Abstract
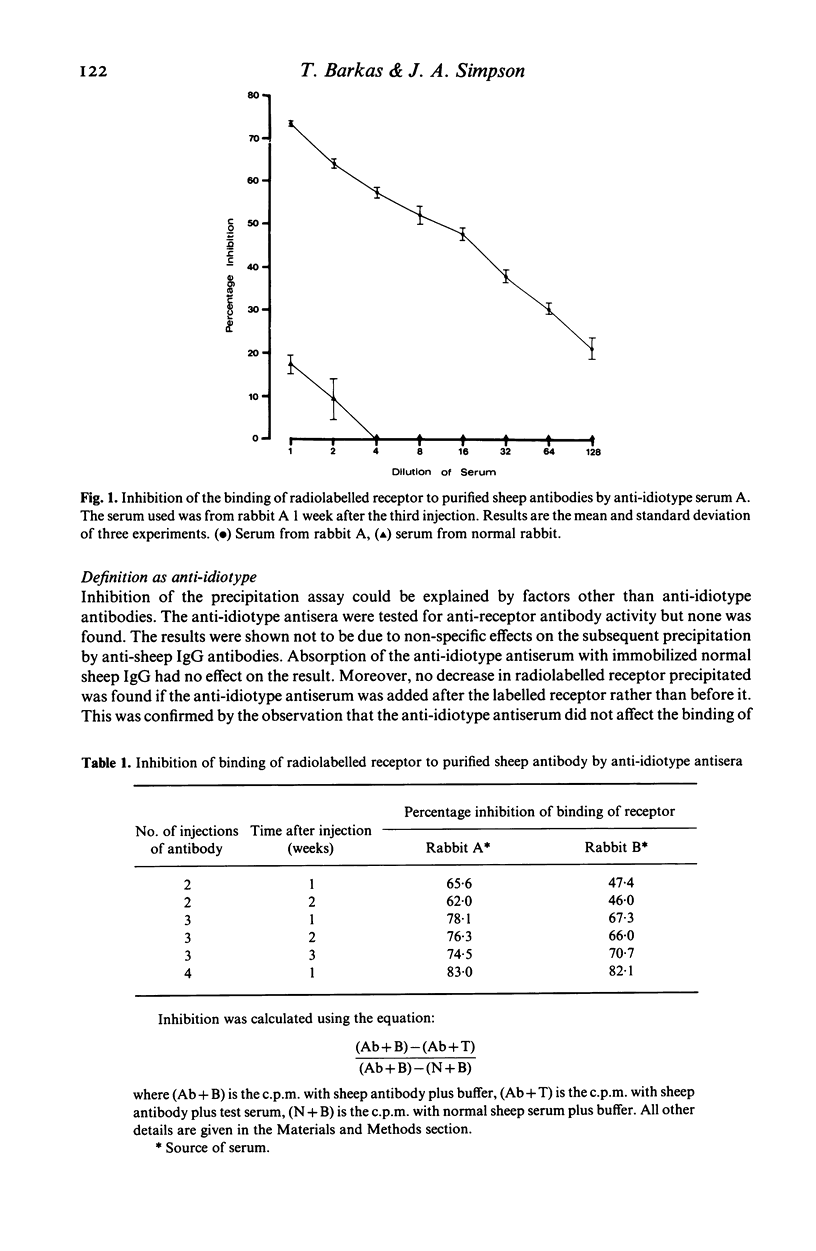
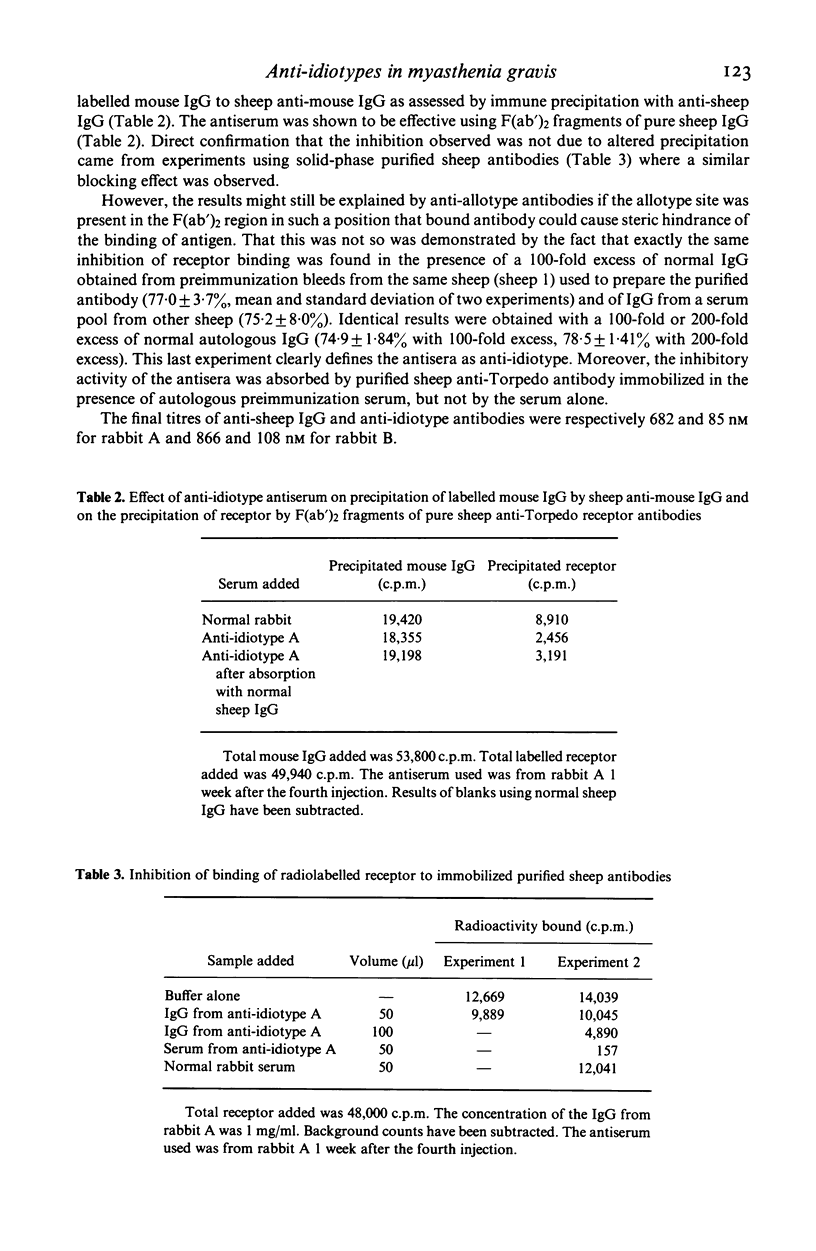
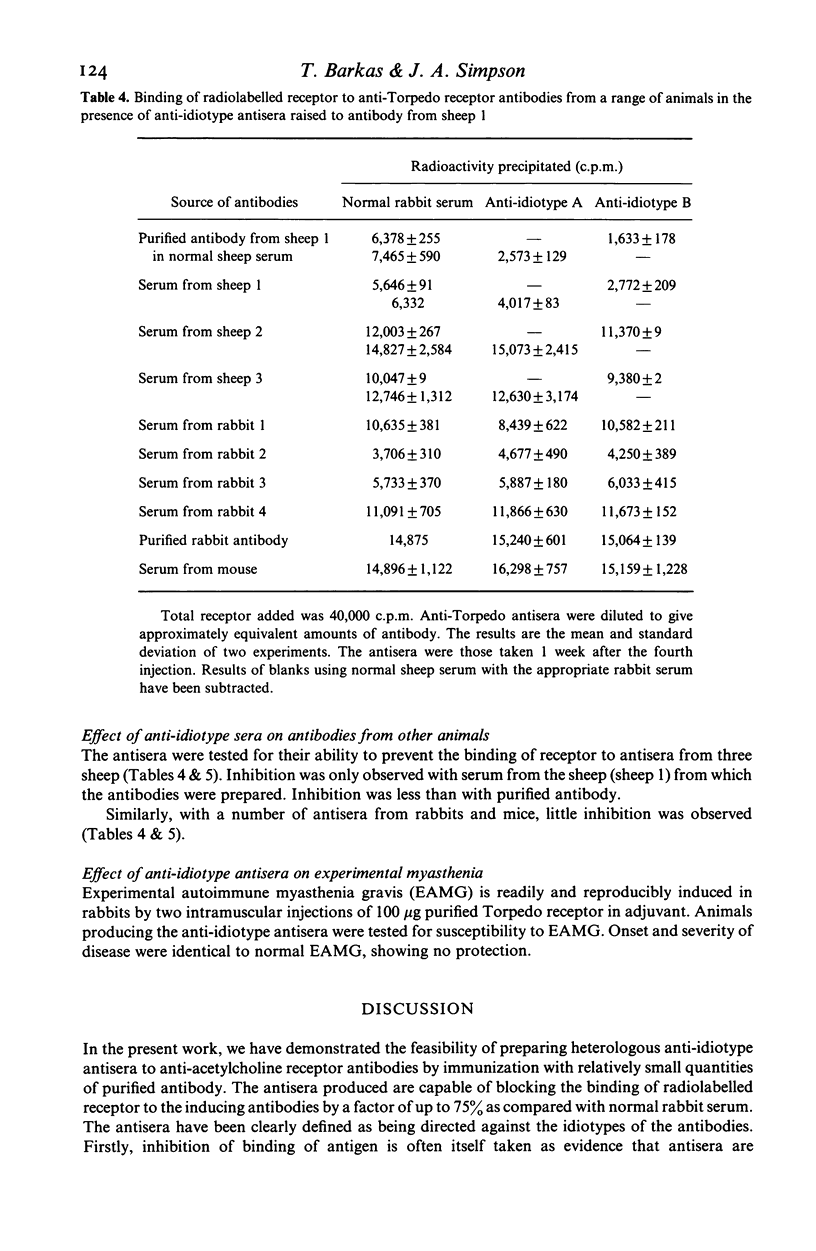
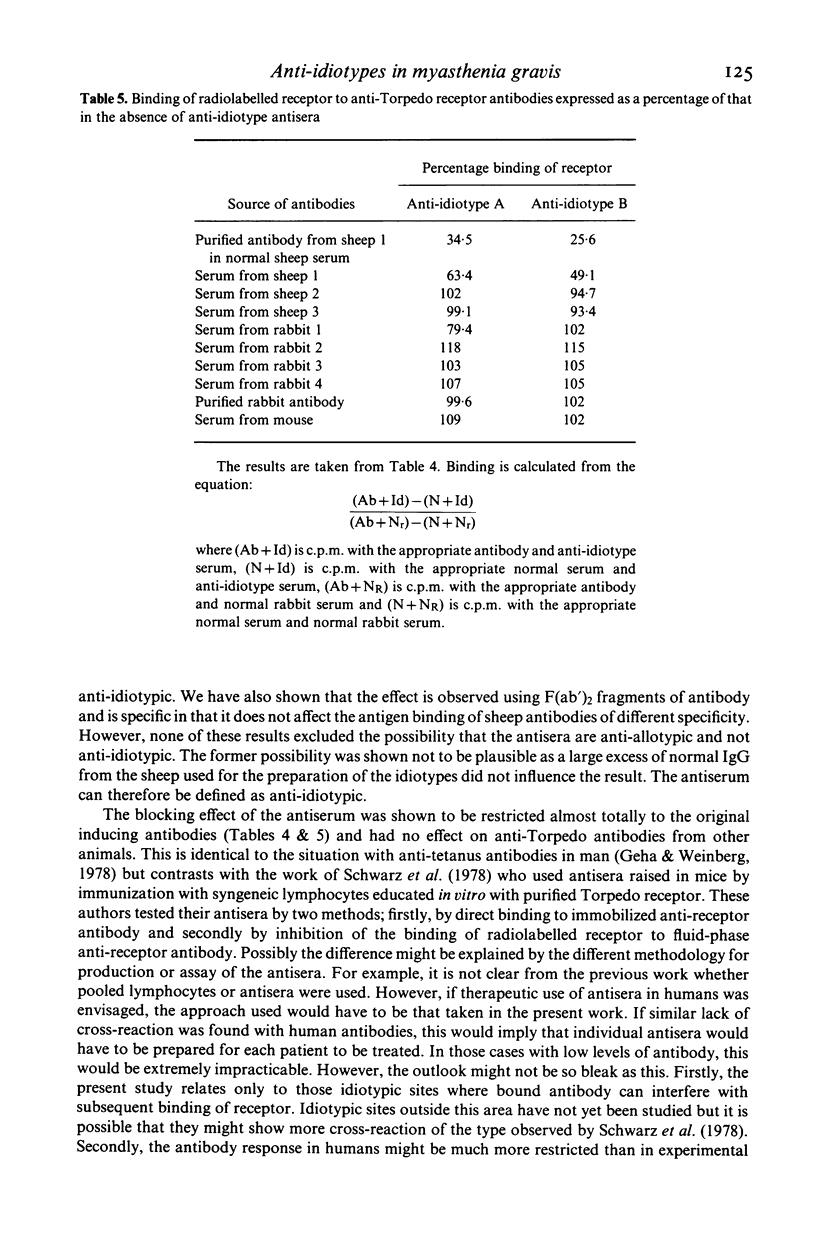
Anti-idiotype antisera were raised in rabbits by immunization with purified sheep anti-Torpedo receptor antibodies. The antisera were able specifically to block the binding of receptor to the inducing antibodies but not anti-Torpedo antibodies from other animals of the same, or other, species. Rabbits producing the anti-idiotype sera were not protected from experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis (EAMG). The implications of these observations for the potential use of anti-idiotype antisera in the treatment of myasthenia gravis are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Harrison R., Lunt G. G., Watson C. M. Immunochemistry of the acetylcholine receptor [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(3):636–638. doi: 10.1042/bst0060636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T. Myasthenia gravis, the acetylcholine receptor and the immune response. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1979;1(4):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(79)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R., Grieve P. A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Weinberg R. P. Anti-idiotypic antisera in man. I. Production and immunochemical characterization of anti-idiotypic antisera to human antitetanus antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1518–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E., Whittingham S. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis and myasthenia gravis: biochemical and immunochemical aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:254–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N. R., Bishop S., Jefferis Use of antibody-coated red cells for the sensitive detection of antigen and in rosette tests for cells bearing surface immunoglobulins. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye L., Pontes de Carvalho L. C., Roitt I. M. Restrictions in the response to autologous thyroglobulin in the human. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh I., March S., Cuatercasas P. Topics in the methodology of substitution reactions with agarose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:77–102. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Novick D., Givol D., Fuchs S. Induction of anti-idiotypic antibodies by immunisation with syngeneic spleen cells educated with acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):543–545. doi: 10.1038/273543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


