Abstract
The characteristics of the solid-phase conglutinin method for the isolation of C3-containing complexes from the synovial effusions of rheumatoid arthritis patients were assessed. All major proteins in such complexes were identified and shown to be either immunoglobulin or complement components. The high proportion of IgM and the association between complexed IgM and latex agglutination titre suggest that IgM rheumatoid factor, probably binding to self-associated IgG antiglobulins, is of major importance in the formation of complement-fixing complexes. A minority of samples contained unidentified trace components and these differed from one fluid to another. The levels of complexed immunoglobulins were closely correlated to the titres of synovial fluid antiglobulins. The data accords with the view that autosensitization to IgG plays the primary role in the development of immunopathological features of rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF


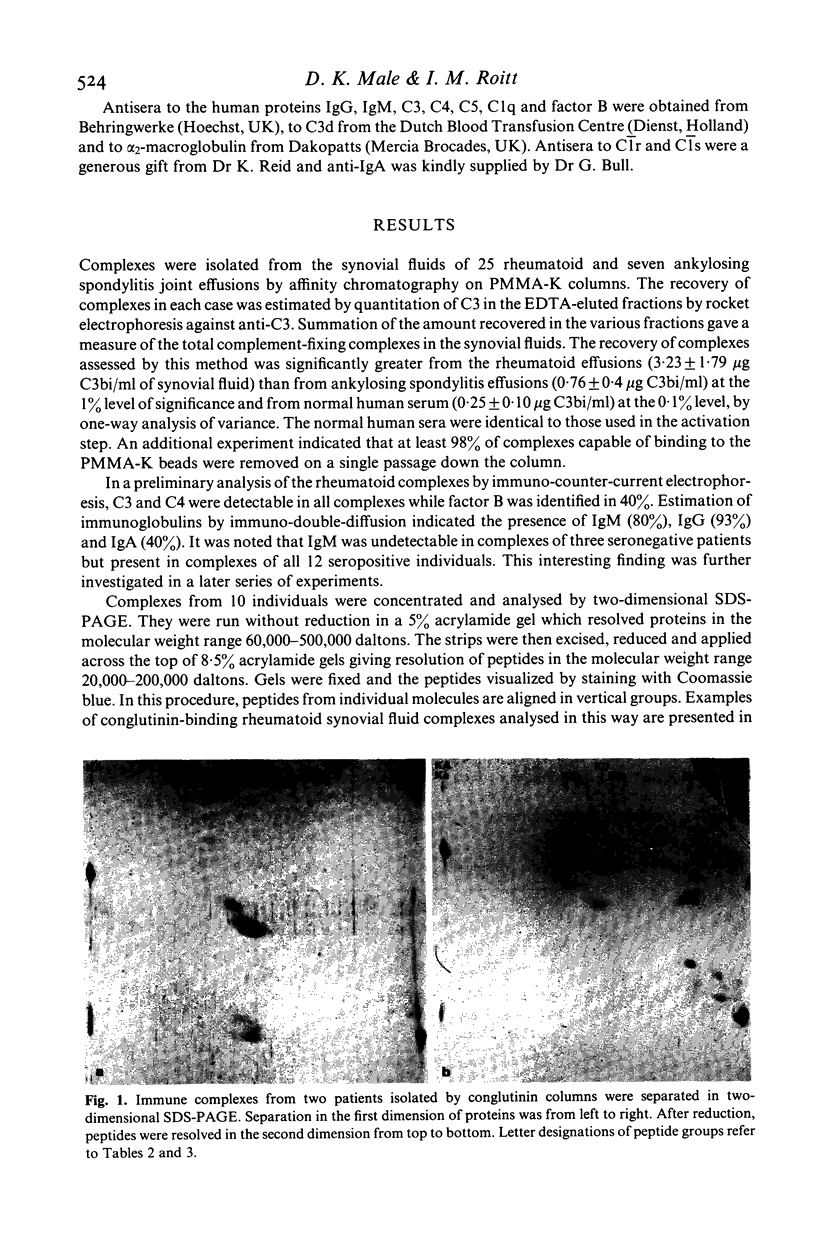
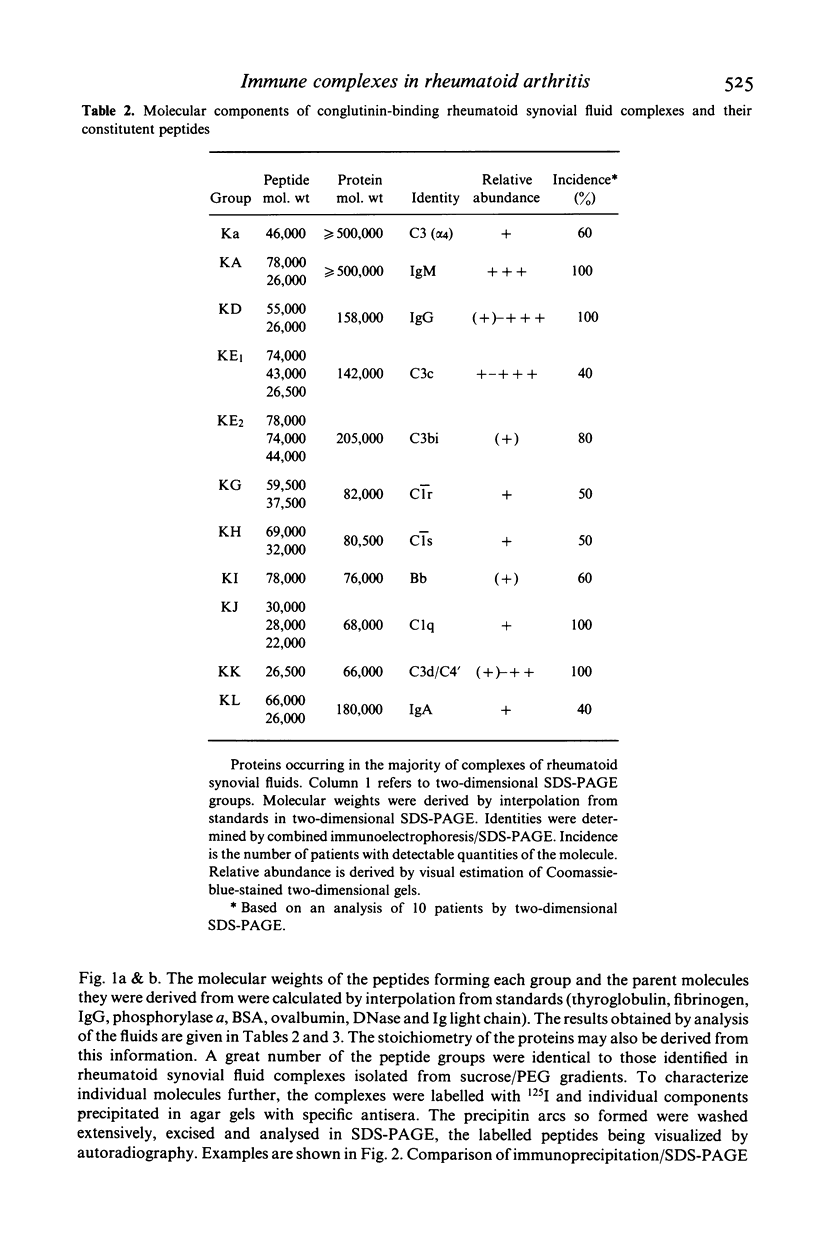

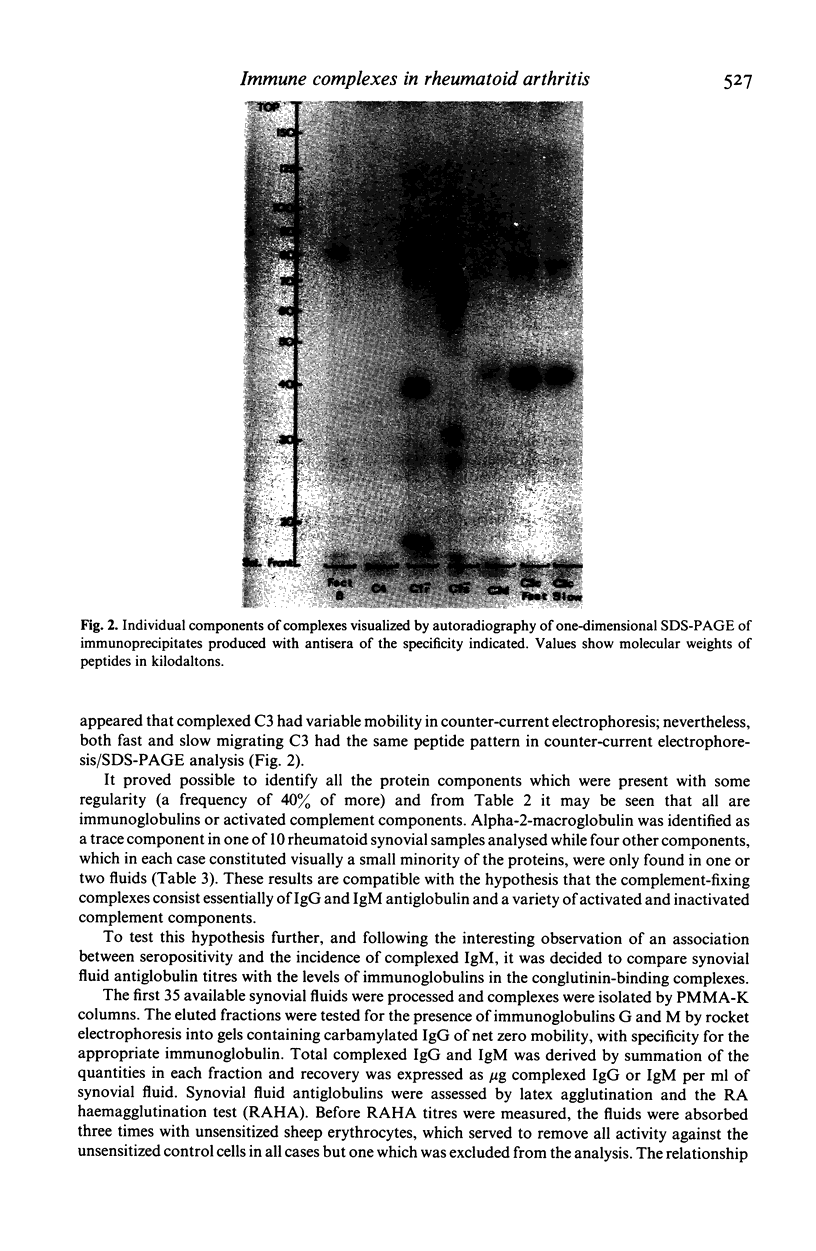


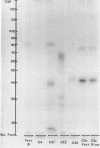
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell C., Talal N., Schur P. H. Antibodies to DNA in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):535–540. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Lambert P. H. Purification of soluble immune complexes from serum using polymethylmetacrylate beads coated with conglutinin or C1q. Application to the analysis of the components of in vitro formed immune complexes and of immune complexes occurring in vivo during leishmaniasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Aug;37(2):295–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Schur P. H. Binding of circulating immune complexes to human peripheral blood lymphocytes: effect of complement. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jun;10(2):202–213. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Roitt I. M. Analysis of the components of immune complexes. Mol Immunol. 1979 Mar;16(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Roitt I. M., Hay F. C. Analysis of immune complexes in synovial effusions of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):297–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani B., Rabinovitch M., Nussenzweig V. Phagocytosis of immune complexes by macrophages. Different roles of the macrophage receptor sites for complement (C3) and for immunoglobulin (IgG). J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):780–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]