Abstract
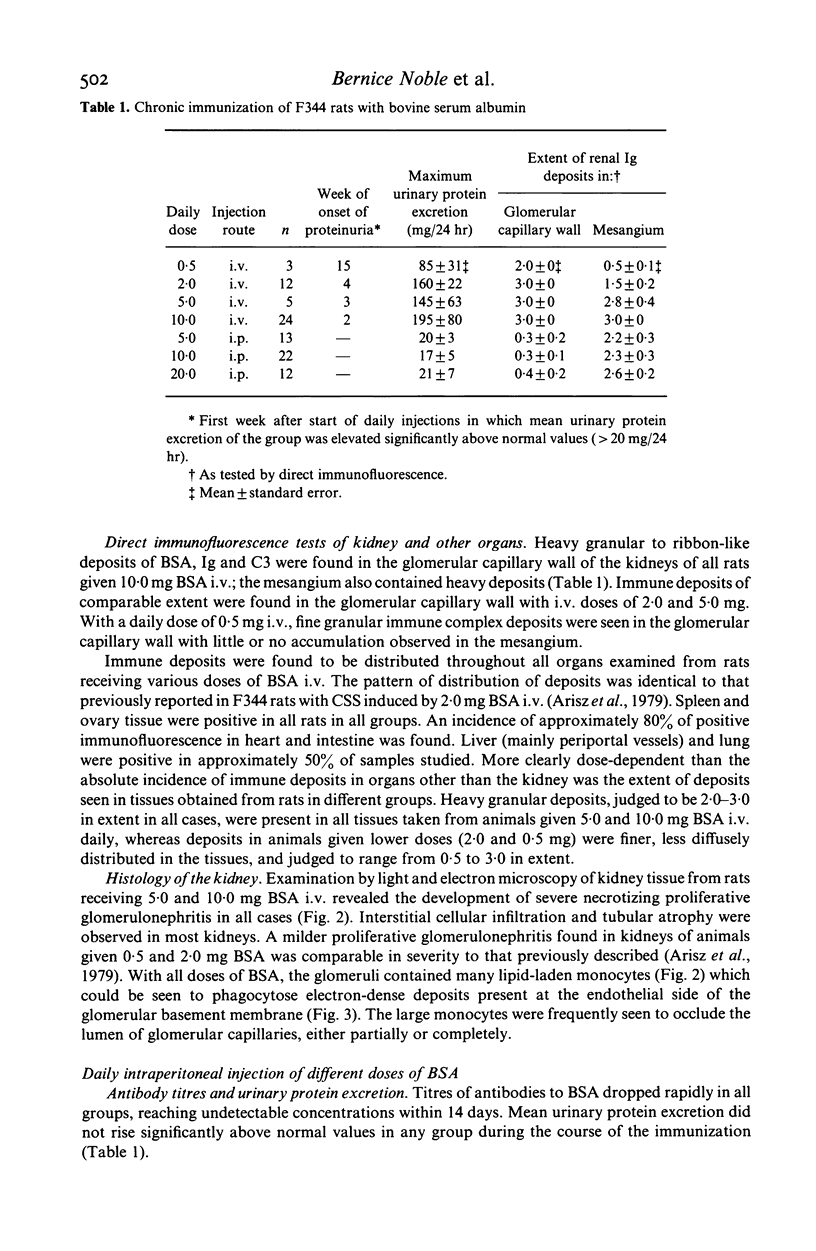
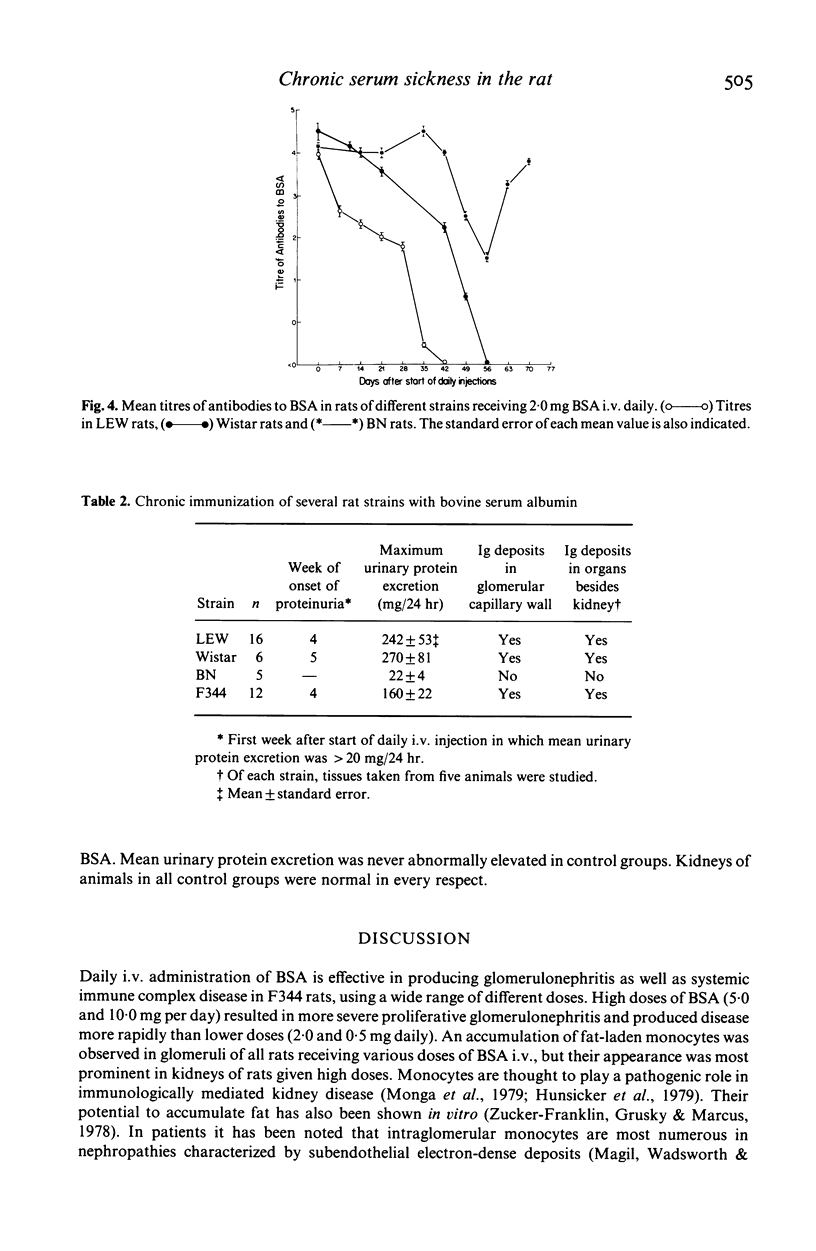
Chronic serum sickness (CSS) with systemic immune complex deposition has been produced in female Fischer (F344) rats by the daily intravenous (i.v.) administration of 2.0 mg bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Arisz et al., 1979). In the experiments described below, daily i.v. doses ranging from 0.5 to 10.0 mg BSA were found to be effective in producing CSS in F344 strain rats. The severity of renal disease and the extent of extrarenal immune complex deposition were increased with higher daily doses of BSA. Daily administration of different doses of BSA by an intraperitoneal (i.p.) route resulted only in slight mesangial glomerular abnormalities and did not cause abnormal elevation of urinary protein excretion. At the same time, extrarenal accumulation of immune deposits similar to that observed in rats given BSA by the i.v. route was seen. Wistar and Lewis (LEW) strain rats were similar to F344 strain rats in susceptibility to the induction of CSS, but daily i.v. injection of 2.0 mg BSA failed to produce the disease in Brown Norway (BN) rats. The latter observation suggests that genetic differences may influence the expression of immune complex disease in this model.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres G. A., Szymanski C., Albini B., Brentjens J., Milgrom M., Noble B., Ossi E., Steblay R. Structural observations on epithelioid and giant cells in experimental autoimmune tubulointerstitial nephritis in guinea pigs. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):21–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arisz L., Noble B., Milgrom M., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. A. Experimental chronic serum sickness in rats. A model of immune complex glomerulonephritis and systemic immune complex deposition. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;60(1):80–88. doi: 10.1159/000232325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., O'Connell D. W., Albini B., Andres G. A. Experimental chronic serum sickness in rabbits that received daily multiple and high doses of antigen: a systemic disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., O'Connell D. W., Pawlowski I. B., Andres G. A. Extra-glomerular lesions associated with deposition of circulating antigen-antibody complexes in kidneys of rabbits with chronic serum sickness. