Abstract
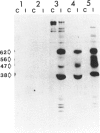
Progressive rubella panencephalitis (PRP), a slowly progressive and fatal central nervous system (CNS) disorder due to rubella virus, is characterized by high cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of immunoglobulins, oligoclonal bands and high CSF:serum rubella antibody titre ratios. Sera, CSF and neutral extracts of brain, spleen, lymph node and kidney obtained at autopsy from a case were analysed for immunoglobulin isotype and content by enzyme linked immunosorbent assays. Comparable titres of rubella specific IgA and IgG were found in sera and CSF, but accounted for a disproportionate amount of the isotype specific immunoglobulins of CSF (0.19%, 14.0%) as compared to serum (0.02%, 0.69%). The percentage of isotype specific immunoglobulins were not increased in extracts of most visceral tissues compared to serum, however, rubella specific IgA and IgG were disproportionately increased in extracts from most regions of brain sampled (1-60-fold and 8-27-fold respectively). No rubella specific IgM could be conclusively demonstrated in any specimen. Immunoprecipitation studies showed that the IgG reacted with the major glycoproteins (gp62, gp47-56 complex) and non-glycosylated polypeptide (p38) of radiolabelled rubella virions and infected cell lysates. These studies support the conclusion that a major portion of the rubella specific antibody is produced within the CNS of patients with PRP.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellini W. J., Trudgett A., McFarlin D. E. Purification of measles virus with preservation of infectivity and antigenicity. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):633–639. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle P. K., Wolinsky J. S. Characterization of immune complexes in progressive rubella panencephalitis. Ann Neurol. 1981 Jun;9(6):557–562. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer N. E., Oshiro L. S., Weil M. L., Lennette E. H., Itabashi H. H., Carnay L. Isolation of rubella virus from brain in chronic progressive panencephalitis. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):143–153. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman N. T., Habicht J., Lachmann P. J. Intracerebral synthesis of antibodies to measles and distemper viruses in patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jan;39(1):44–52. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E. Immunoglobulins in the cerebrospinal fluid: changes during acute viral encephalitis in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Choppin P. W. Measles-virus proteins in the brain tissue of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: absence of the M protein. N Engl J Med. 1981 May 7;304(19):1152–1155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198105073041906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keydar I., Mesa-Tejada R., Ramanarayanan M., Ohno T., Fenoglio C., Hu R., Spiegelman S. Detection of viral proteins in mouse mammary tumors by immunoperoxidase staining of paraffin sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1524–1528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Shekarchi I., Dorsett P., Sever J. L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay determination of specific rubella antibody levels in micrograms of immunoglobulin G per milliliter of serum in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Oct;8(4):419–423. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.4.419-423.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M., Johnson R. T. A comparison of the structural polypeptides of five strains of mumps virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):15–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. D., Kane A., Thormar H. Quantitation of measles virus-specific immunoglobulins in serum, CSF, and brain extract from patients with subactue sclerosing panencephalitis. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2254–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. D., Thormar H., Wisniewski H. M. Quantitation of measles-specific IgG. Its presence in CSF and brain extracts of patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1980 Oct;37(10):607–609. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500590031002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mingioli E. S., Strober W., Tourtellotte W. W., Whitaker J. N., McFarlin D. E. Quantitation of IgG, IgA and IgM in the CSF by radioimmunoassay. Neurology. 1978 Oct;28(10):991–995. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.10.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerenberg S. T., Prasad R., Rothman M. E. Cerebrospinal fluid IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE levels in central nervous system disorders. Neurology. 1978 Oct;28(10):988–990. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.10.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payment P., Ajdukovic D., Pavilanis V. Le virus de la rubéole. I. Morphologie et protéines structurales. Can J Microbiol. 1975 May;21(5):703–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Suni J., Wager O. Rheumatoid factor in acute viral infections: interference with determination of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies in an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller E., Delasnerie N., Allinquant B., Lebon P. Intrathecal Rubella and RNA antibody synthesis in multiple sclerosis and progressive rubella panencephalitis. Biomedicine. 1977 Jun;27(4):139–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. W., Ma B. I., Brandes D. B., Walsh M. J., Potvin A. R. Quantification of de novo central nervous system IgG measles antibody synthesis in SSPE. Ann Neurol. 1981 Jun;9(6):551–556. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. W., Ma B. I. Multiple sclerosis: the blood-brain-barrier and the measurement of de novo central nervous system IgG synthesis. Neurology. 1978 Sep;28(9 Pt 2):76–83. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.9_part_2.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend J. J., Stroop W. G., Baringer J. R., Wolinsky J. S., McKerrow J. H., Berg B. O. Neuropathology of progressive rubella panencephalitis after childhood rubella. Neurology. 1982 Feb;32(2):185–190. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Hovi T. Structural proteins and subunits of rubella virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):10–16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.10-16.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandvik B., Weil M. L., Grandien M., Norrby E. Progressive rubella virus panencephalitis: synthesis of oligoclonal virus-specific IgG antibodies and homogeneous free light chains in the central nervous system. Acta Neurol Scand. 1978 Jan;57(1):53–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1978.tb04497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Berg B. O., Maitalnd C. H. Progressive rubella panencephalitis. Arch Neurol. 1976 Oct;33(10):722–723. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500100056016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]