Abstract
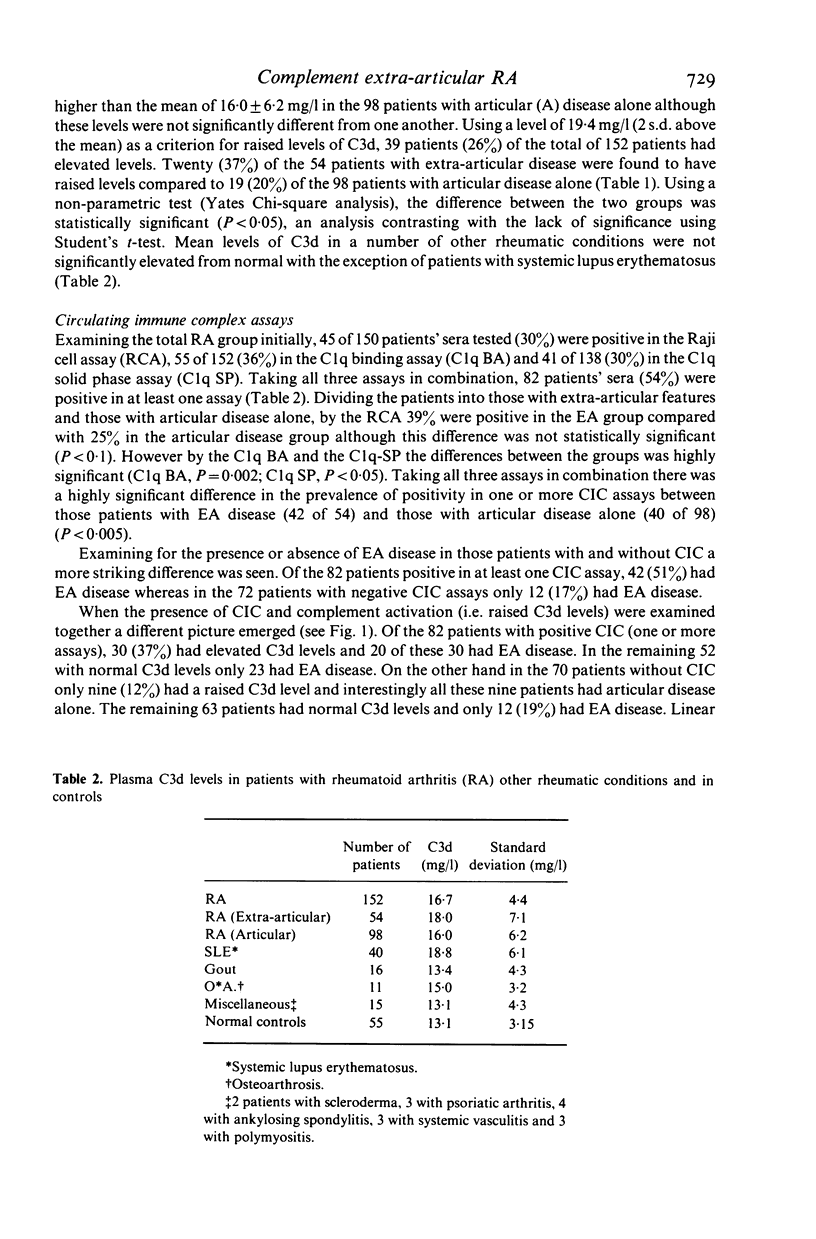
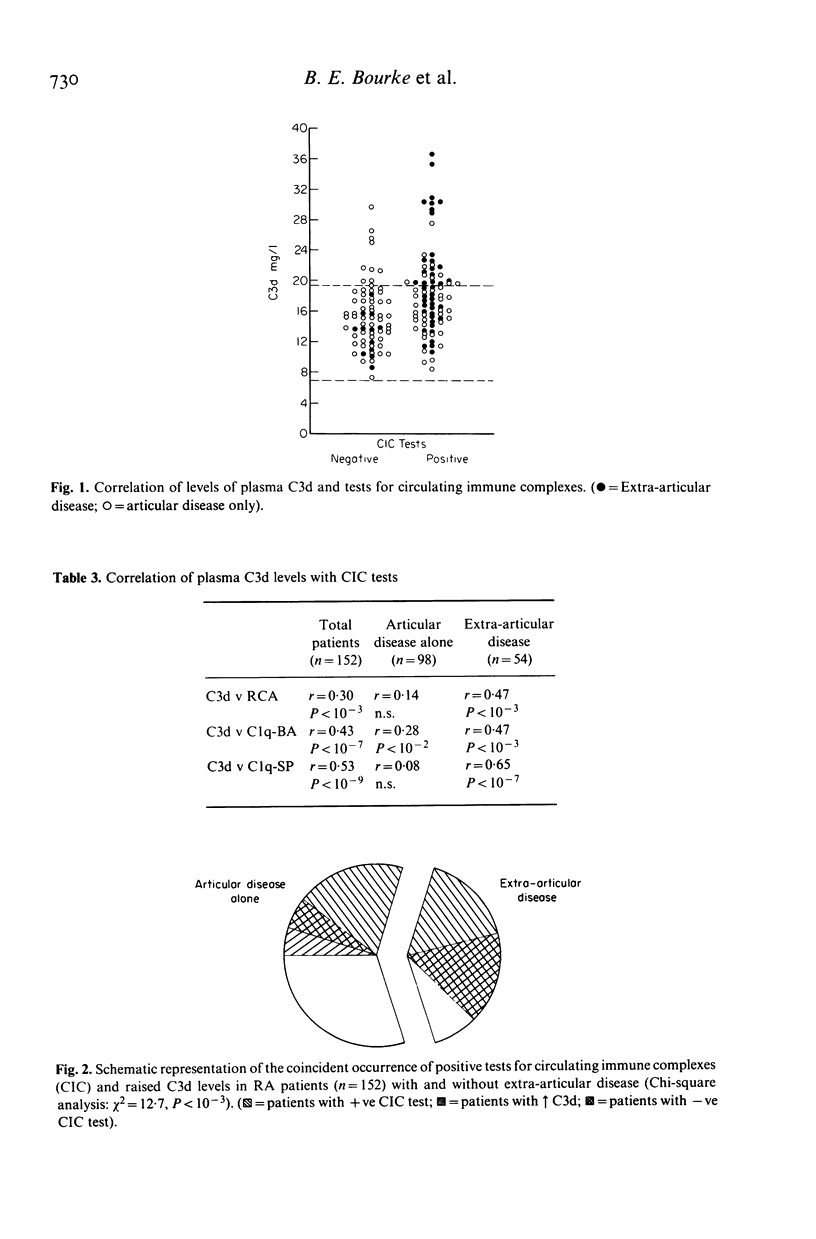
The hypothesis that the pathogenicity of putative circulating immune complexes (CIC) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is related to their ability to fix complement was investigated. Three assays for CIC were employed; (a) the 125I C1q binding assay (C1q BA), (b) the C1q solid phase assay (C1q SP) and (c) the Raji cell assay (RCA). Evidence for hypercatabolism of complement was obtained by using a highly sensitive quantitative assay for C3d (a breakdown product of C3) by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. One hundred and fifty-two patients with classical or definite RA were studied; 54 had clinical evidence of extra-articular disease including vasculitis, nodules, scleritis, neuropathy and lung disease; 98 patients had clinical evidence of joint disease alone. Plasma levels of C3d were significantly elevated in the RA group as a whole 16.7 +/- 4.4 mg/l (mean +/- 1 s.d.) compared with 13.1 +/- 3.25 mg/l in a group of 55 normal controls (P less than 0.01). Elevated levels of C3d were found in 26% of all patients but occurred significantly more often in the extra-articular disease group (P less than 0.05). Fifty-four percent of patients had at least one positive assay for CIC although no individual assay was positive in more than 36% of the group as a whole. The prevalence of positive CIC was significantly greater in those patients with extra-articular disease than in those with joint disease alone (P less than 0.005). Of the total of 82 patients with putative CIC, 30 (37%) had a raised C3d level. The coincident finding of positive tests for CIC and an elevated C3d level was very significantly correlated with the presence of extra-articular disease (chi 2 = 12.7 P = 10(-3)). Whilst putative CIC are frequent in RA (54%) these findings in contrast to previous work, suggest that the majority are not associated with abnormal complement activation and may account for the relative infrequency of clinically detectable active extra-articular disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourke B. E., Moss I. K., Maini R. N. Measurement of the complement C3 breakdown product C3d by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Ghobarey A., Whaley K. Alternative pathway complement activation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1980 Jul-Aug;7(4):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erhardt C. C., Mumford P., Maini R. N. The association of cryoglobulinaemia with nodules, vasculitis and fibrosing alveolitis in rheumatoid arthritis and their relationship to serum C1q binding activity and rheumatoid factor. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):405–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):396–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg H., Lundh B., Laurell A. B. Studies of the third component of complement in synovial fluid from arthritic patients. II. Conversion and its relation to total complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):707–712. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., McDuffie F. C., Clark R. J. Consumption of C3 via the classical and alternative complement pathways by sera and synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):269–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Depressed synovial fluid levels of properdin and properdin factor B in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):289–295. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Nydegger U., Perrin L. H., Fehr K., McCormick J., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Circulating and intra-articular immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation of 125I-Clq binding activity with clinical and biological features of the disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1308–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI108399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



