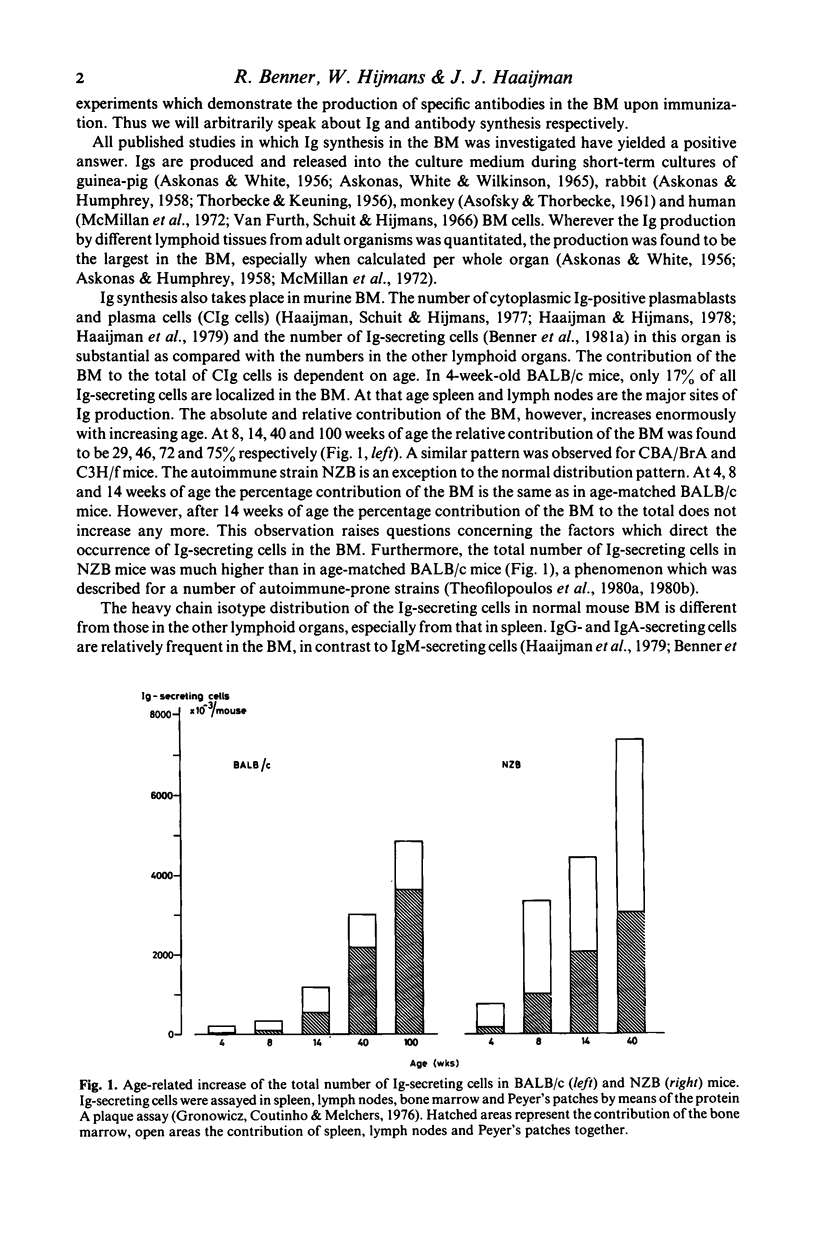
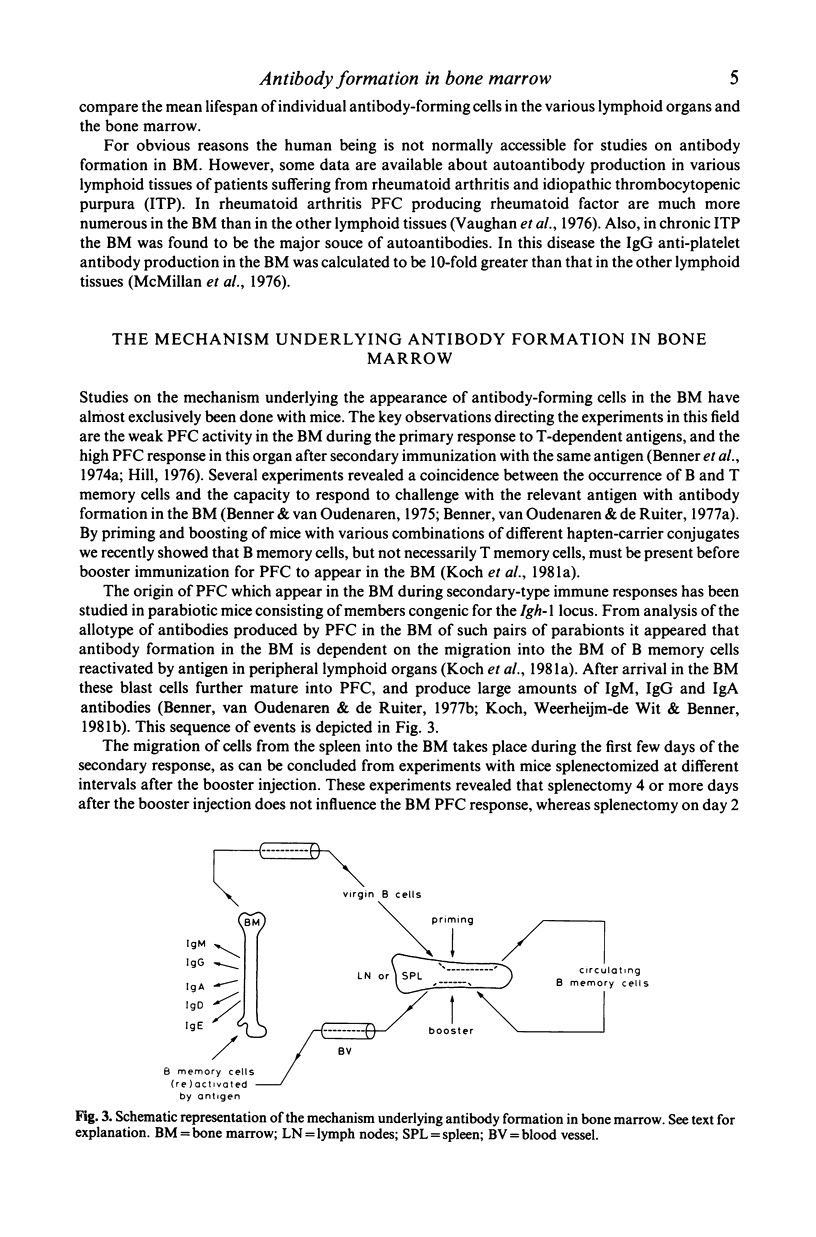
Abstract
Immunoglobulin (Ig) secreting cells occur in all lymphoid tissues, including the bone marrow (BM). There are important differences between the various organs with respect to their number of Ig-secreting cells and the heavy chain isotype distribution of the secreted Igs. Furthermore, both distribution patterns depend on age. Early in life most Ig-secreting cells are localized in spleen and lymph nodes. In adults, however, the majority of all Ig-secreting cells of the individual are localized in the BM. Immunization can lead to the appearance of substantial numbers of antibody-forming cells in BM. The kinetics of the BM response are different from the response in the peripheral lymphoid tissues. Shortly after immunization most antibody-forming cells occur in the peripheral lymphoid tissues, but later on, especially during secondary type responses, most antibody-forming cells are localized in the BM. Apparently, antibody formation is regulated in such a way that peripheral lymphoid tissues respond rapidly, but only for a short period, whereas the BM response starts slowly, but takes care of a long-lasting massive production of antibodies to antigens which repeatedly challenge the organism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A., HUMPHREY J. H. Formation of specific antibodies and gamma-globulin in vitro; a study of the synthetic ability of various tissues from rabbits immunized by different methods. Biochem J. 1958 Feb;68(2):252–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0680252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKONAS B. A., WHITE R. G. Sites of antibody production in the guinea-pig; the relation between in vitro synthesis of anti-ovalbumin and gamma-globulin and distribution of antibody-containing plasma cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Feb;37(1):61–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askonas B. A., White R. G., Wilkinson P. C. Production of gamma-1- and gamma-2-antiovalbumin by various lymphoid tissues of the guinea pig. Immunochemistry. 1965 Dec;2(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asofsky R., Thorbecke G. J. SITES OF FORMATION OF IMMUNE GLOBULINS AND OF A COMPONENT OF C'(3): II. PRODUCTION OF IMMUNOELECTROPHORETICALLY IDENTIFIED SERUM PROTEINS BY HUMAN AND MONKEY TISSUES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1961 Sep 30;114(4):471–483. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.4.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Characterization of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide at the cellular level. I. Dose-response studies and the effect of prior immunization on the magnitude of the antibody response. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):469–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Haaijman J. J. Aging of the lymphoid system at the organ level. With special reference to the bone marrow as site of antibody production. Dev Comp Immunol. 