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Sep;3(1):112–126. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., O'Connell D. W., Pawlowski I. B., Hsu K. C., Andres G. A. Experimental immune complex disease of the lung. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling certain human interstitial lung diseases. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):105–125. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J., Ossi E., Albini B., Sepulveda M., Kano K., Sheffer J., Vasilion P., Marine E., Baliah T., Jockin H. Disseminated immune deposits in lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 May;20(4):962–968. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feld L. G., Van Liew J. B., Galaske R. G., Boylan J. W. Selectivity of renal injury and proteinuria in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Kidney Int. 1977 Nov;12(5):332–343. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennell R. H., Jr, Pardo V. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in rats. Lab Invest. 1967 Nov;17(5):481–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERMUTH F. G., Jr A comparative histologic and immunologic study in rabbits of induced hypersensitivity of the serum sickness type. J Exp Med. 1953 Feb 1;97(2):257–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARE R. S. Endogenous creatinine in serum and urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 May;74(1):148–151. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-17837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagstrom G. L., Bloom P. M., Yum M. N., Lavelle K. J., Luft F. C. Ferritin- and apoferritin-induced immune complex glomerulonephritis in mice. Nephron. 1979;24(3):127–133. doi: 10.1159/000181700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Shearer T. P., Plattner S. B., Weisenburger D. The role of monocytes in serum sickness nephritis. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):413–425. