Abstract
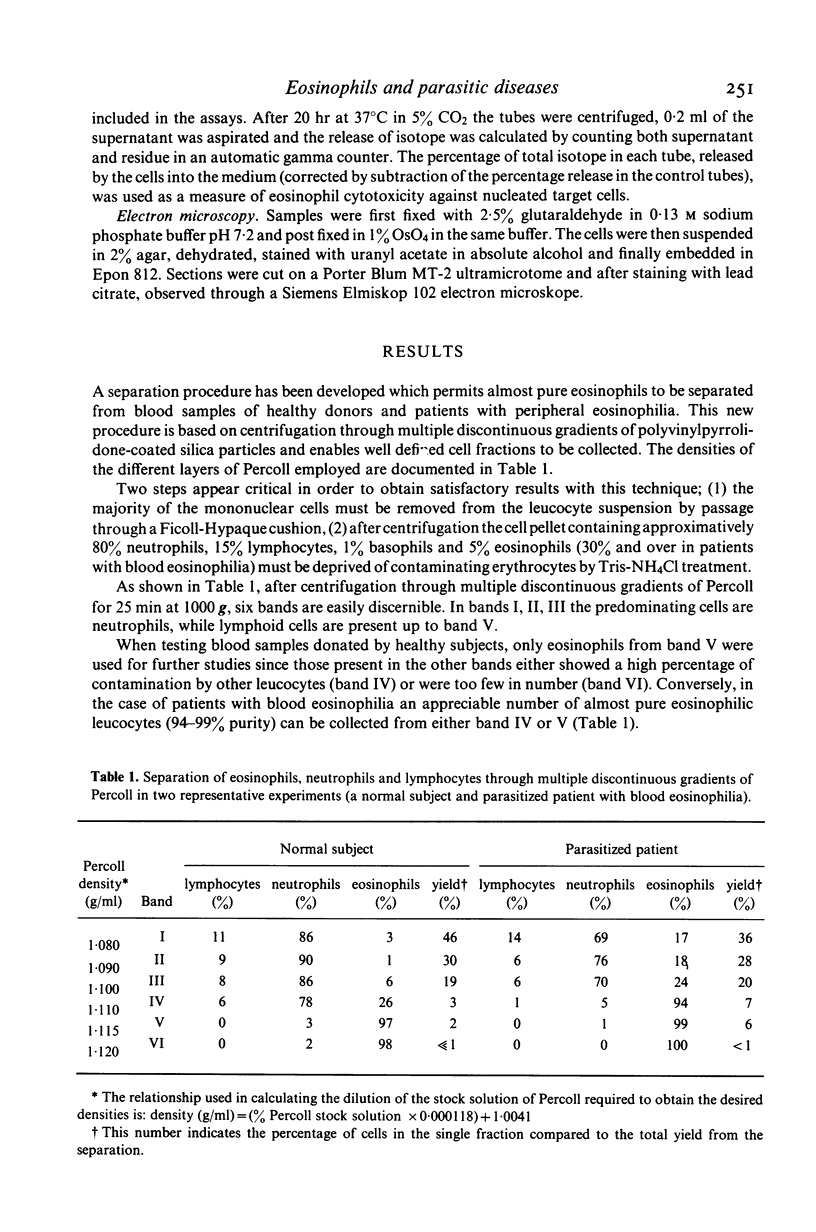
A new procedure, based on centrifugation through multiple discontinuous gradients of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silica particles has been developed for the separation of almost pure eosinophils from blood samples of healthy donors. When this technique is employed for the purification of eosinophils from the peripheral blood of patients with parasitic diseases, two cell fractions almost pure in eosinophil granulocytes are harvested at different densities. Preliminary results, concerning the characterization of these cell fractions, indicate that in the terms of detectable membrane receptors and K cell activity, two distinct eosinophil subpopulations can be recognized.
