Abstract
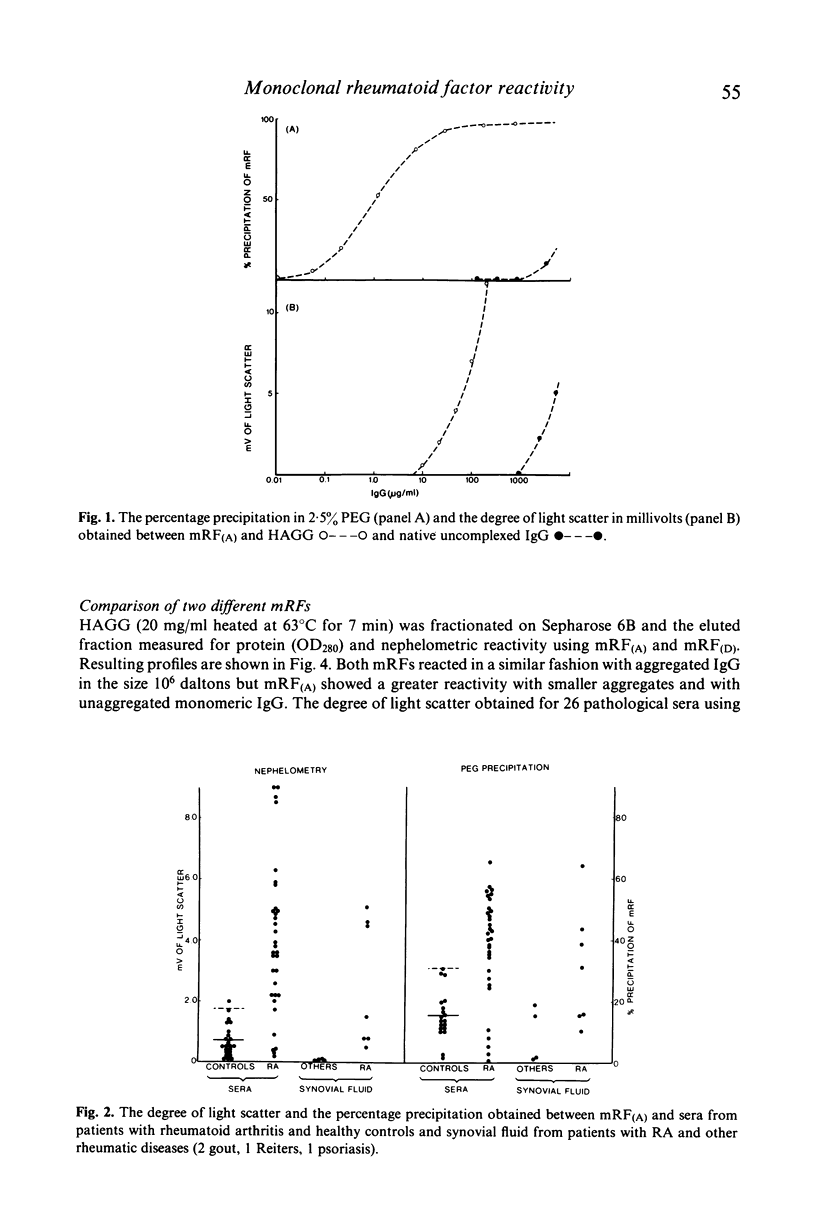
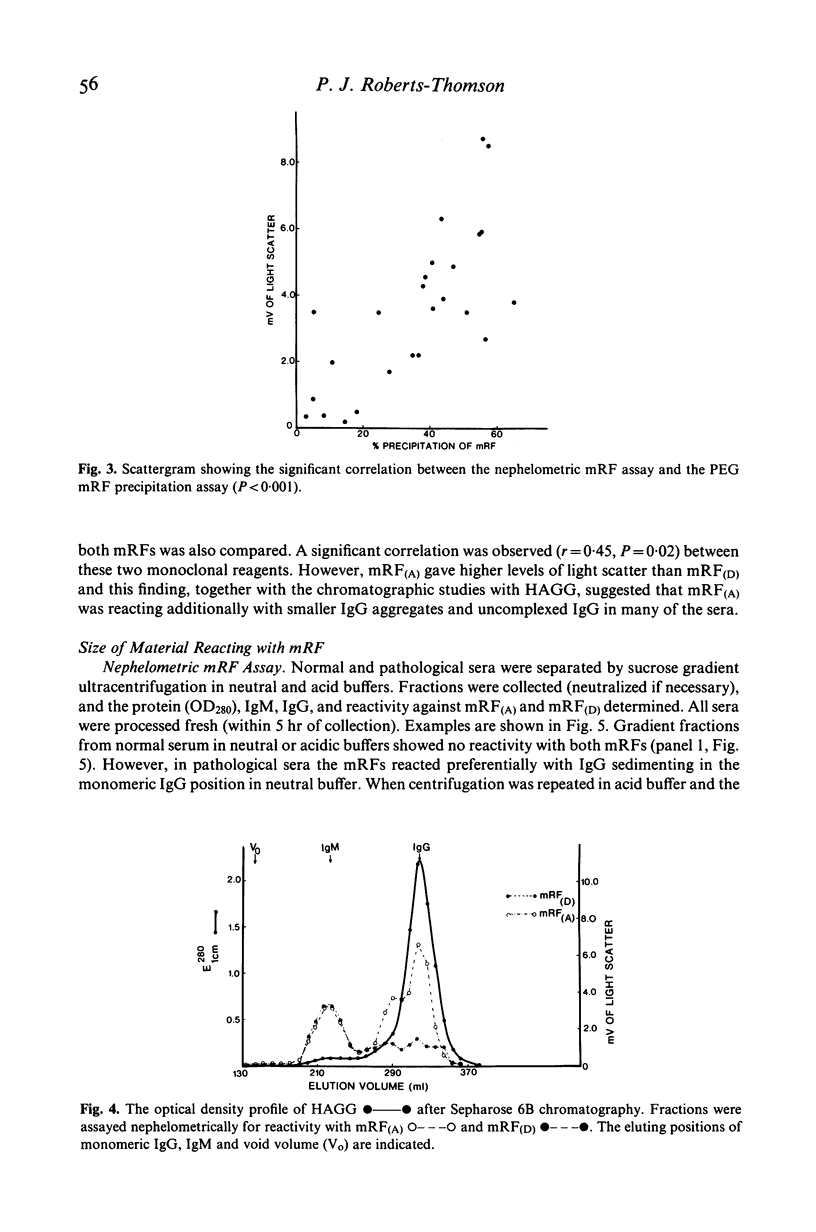
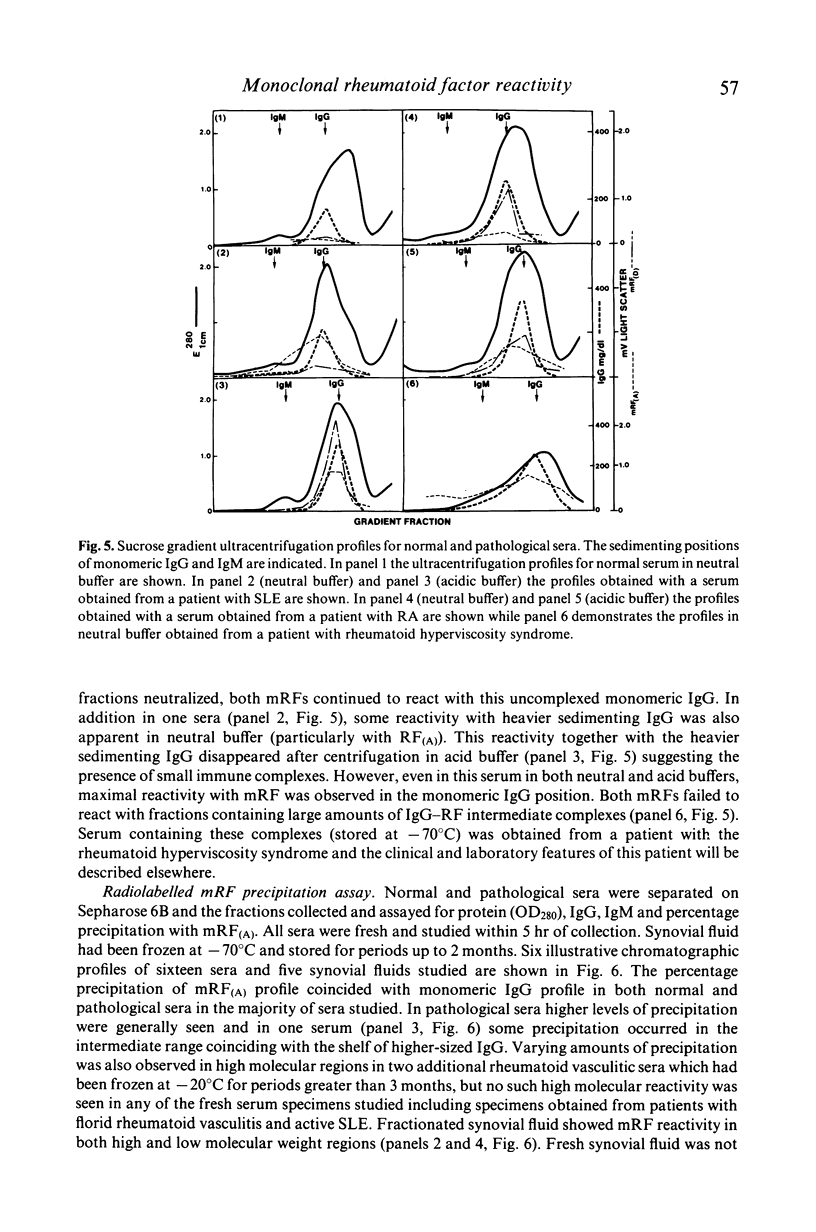
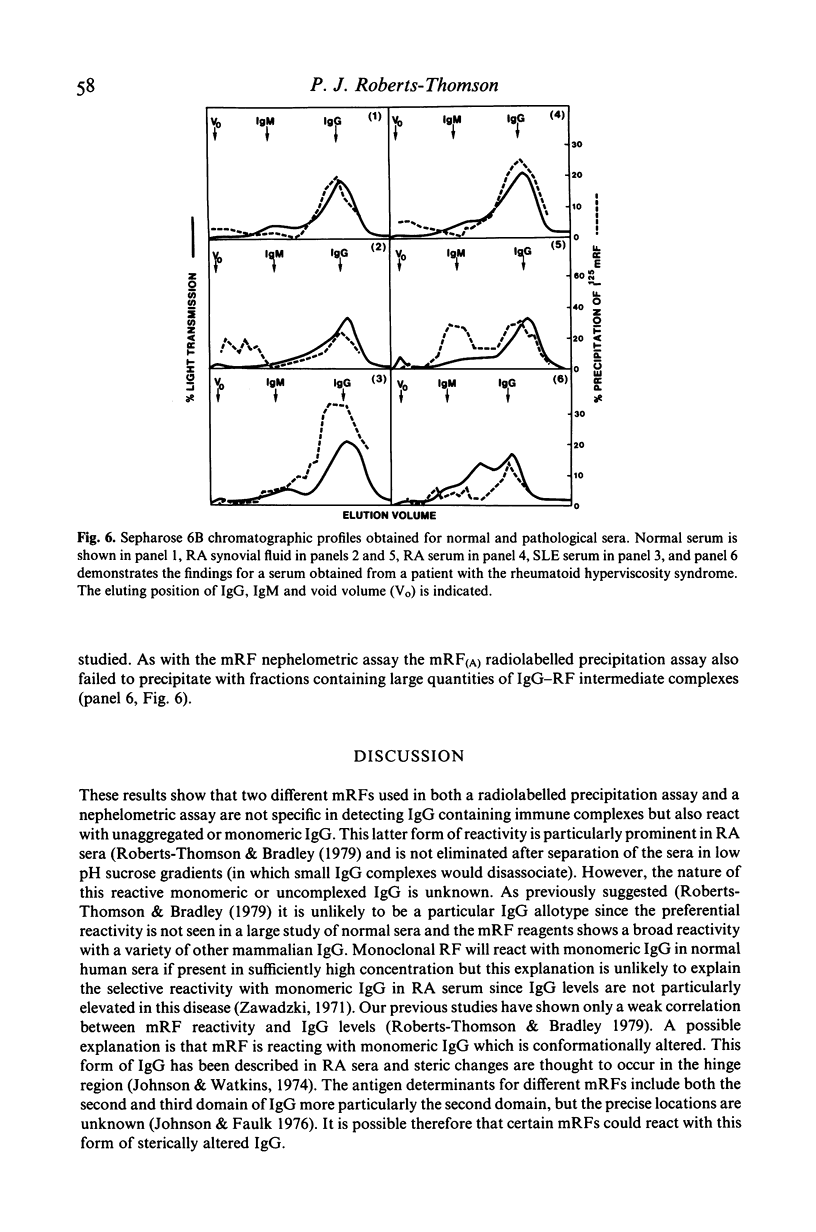
Assays involving monoclonal rheumatoid factor (mRF) reagents are frequently used for the detection of circulating immune complexes, particularly in the rheumatic diseases. A study has been performed to investigate the interaction of two purified mRF reagents with normal sera, sera and synovial fluid from patients with rheumatic diseases and with heat-aggregated human IgG used as a model of immune complexes. Interaction has been measured by a simple laser nephelometric technique and a sensitive radiolabelled mRF precipitation assay. Both mRF reagents showed little reactivity with normal sera but reacted strongly with many of the pathological specimens. Similarly both mRFs reacted with large molecular sized heat aggregates of IgG while a variable reactivity was found with uncomplexed or monomeric IgG. However in pathological sera, both mRFs reacted predominantly with monomeric IgG and a significant correlation was found between the two reagents. This reactivity with monomeric IgG remained after separation of pathological sera in low pH sucrose