1980 Fall;4(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(80)80062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Meima F., Van der Meulen G. M., van Ewijk W. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. III. Effects of route of priming and antigen dose. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):747–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Meima F., van der Meulen G. M., van Muiswinkel W. B. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. I. Evidence for the development of plaque-forming cells in situ. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):247–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Rijnbeek A. M., Bernabé R. R., Martinez-Alonso C., Coutinho A. Frequencies of background immunoglobulin-secreting cells in mice as a function if organ, age, and immune status. Immunobiology. 1981;158(3):225–238. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(81)80072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., van Oudenaren A. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. IV. The influence of splenectomy on the bone marrow plaque-forming cell response to sheep red blood cells. Cell Immunol. 1975 Oct;19(2):167–182. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., van Oudenaren A. Corticosteroids and the humoral immune response of mice. II. Enhancement of bone marrow antibody formation to lipopolysaccharide by high doses of corticosteroids. Cell Immunol. 1979 Dec;48(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., van Oudenaren A., Haaijman J. J. Deficient antibody formation in the bone marrow of nude mice. Immunology. 1978 Oct;35(4):619–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., van Oudenaren A., de Ruiter H. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. IX. Peripheral lymphoid organs are involved in the initiation of bone marrow antibody formation. Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., van Oudenaren Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. V. The response to the thymus-independent antigen Ecsherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Immunology. 1976 Jan;30(1):49–57. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braley-Mullen H. Regulatory role of T cells in IgG antibody formation and immune memory to type III Pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1909–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaperon E. A., Selner J. C., Claman H. N. Migration of antibody-forming cells and antigen-sensitive precursors between spleen, thymus and bone marrow. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):553–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel G. Les nodules lymphoïdes de la moelle osseuse. Aspect physiologique et pathologique. Essai d'interprétation. Presse Med. 1968 Oct 26;76(41):1947–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipert E. F., Klempau A. E., Lallone R. L., Cooper E. L. Bone marrow as a major lymphoid organ in Rana. Cell Immunol. 1979 Sep 1;46(2):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90416-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollapudi V. S., Kind L. S. Phenotypic correction of low reagin production: a genetic defect in the SJL mouse. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):906–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaijman J. J., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. Immunoglobulin-containing cells in different lymphoid organs of the CBA mouse during its life-span. Immunology. 1977 Apr;32(4):427–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaijman J. J., Slingerland-Teunissen J., Benner R., Van Oudenaren A. The distribution of cytoplasmic immunoglobulin containing cells over various lymphoid organs of congenitally athymic (nude) mice as a function of age. Immunology. 1979 Feb;36(2):271–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaijman J. J., Slingerland-Teunissen J., Van Oudenaren A., Mink J. G., Benner R. Kinetics of recovery of serum Ig levels and of cytoplasmic Ig positive cells in various lymphoid organs of nude mice after thymus transplantation. Immunology. 1980 Oct;41(2):279–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Gyure L. A., Payne A. W. Comparative aspects of the transport of immunoglobulin A from blood to bile. Immunology. 1980 Dec;41(4):899–902. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Hulsing-Hesselink E. An immunofluorescence study on intracellular immunoglobulins in human bone marrow cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:290–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. W. Distribution of plaque-forming cells in the mouse for a protein antigen. Evidence for highly active parathymic lymph nodes following intraperitoneal injection of hen lysozyme. Immunology. 1976 Jun;30(6):895–906. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janković B. D., Isaković K., Petrović S. Direct stimulation of lymphoid tissue of the chicken. 3. Haemagglutinin production, haemolysin-forming cells and changes in lymphoid tissues following injection of guinea-pig erythrocytes into the bone marrow. Immunology. 1973 Oct;25(4):663–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janković B. D., Paunović V. R. Immunological responses in the mole rat (Spalax leucodon). I. Antibody production, delayed hypersensitivity and lymphatic tissue. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1973 Feb;124(1):133–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kind L. S., Malloy W. F. Development of reaginic antibody-forming cells in the spleen and bone marrow of immunized mice. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1609–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe R., Herrlinger J. D., Müller-Ruchholtz W. B cell activity in rat bone marrow and spleen during primary and secondary response: dependence on strength of antigen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;59(1):99–103. doi: 10.1159/000232245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Hyun B. H., Rebuck J. W. Lymphoid follicles in bone marrow aspirates. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jan;67(1):41–48. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R., Longmire R. L., Yelenosky R., Lang J. E., Heath V., Craddock C. G. Immunoglobulin synthesis by human lymphoid tissues: normal bone marrow as a major site of IgG production. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1386–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J. Antibody-producing cells in bone marrow and other lymphoid tissues during the primary immune response in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(2):248–255. doi: 10.1159/000230409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Hijmans W., Scherz R. Cytoplasmic immunofluorescence of bone marrow plasma cells producing immunoglobulins of the four IgG subclasses. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):579–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E., Peppard J., Reynolds J., Hall J. Rapid active transport of immunoglobulin A from blood to bile. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):588–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBECKE G. J., ASOFSKY R. M., HOCHWALD G. M., SISKIND G. W. Gamma globulin and antibody formation in vitro. III. Induction of secondary response at different intervals after the primary; the role of secondary nodules in the preparation for the secondary response. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:295–310. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBECKE G. J., KEUNING F. J. Antibody and gamma globulin formation in vitro in hemopoietic organs. J Infect Dis. 1956 Mar-Apr;98(2):157–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORBECKE G. J., KEUNING F. J. Antibody formation in vitro by haemopoietic organs after subcutaneous and intravenous immunization. J Immunol. 1953 Feb;70(2):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., McConahey P. J., Izui S., Eisenberg R. A., Pereira A. B., Creighton W. D. A comparative immunologic analysis of several murine strains with autoimmune manifestations. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):258–278. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Shawler D. L., Eisenberg R. A., Dixon F. J. Splenic immunoglobulin-secreting cells and their regulation in autoimmune mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):446–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turesson I. Distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in human bone marrow and lymphoid tissues. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(4):293–304. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Chihara T., Moore T. L., Robbins D. L., Tanimoto K., Johnson J. S., McMillan R. Rheumatoid factor-producing cells detected by direct hemolytic plaque assay. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):933–941. doi: 10.1172/JCI108546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Camp B. G., Shuit H. R., Hijmans W., Radl J. The cellular basis of double paraproteinemia in man. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jan;9(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. 3. Spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow and thymus. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):19–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