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison P. J., Reichlin M. Deposition of antibodies to a soluble cytoplasmic antigen in the kidneys of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Aug;22(8):858–863. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magil A. B., Wadsworth L. D., Loewen M. Monocytes and human renal glomerular disease: a quantitative evaluation. Lab Invest. 1981 Jan;44(1):27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monga G., Mazzucco G., di Belgiojoso G. B., Busnach G. The presence and possible role of monocyte infiltration in human chronic proliferative glomerulonephritides. Light microscopic, immunofluorescence, and histochemical correlations. Am J Pathol. 1979 Feb;94(2):271–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble B., Olson K. A., Milgrom M., Albini B. Tissue deposition of immune complexes in mice receiving daily injections of bovine serum albumin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):255–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachas W. N., Linscheer W. G., Pinals R. S. Protein-losing enteropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1971 Feb;55(2):162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W. Chronic immune complex disease in mice: the role of antibody affinity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):414–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stilmant M. M., Couser W. G., Cotran R. S. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the mouse associated with mesangial deposition ofautologous ferritin immune complexes. Lab Invest. 1975 Jun;32(6):746–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Aarden L. A., Statius van Eps L. W., Feltkamp T. E. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):226–235. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Masi A. T. Systemic lupus erythematosus with a protein-losing enteropathy. JAMA. 1976 Jul 19;236(3):287–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Wochner R. D., Strober W. The role of the gastrointestinal tract in plasma protein metabolism. Studies with 51Cr-albumin. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Grusky G., Marcus A. Transformation of monocytes into "fat" cells. Lab Invest. 1978 May;38(5):620–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]