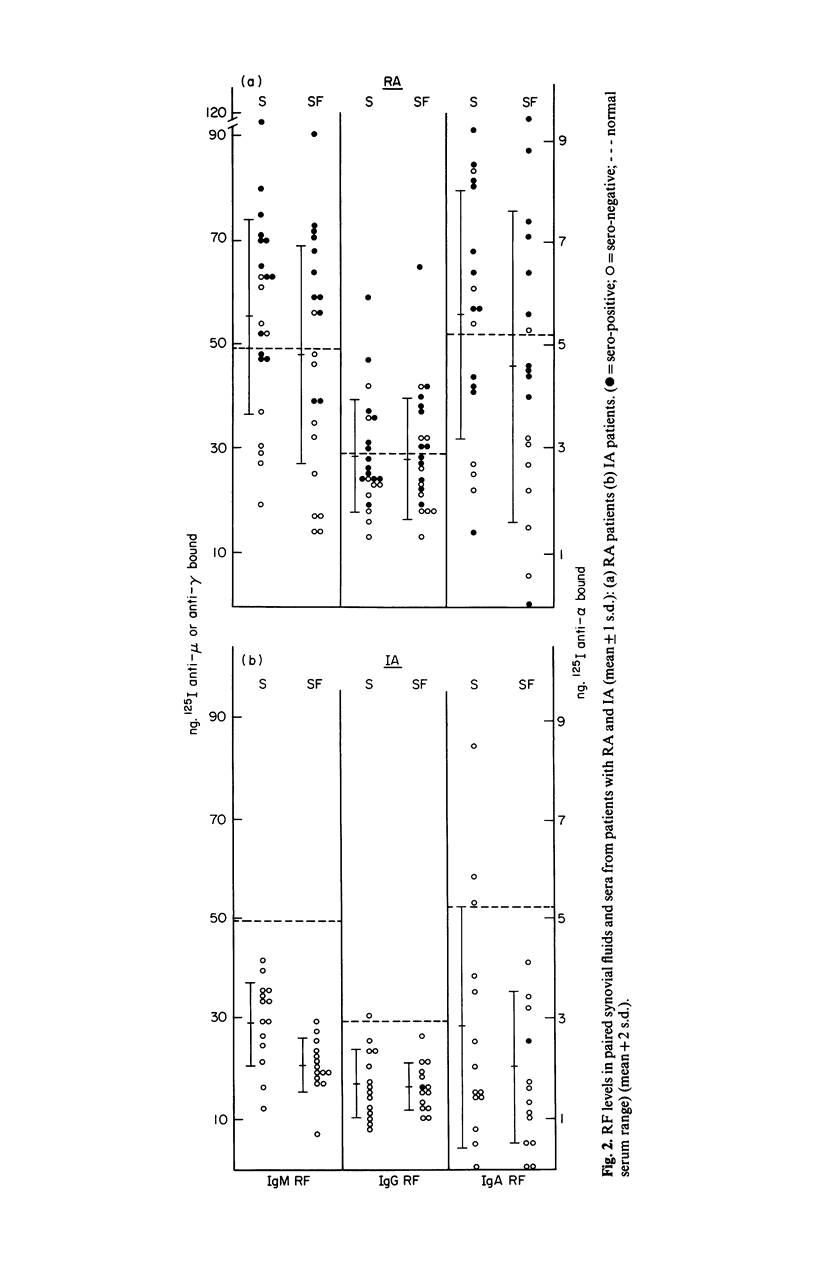
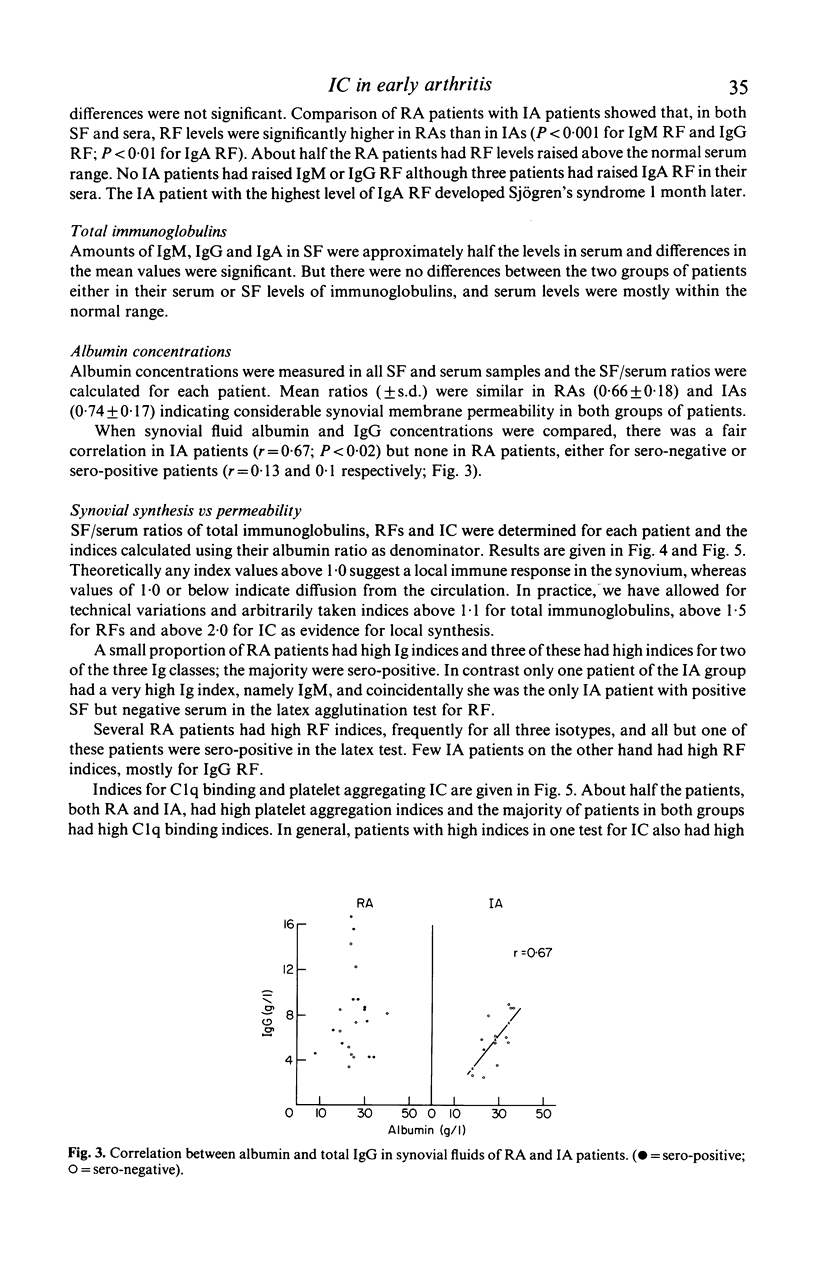
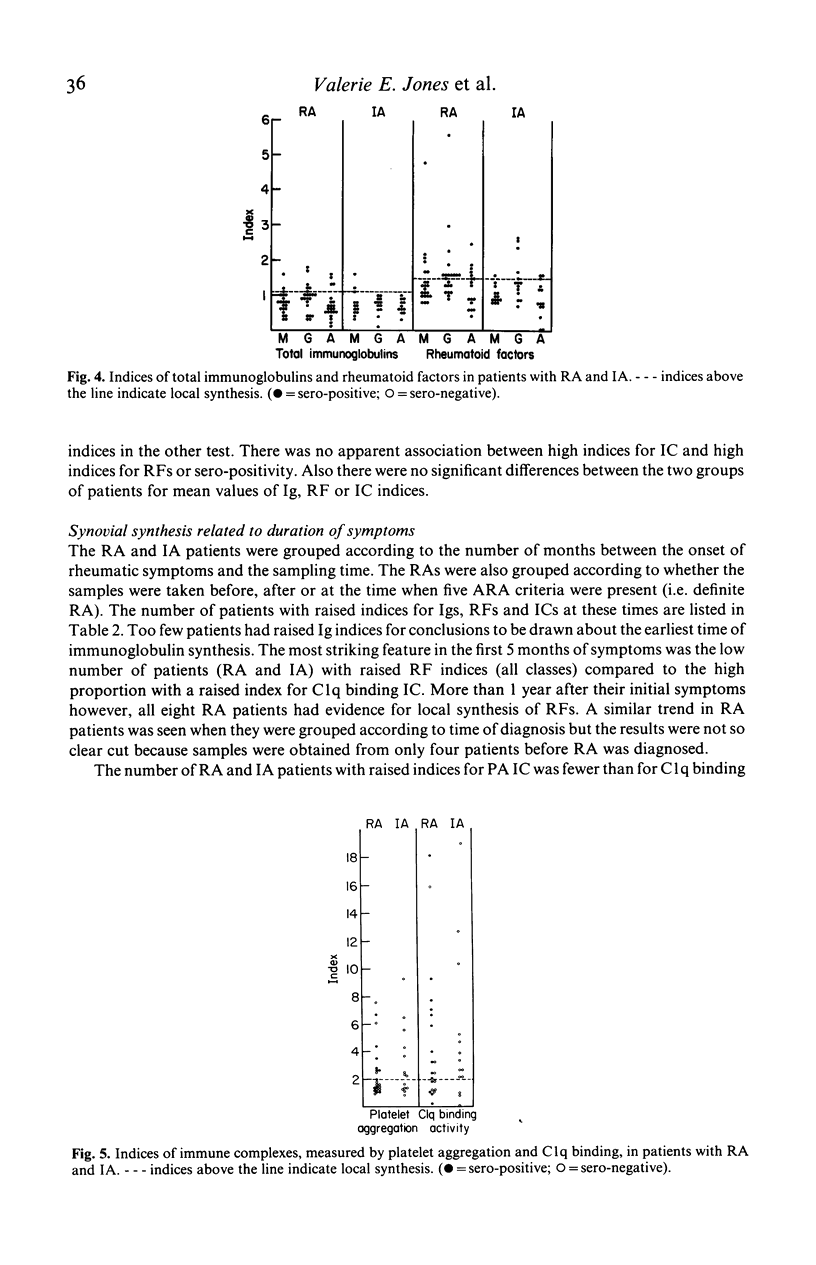
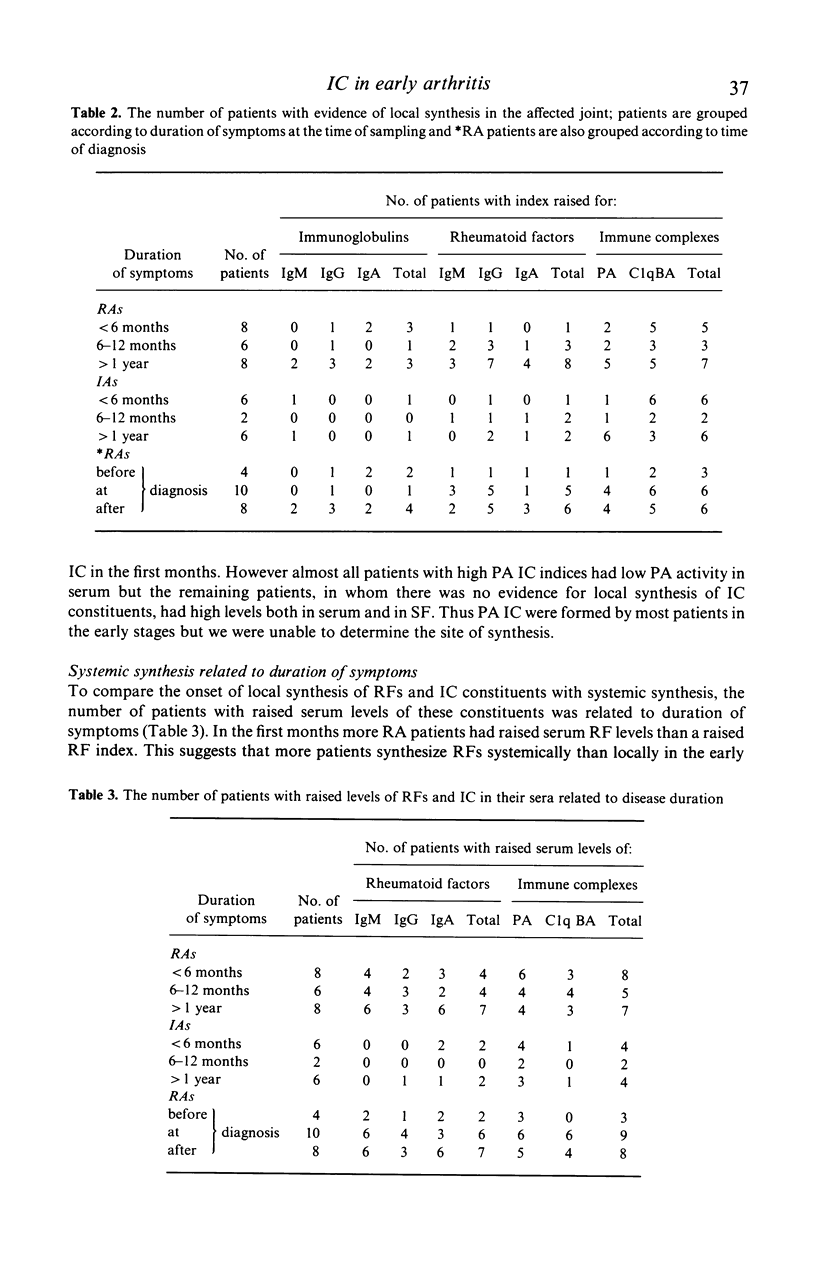
Abstract
Synovial fluids and paired sera taken from patients either before, after or at the time of diagnosis of definite rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were compared with samples from patients with unclassified inflammatory arthropathies (IA). Raised levels of immune complexes (IC) were detected in some RA patients by C1q binding activity but in the majority of both RA and IA patients by the platelet aggregation test; levels were usually higher in joint fluids than in sera. IgM rheumatoid factors (RF) and IgA RFs were lower in synovial fluids but IgF RF levels were similar in matched samples. Synovial fluid to serum albumin ratios were used to estimate synovial permeability (inflammation) and then to calculate which patients synthesized macromolecules locally in the synovium. Local synthesis of RFs was detected in a greater proportion of RA than IA patients and only two patients formed RFs locally in the first months of symptoms. Half the patients in both groups however appeared to synthesize or trap IC constituents and in many patients there was evidence of local synthesis within 6 months after their symptoms had started. We conclude that local synthesis of large amounts of RFs is uncommon in the early stages of RA but that IC of unknown composition are synthesized or localized in the affected joints of many patients with RA and inflammatory arthropathies shortly after their symptoms appear.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnello V., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Precipitin reactions of the C1q component of complement with aggregated gamma-globulin and immune complexes in gel diffusion. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):909–919. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone R., Cracchiolo A., 3rd, Goldberg L. S., Pearson C. M. Catabolism and synovial transport of rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Jan;29(1):47–55. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Lawrance S., Catalano M. A., Vaughan J. H., Abraham G. Radioimmunoassay of IgG and IgM rheumatoid factors reacting with human IgG. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):295–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAGNOSTIC criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: 1958 revision by a committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Ann Rheum Dis. 1959 Mar;18(1):49–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. C., Piening U., Fricke P. M., Deicher H. Platelet aggregation and aggregation inhibition by different antiglobulins and antiglobulin complexes from sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Aug;22(8):896–903. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Perumal R., Roitt I. M. Intra-articular and circulating immune complexes and antiglobulins (IgG and IgM) in rheumatoid arthritis; correlation with clinical features. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Feb;38(1):1–7. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for detection of IgG and IgM antiglobulins in seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 26;3(5977):203–204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5977.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. E., Cowley P. J., Allen C., Elson C. J. The isolation of immune complexes containing IgM rheumatoid factor and recovery of IgG rheumatoid factor from the complexes. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. E., Jacoby R. K., Wallington T., Holt P. Immune complexes in early arthritis. L Detection of immune complexes before rheumatoid arthritis is definite. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):512–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Somerville J. A. Permeability of human synovial membrane to plasma proteins. Relationship to molecular size and inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Sep-Oct;14(5):560–570. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Characterization of IgG complexes in eluates from rheumatoid tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):249–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Immunglobulin classes, subclasses and complexes of IgG rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid plasma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Sep;12(1):55–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Munthe E. Self-associating IgG rheumatoid factor represents a major response of plasma cells in rheumatoid inflammatory tissue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:88–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panush R. S., Bianco N. E., Schur P. H. Serum and synovial fluid IgG, IgA and IgM antigammaglobulins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):737–747. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDBLAD L., JONSSON E., NETTELBLADT E. Permeability of the synovial membrane to glycoproteins. Nature. 1961 Dec 23;192:1192–1192. doi: 10.1038/1921192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Jr Synovial membrane and fluid morphologic alterations in early rheumatoid arthritis: microvascular injury and virus-like particles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:39–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R. Antigammaglobulin (rheumatoid factor) activity of human IgG subclasses. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Feb;37(1):12–17. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakib F., Stanworth D. R. IgG subclass composition of rheumatoid arthritic sera and joint fluids. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Jun;35(3):263–266. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapleigh C., Valone F. H., Schur P. H., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Platelet-activating activity in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and noninflammatory arthropathies. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jul;23(7):800–807. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Chihara T., Moore T. L., Robbins D. L., Tanimoto K., Johnson J. S., McMillan R. Rheumatoid factor-producing cells detected by direct hemolytic plaque assay. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):933–941. doi: 10.1172/JCI108546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON M., JONES B. S. Serum and synovial fluid proteins in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1962 Mar;21:51–58. doi: 10.1136/ard.21.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Gamma globulin complexes in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Partial characterization and relationship to lowered complement levels. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):689–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