Full text
PDF

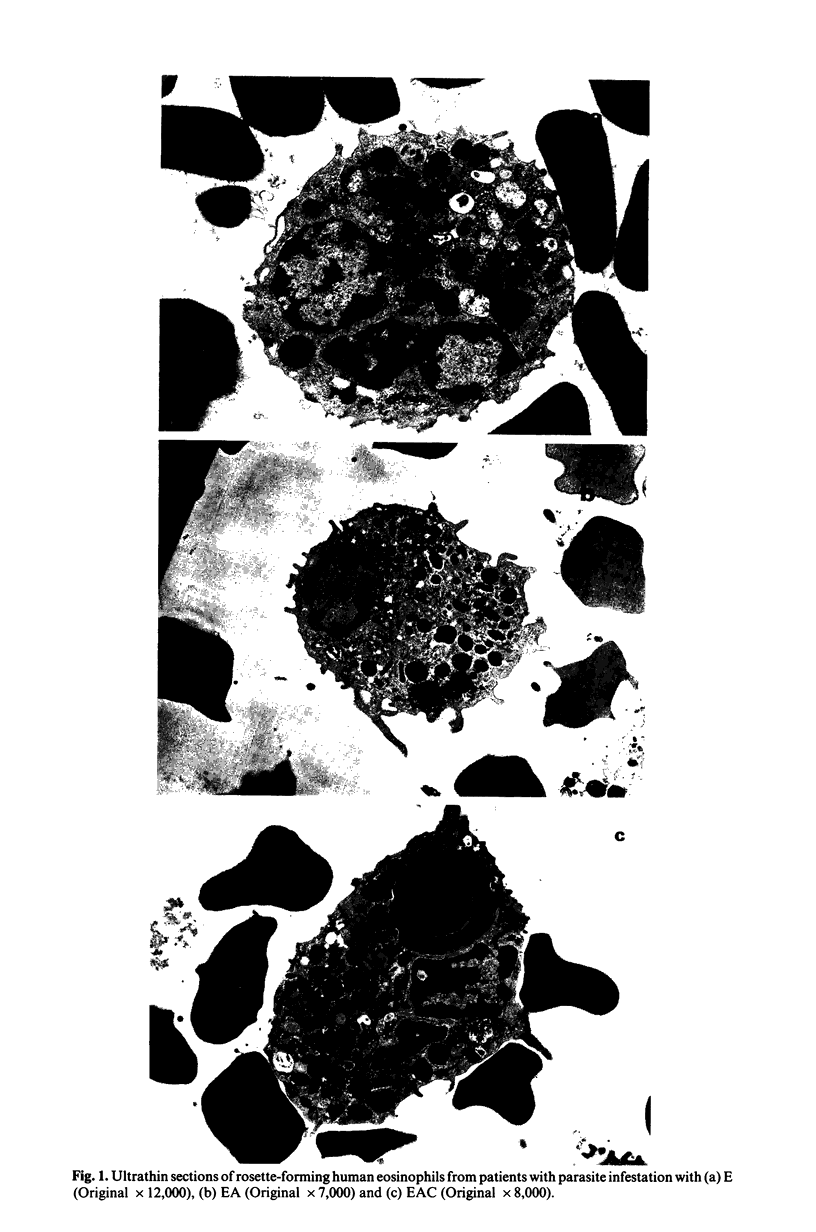



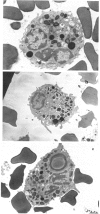
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. F., Spriggs A. I. A method for obtaining concentrates of eosinophils from blood. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Mar;15(2):188–189. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.2.188-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., David J. R., Franks D., Mahmoud A. A., David P. H., Sturrock R. F., Houba V. Antibody-dependent eosinophil-mediated damage to 51Cr-labeled schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: damage by purieid eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):136–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner I. Separation of human eosinophils in density gradients of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silica gel (Percoll). Immunology. 1980 May;40(1):133–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Human eosinophils. Purification and cytotoxic capability of eosinophils from patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 1978 Mar;51(3):457–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Purification of normal human eosinophils using the different binding capacities of blood leucocytes for complexed rabbit IgG. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):256–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Simone C., Donelli G., Meli D., Rosati F., Sorice F. Human eosinophils and parasitic diseases: light and electron microscopy evidence of interaction with sheep erythrocyte. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jan;39(1):247–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]