Abstract
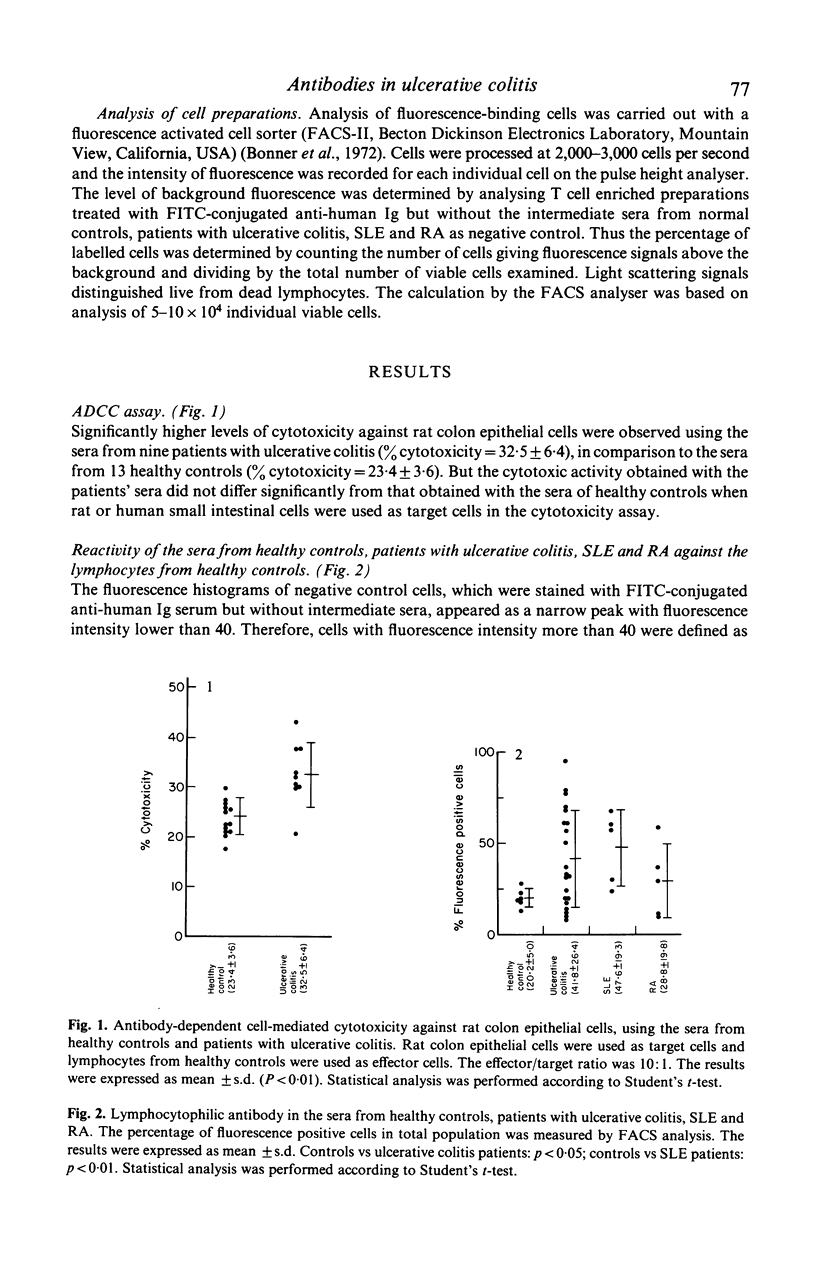
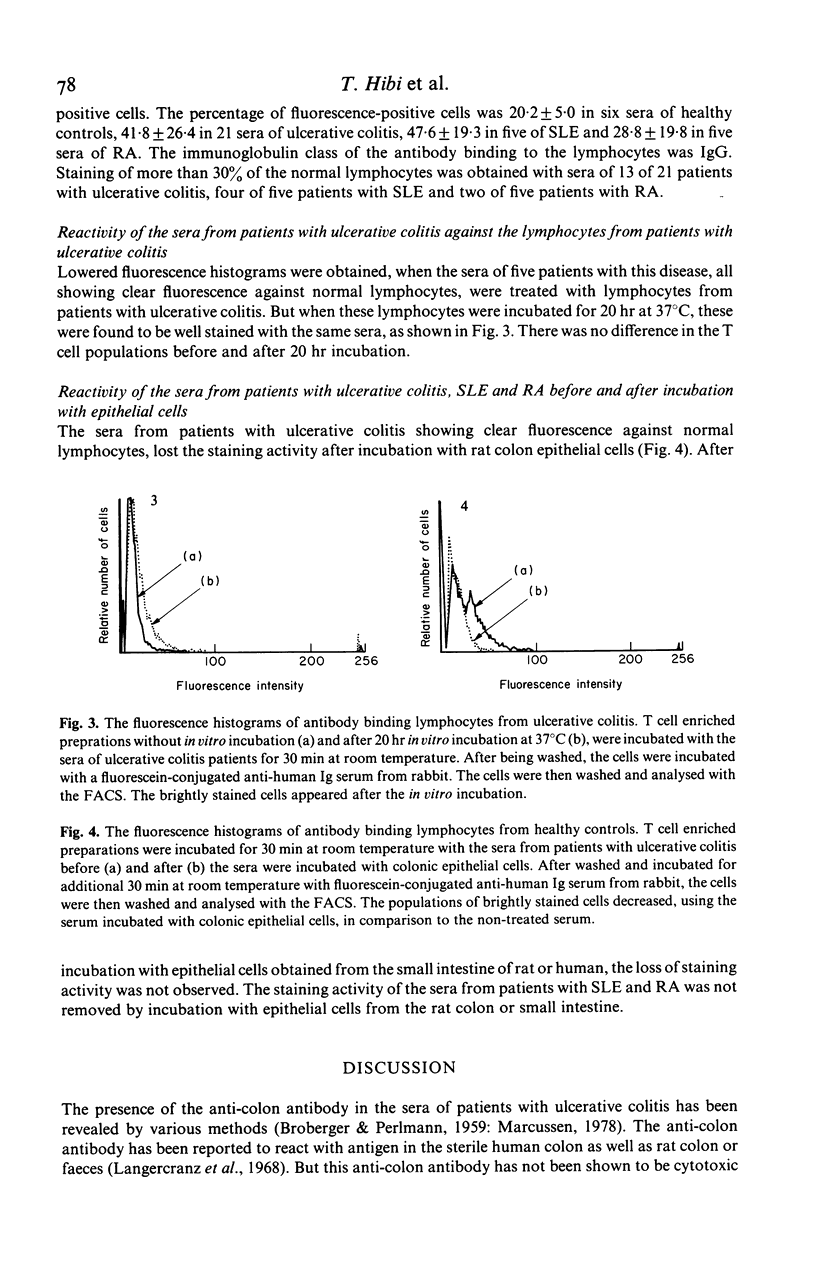
The presence of anti-colon antibody in the sera from patients with ulcerative colitis was demonstrated by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) assay. In addition, the high prevalence of lymphocytophilic antibody in the sera from patients with ulcerative colitis was obtained by fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis. This lymphocytophilic antibody was absorbed by rat colon epithelial cells. Moreover the lymphocytes from ulcerative colitis showed lower binding capacity to this antibody, but acquired higher binding capacity after 20 hr incubation at 37 degrees C in vitro. These data suggest that ADCC may have some role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiso S., Asakura H., Tanaka T., Tsuchiya M. Lymphocyte response to colonic antigen its role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Biochem Exp Biol. 1980;16(3):287–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROBERGER O., PERLMANN P. Autoantibodies in human ulcerative colitis. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:657–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROBERGER O., PERLMANN P. In vitro studies of ulcerative colitis. I. Reactions of patients' serum with human fetal colon cells in tissue cultures. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:705–716. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton P. M., Owen E., Heatley R. V., Williams W. J., Hughes L. E. Negative findings in laboratory animals for a transmissible agent in Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1973 Nov 17;2(7838):1122–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90937-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. A., Hulett H. R., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence activated cell sorting. Rev Sci Instrum. 1972 Mar;43(3):404–409. doi: 10.1063/1.1685647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das K. M., Dubin R., Nagai T. Isolation and characterization of colonic tissue-bound antibodies from patients with idiopathic ulcerative colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4528–4532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENLE G., DEINHARDT F. The establishment of strains of human cells in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1957 Jul;79(1):54–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Wands J. R., Isselbacher K. J. Decreased suppressor cell activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jun;32(3):451–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell D. P., MacLennan I. C. Circulating immune complexes in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S., Strickland R. G., Wilson I. D., Williams R. C., Jr Serum lymphocytotoxic and lymphocytophilic antibody activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1974 Oct;67(4):578–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz R., Hammarström S., Perlmann P., Gustafsson B. E. Immunological studies in ulcerative colitis. IV. Origin of autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1339–1352. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcussen H. Fluorescent anti-colonic and E. coli antibodies in ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(3):277–281. doi: 10.3109/00365527809179820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Rossen R. D., Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Butler W. T. Lymphocyte cytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1255–1256. doi: 10.1038/2251255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata Y., Ikeda H., Stockert E., Boyse E. A. Relation of GIX antigen of thymocytes to envelope glycoprotein of murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):188–197. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin B. S., Herrington E. Antibody-mediated complement-dependent cytotoxicity in immunologically induced experimental colon disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;63(2):205–211. doi: 10.1159/000232628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Spencer R. J., Huizenga K. A., Hallenbeck G. A. Inhibition of in vitro cytotoxicity of lymphocytes from patients with ulcerative colitis and granulomatous colitis for allogeneic colonic epithelial cells using horse anti-human thymus serum. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):227–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Tomasi T. B., Huizenga K. A., Spencer R. J., Shorter R. G. In vitro studies of inflammatory bowel disease. Surface receptors of the mononuclear cell required to lyse allogeneic colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. G., Miller W. C., Volpicelli N. A., Gaeke R. F., Wilson I. D., Kirsner J. B., Williams R. C., Jr Lymphocytotoxic antibodies in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and their spouses--evidence for a transmissible agent. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):188–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


