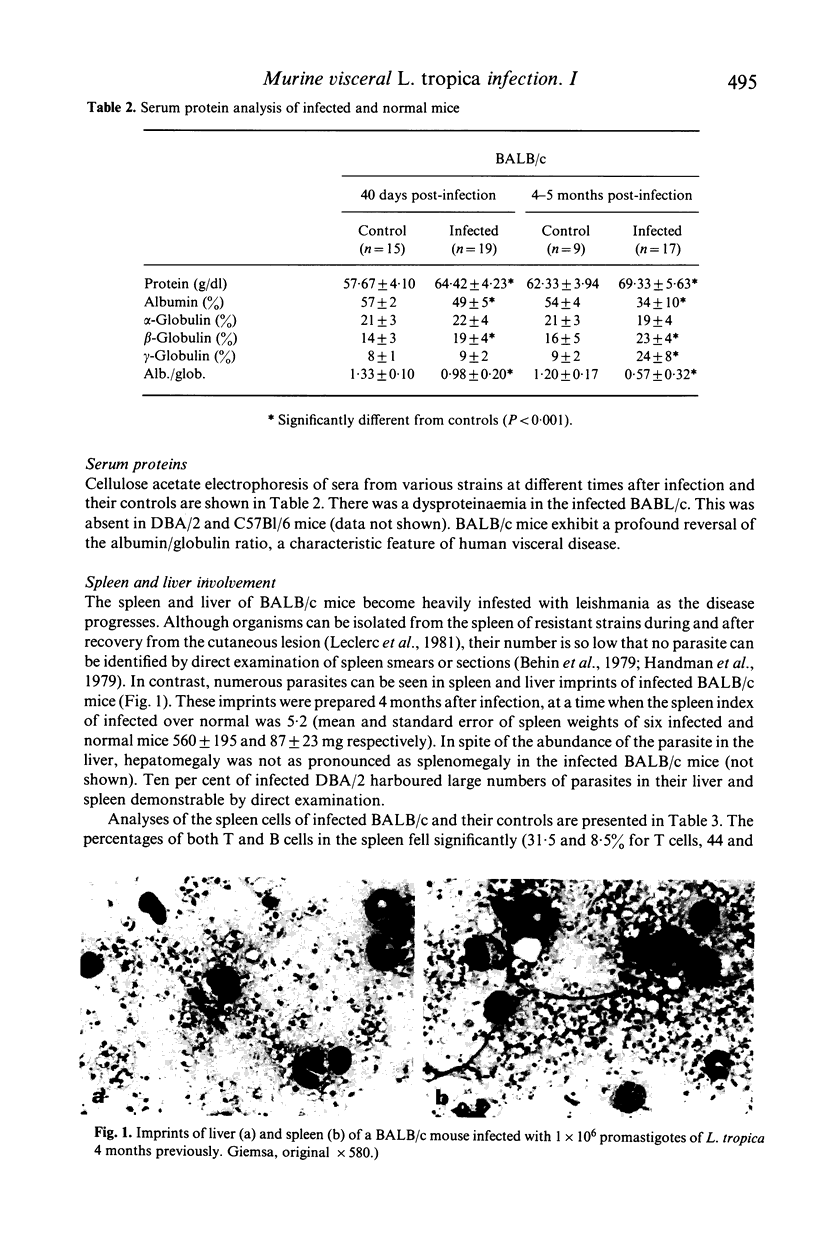
Abstract
The visceral and lethal infection produced in BALB/c mice by Leishmania tropica (major) is accompanied by splenomegaly, anaemia and reversal of albumin-to-globulin ratio. The percentages of both B and T cells are decreased in the spleen. The spleen and lymph nodes become populated with large Ig-, Thy 1.2- 'null' cells. The similarity of some of these parameters with those produced in human kala-azar is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorvatn B., Neva F. A. A model in mice for experimental leishmaniasis with a West African strain of Leishmania tropica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):472–479. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J., Freeman J., Bradley D. Influence of H-2 complex on acquired resistance to Leishmania donovani infection in mice. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):72–74. doi: 10.1038/283072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Kirkley J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. I. the variable course of Leishmania donovani infections in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D. Immunological aspects of clinical leishmaniasis. Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Oct;63(10):1056–1060. doi: 10.1177/003591577006301048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. A., Holbrook T. W., Parker B. W. Visceral leishmaniasis in mice: protective effect of glucan. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Jun;27(6):567–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose A. C., Chowdhury A. B. Immunoglobulin studies in malaria and kala-azar infections. Indian J Med Res. 1977 Oct;66(4):566–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Ceredig R., Mitchell G. F. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: disease patterns in intact and nude mice of various genotypes and examination of some differences between normal and infected macrophages. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Feb;57(1):9–29. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Chan-Liew W. L. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. 1. Immunogenetic aspects of susceptibility to Leishmania tropica in mice. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Winter;2(4):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. III. Nature and significance of specific suppression of cell-mediated immunity in mice highly susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):594–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Immunological regulation of experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. IV. Prophylactic effect of sublethal irradiation as a result of abrogation of suppressor T cell generation in mice genetically susceptible to Leishmania tropica. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):557–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javadian E., Nadim A., Tahvildare-Bidruni G., Assefi V. Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran: B. Khorassan Part V: Report on a focus of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Esferayen. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1976 Mar-Apr;69(2):140–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellina O. I. O razlichiiakh v chuvstvitel'nosti inbrednykh myshei raznykh linii k Leishmania tropica major. Med Parazitol (Mosk) 1973 May-Jun;42(3):279–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight R., Woodruff A. W., Pettitt L. E. The mechanism of anaemia in kala-azar. A study of 2 patients. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1967;61(5):701–705. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(67)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor-Withey K. S., Clayton C. E., Roelants G. E., Askonas B. A. Trypanosomiasis leads to extensive proliferation of B, T and null cells in spleen and bone marrow. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Dec;34(3):359–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musumeci S., Fischer A., Pizzarelli G. Dysproteinaemia in kala-azar. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(2):176–177. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Modabber F. Z. Generalized infection and lack of delayed hypersensitivity in BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania tropica major. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):611–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.611-614.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston P. M., Behbehani K., Dumonde D. C. Experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis: VI: anergy and allergy in the cellular immune response during non-healing infection in different strains of mice. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1978 Nov;1(3):207–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rezai H. R., Ardehali S. M., Amirhakimi G., Kharazmi A. Immunological features of kala-azar. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1079–1083. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANKER A. Electrophoretic differential serum protein pattern in kala-azar. Br Med J. 1959 May 9;1(5131):1221–1223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5131.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrkovski L. L., Larson C. L. Effect of treatment with BCG on the course of visceral leishmaniasis in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):249–257. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.249-257.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter E. R., Peters W., Robinson B. L. The experimental chemotherapy of leishmaniasis, IV. The development of a rodent model for visceral infection. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1980 Apr;74(2):127–138. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1980.11687322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veress B., Omer A., Satir A. A., El Hassan A. M. Morphology of the spleen and lymph nodes in fatal visceral leishmaniasis. Immunology. 1977 Nov;33(5):605–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub J., Weinbaum F. I. The effect of BCG on experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis in mice. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2288–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]