gradients suggesting it was not due to the presence of small immune complexes of the classical type. In addition no reactivity was found with either reagent with IgG-RF intermediate complexes. It is concluded that mRF reagents are not specific for IgG containing immune complexes. They also react with monomeric IgG and this reactivity is particularly prominent in certain pathological sera. The possible nature of this reactive monomeric IgG is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barratt J., Naish R. A simple radiolabelled rheumatoid factor binding assay for the measurement of circulating immune complexes. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(2):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton W. D., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of antibodies and soluble antigen-antibody complexes by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1219–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel A., Jr, Agnello V. Detection of immune complexes. The use of radioimmunoassays with Clq and monoclonal rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):990–1001. doi: 10.1172/JCI108722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K. Presence of aggregated gamma-G-globulin in certain rheumatoid synovial effusions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jul;2(4):511–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Faulk W. P. Rheumatoid factor: its nature, specificity, and production in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Nov;6(3):414–430. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Watkins J. Proceedings: Differences in serum IgG structure in health and rheumatoid arthritis as studied by circular dichroic spectra. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jan;33(1):108–108. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.1.108-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra H. S., McDuffie F. C., Hunder G. G., Samayoa E. A. Immune complexes in sera and synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Radioimmunoassay with monocylonal rheumatoid factor. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):458–466. doi: 10.1172/JCI108112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLSON A., POTGIETER G. M., LARGIER J. F., MEARS G. E., JOUBERT F. J. THE FRACTIONATION OF PROTEIN MIXTURES BY LINEAR POLYMERS OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 16;82:463–475. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A. B., Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Detection and partial characterization of circulating immune complexes with solid-phase anti-C3. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):763–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson P. J., Bradley J. A nephelometric study of the reaction of monoclonal rheumatoid factor with heat aggregated gamma globulin and sera from patients with immune complex diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Sep;37(3):408–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson P. J., Neoh S. H., Bradley J., Milazzo S. C. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative study of the C1q binding and monoclonal rheumatoid factor assays. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Oct;39(5):438–444. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G., Agnello V. Occurrence of -globulin complexes in serum and joint fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients: use of monoclonal rheumatoid factors as reagents for their demonstration. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):286s–295s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


