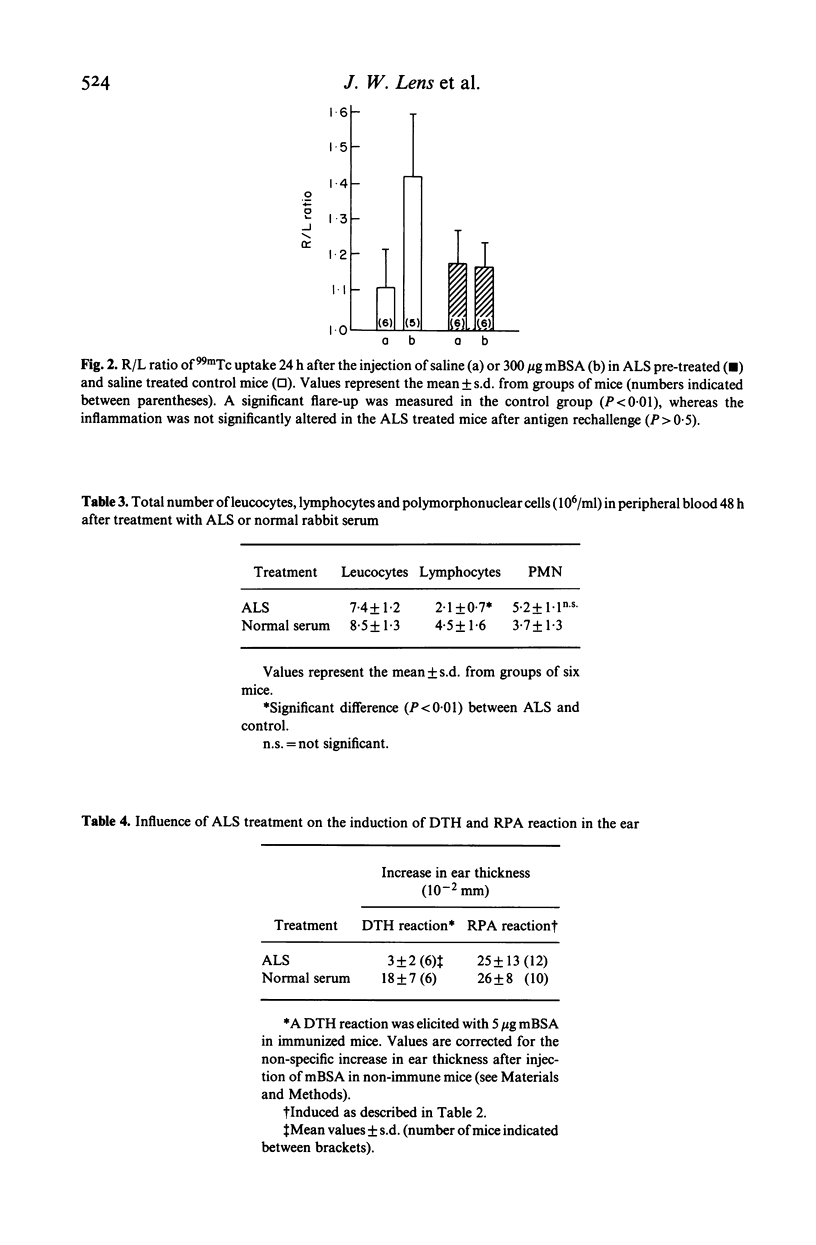
Intravenous injection of methylated bovine serum albumin (mBSA) into mice with unilateral chronic mBSA-induced arthritis (AIA) causes a flare-up of the joint inflammation without affecting the contralateral non-arthritic knee joint. We studied the mechanism of the flare-up by decomplementation with cobra venom factor (CoVF) and by treatment with anti-lymphocyte serum (ALS) prior to the induction of the flare-up. Treatment of mice with CoVF had no effect on the induction of the flare-up reaction whereas a reversed passive Arthus reaction (RPA) in the ear of similarly treated mice was clearly suppressed. The complement activity in the serum was zero at 2 h after CoVF treatment and remained for 24 h. This indicates that this type of flare-up reaction is not complement-dependent. On the other hand, the flare-up reaction was completely abolished after treatment with ALS. Control experiments revealed that ALS treatment diminished the number of lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and clearly suppressed a delayed hypersensitivity reaction in the ear, but had no effect on an RPA. These results suggest an important role of T lymphocytes in the mechanism of the flare-up of arthritis. T lymphocytes were demonstrated in the synovial tissue of chronically inflamed joints by immunofluorescence and appeared to be diminished after ALS treatment. Interaction between exogenous antigen and antigen reactive T lymphocytes present in chronically inflamed joints, may be an important principle in the exacerbation and propagation of joint inflammation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berden J. H., Gerlag P. G., Hagemann J. F., Koene R. A. Role of antiserum and complement in the acute antibody-mediated rejection of mouse skin allografts in strain combinations with increasing histoincompatibility. Transplantation. 1977 Sep;24(3):175–182. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berden J. H., Hagemann J. F., Koene R. A. A sensitive haemolytic assay of mouse complement. J Immunol Methods. 1978;23(1-2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogman M. J., Berden J. H., Cornelissen I. M., Maass C. N., Koene R. A. The role of complement in the induction of acute antibody-mediated vasculitis of rat skin grafts in the mouse. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):97–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Mackay I. R. Antigen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Induction of arthritis in various strains of mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Vadas M. A., Mackay I. R. Studies on antigen-induced arthritis in mice. III. Cell and serum transfer experiments. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1645–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. I. The role of antigen on the local immune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):327–337. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J. Delayed hypersensitivity in the mouse. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:197–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weck A. L., Frey J. R., Geleick H. Immunologic specificity of the localized Shwartzman phenomenon induced in guinea pigs by simple chemical haptens. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. H., Strober S., Hoppe R. T., Calin A., Engleman E. G., Kotzin B. L., Tanay A. S., Calin H. J., Terrell C. P., Kaplan H. S. Sustained improvement of intractable rheumatoid arthritis after total lymphoid irradiation. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;26(8):937–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg V. M., Lance E. M., Davis P. Experimental immune synovitis in the rabbit. Relative roles of cell mediated and humoral immunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Nov-Dec;17(6):993–1005. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. G., Monaco A. P., Wood M. L., Russell P. S. Studies on heterologous anti-lymphocyte serum in mice. I. In vitro and in vivo properties. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen L. H., Bleumink E. Flare and rash reactions in contact allergy of the guinea-pig. Br J Dermatol. 1970;83(Suppl):48–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijsen M. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., van den Broek W. J. Detection and quantification of experimental joint inflammation in mice by measurement of 99mTc-pertechnetate uptake. Agents Actions. 1981 Dec;11(6-7):640–642. doi: 10.1007/BF01978775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Flare-up of antigen-induced arthritis in mice after challenge with intravenous antigen: studies on the characteristics of and mechanisms involved in the reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):287–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. H., Stewart A. G., Fennessy M. R. Platelet serotonin release in rheumatoid arthritis: a study in food-intolerant patients. Lancet. 1983 Aug 6;2(8345):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. A superoxide-activated chemotactic factor and its role in the inflammatory process. Agents Actions. 1980 Dec;10(6):522–527. doi: 10.1007/BF02024157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Campion J. P., Kapnick S. J. Antilymphocyte globulins. Clinical use of antilymphocyte globulin. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):1007–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Wood M. L., Gray J. G., Russell P. S. Studies on heterologous anti-lymphocyte serum in mice. II. Effect on the immune response. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke A. L., Hughes G. R. Rheumatoid arthritis and food: a case study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jun 20;282(6281):2027–2029. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6281.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijntjes N. V., Van de Putte L. B., Van der Pol M., Guelen P. J. Cryosectioning of undecalcified tissues for immunofluorescence. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheper R. J., von Blomberg M., Boerrigter G. H., Bruynzeel D., van Dinther A., Vos A. Induction of immunological memory in the skin. Role of local T cell retention. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jan;51(1):141–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Wilder R. L., Katona I. M., Wahl L. M., Allen J. B., Scher I., Decker J. L. Leukapheresis in rheumatoid arthritis. Association of clinical improvement with reversal of anergy. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Sep;26(9):1076–1084. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. Rheumatoid arthritis and food: a case study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Aug 22;283(6290):563–563. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6290.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Maarsseveen A. C., Bomhof G., Scheper R. J. Demonstration of accelerated and increased migration inhibition factor release in vivo in a PPD retest reaction. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;67(1):1–6. doi: 10.1159/000232979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte L. B., Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., Kruijsen M. W. Exacerbation of antigen-induced arthritis after challenge with intravenous antigen. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):161–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Lens J. W., van de Putte L. B., van Beusekom H. J. Antigen induced arthritis: antigen handling and chronicity of joint inflammation. Agents Actions Suppl. 1982;11:233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



