Abstract
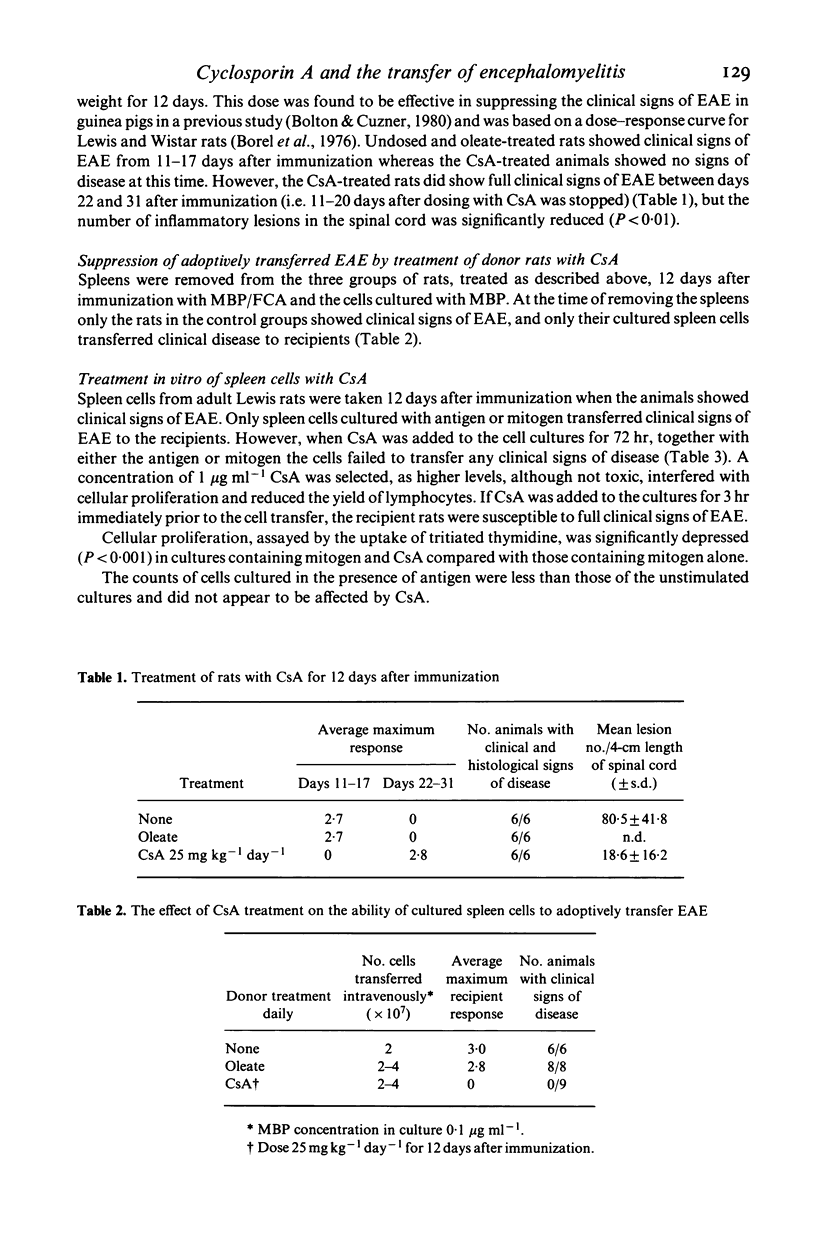
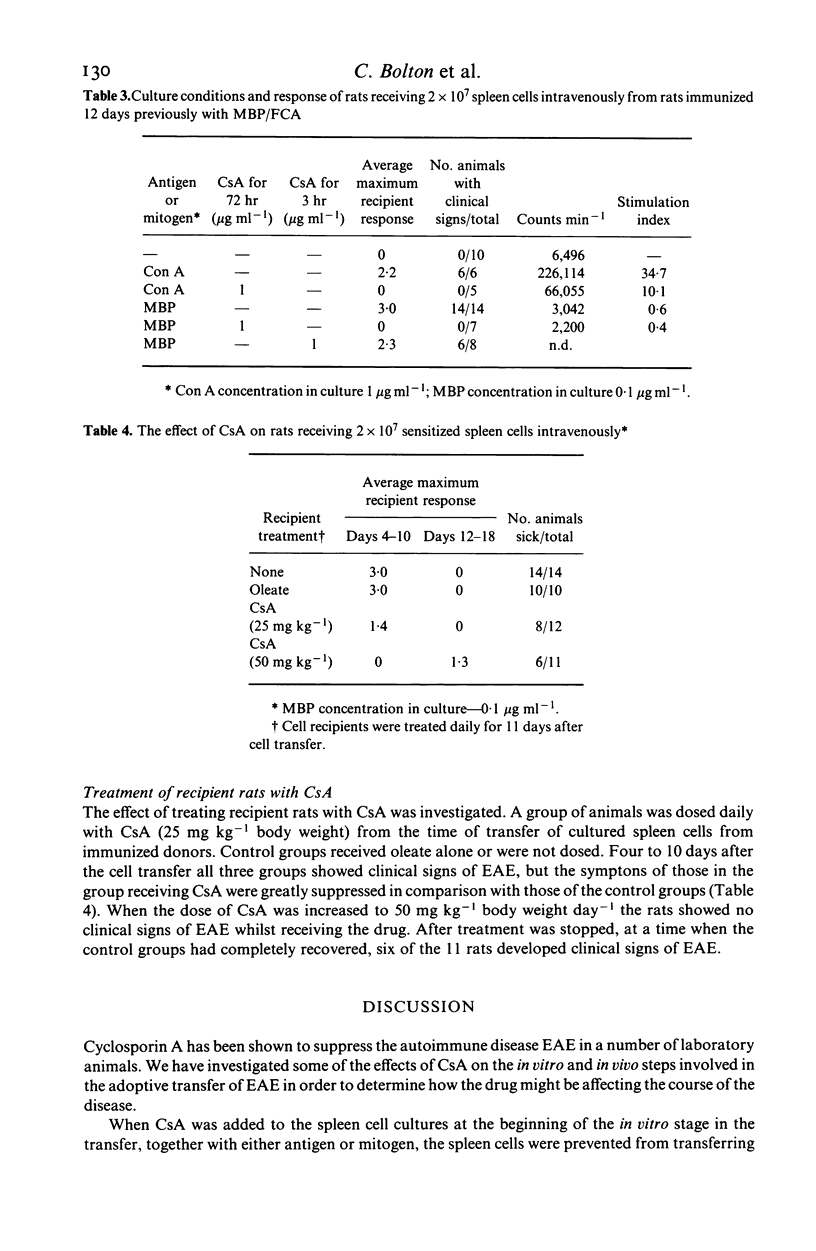
Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) can be adoptively transferred in Lewis rats with spleen cells from immunized animals, after culture with concanavalin A or myelin basic protein (MBP). The effect of the immunosuppressive drug cyclosporin A (CsA) on the in vitro and in vivo steps of the cell transfer has been investigated. Clinical signs of EAE were completely suppressed by CsA in rats immunized with MBP in Freund's complete adjuvant and spleen cells from these animals, cultured with the antigen, did not transfer the disease. The incidence of transferred disease was also reduced, if recipients were treated with CsA, although a higher dose of drug than that needed to suppress active EAE was required. In both instances complete suppression of EAE was only accomplished for the period of dosing, although the clinical signs of disease which appeared after withdrawal of the drug were significantly reduced in severity. These results imply that an immune response in the host animal is a prerequisite for adoptive transfer of EAE or suggest that CsA can regulate the action of lymphocytes already primed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borel J. F. Comparative study of in vitro and in vivo drug effects on cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1976 Oct;31(4):631–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Gubler H. U., Stähelin H. Biological effects of cyclosporin A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions. 1976 Jul;6(4):468–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01973261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):139–165. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holda J. H., Welch A. M., Swanborg R. H. Autoimmune effector cells. I. Transfer of experimental encephalomyelitis with lymphoid cells cultured with antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):657–659. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leapman S. B., Filo R. S., Smith E. J., Smith P. G. In vitro effects of cyclosporin A on lymphocyte subpopulations. 1. Suppressor cell sparing by cyclosporin A. Transplantation. 1980 Dec;30(6):404–408. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198012000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Suppression of the hyperacute form of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by drugs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1977 Dec;230(2):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S. Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with activated spleen cells: comparison of in vitro activation by concanavalin a and myelin basic protein. Cell Immunol. 1980 Nov;56(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., McFarlin D. E. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: enhancement of cell-mediated transfer by concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1134–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richert J. R., Driscoll B. F., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: incubation of rat spleen cells with specific antigen. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):494–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. H. Transfedotr of Allergic Encephalomyelitis by Lymph Node Cells in Inbred Guinea Pigs. Science. 1961 Sep 1;134(3479):619–620. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3479.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesinger D., Borel J. F. Studies on the mechanism of action of cyclosporin A. Immunobiology. 1980 Jan;156(4-5):454–463. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(80)80078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


