Abstract
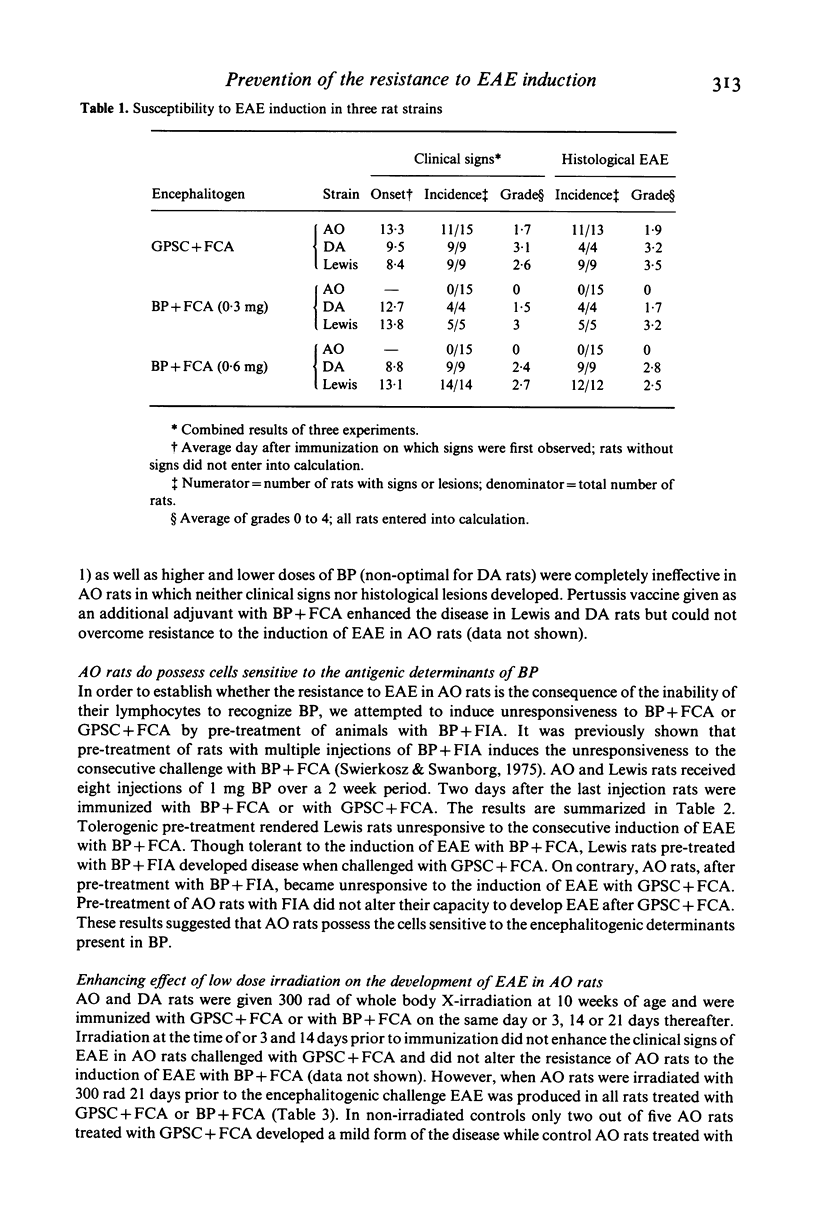
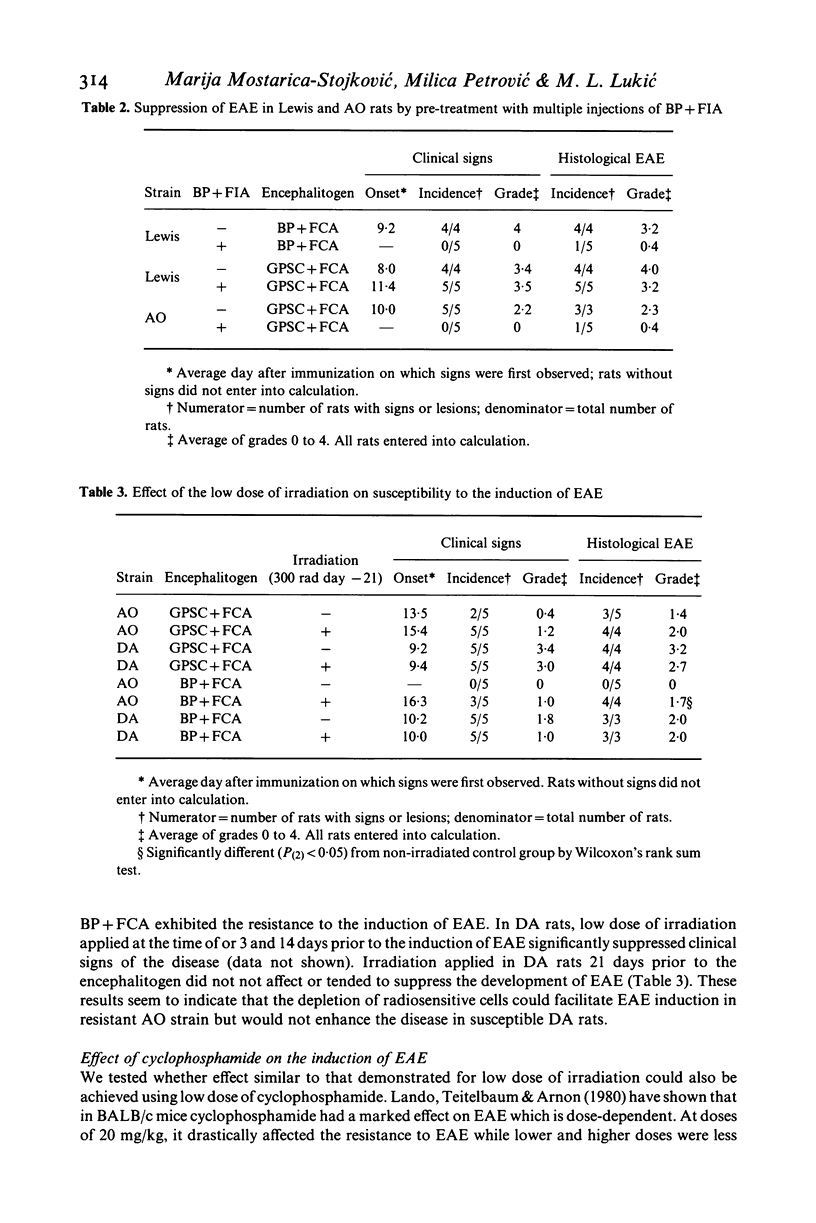
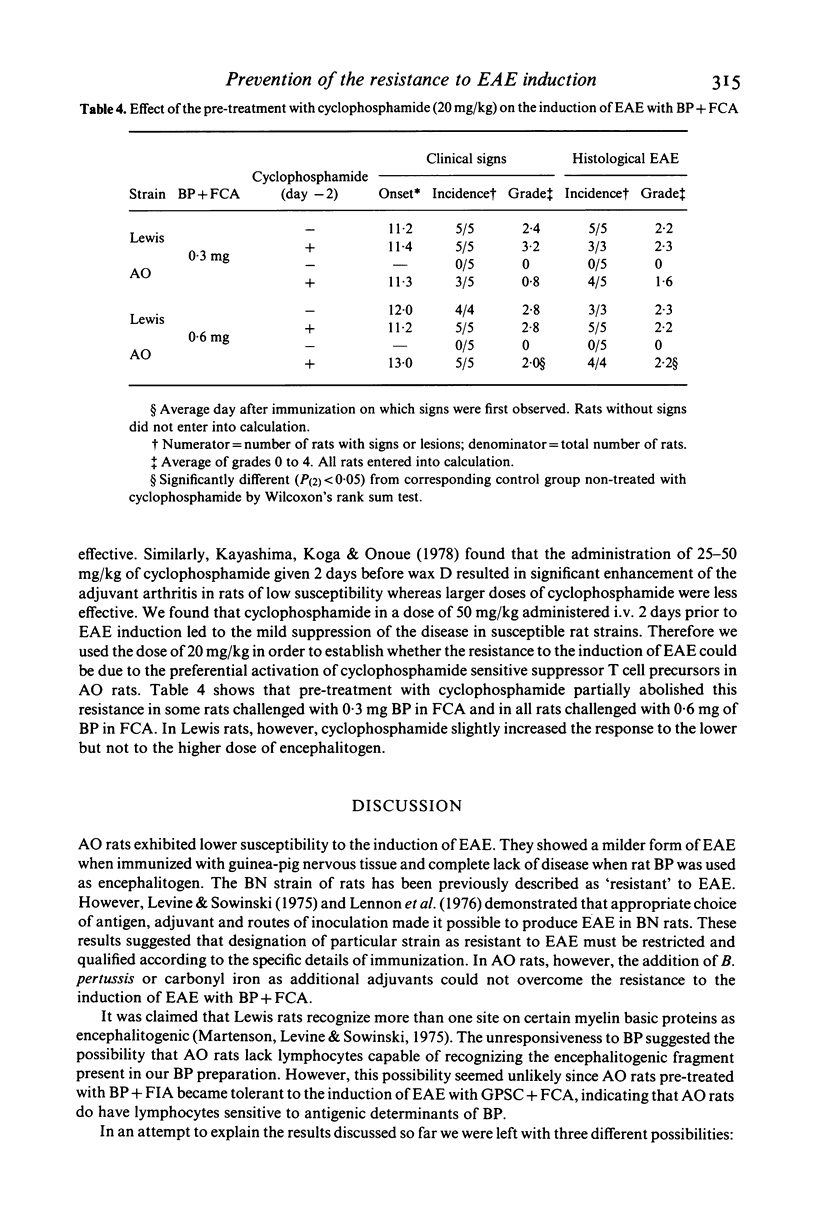
Susceptibility to the induction of EAE was compared in AO, DA and Lewis strain of rats. As evaluated by clinical and histological criteria, AO rats exhibited significantly lower susceptibility to EAE induced with guinea-pig spinal cord (GPSC) tissue and complete resistance to the encephalitogenic challenge with rat myelin basic protein (BP) irrespective of antigen dose and adjuvant used. AO rats pre-treated with BP + Freund's incomplete adjuvant became completely unresponsive to the induction of EAE with GPSC + Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA) indicating that they do possess cells sensitive to some antigenic determinants of rat BP. In order to test whether the resistance to EAE is due to an active suppression, low dose of irradiation (300 rad) and cyclophosphamide (20 mg/kg) was applied prior to the induction of EAE. Selective depletion of radiosensitive cells facilitated the induction of EAE. Similarly, cyclophosphamide given 2 days prior to BP + FCA completely abrogated the resistance to EAE induction. Thus, it appears that the inability of BP + FCA to produce EAE in AO rats is due to the disproportionate activation of suppressor cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. I. Evidence for the regulatory function of thymus-derived cells in the induction of the disease. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1878–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. II. Different subpopulations of T lymphocytes functioning in the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblum J. The application of the irradiated hamster test to the study of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):702–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando Z., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in genetically resistant strains of mice. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):551–552. doi: 10.1038/287551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Westall F. C., Thompson M., Ward E. Antigen, host and adjuvant requirements for induction of hyperacute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Nov;6(11):805–810. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Allergic encephalomyelitis in the reputedly resistant Brown Norway strain of rats. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in inbred and outbred mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):139–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukic M. L., Leskowitz S. Tolerance induction with bovine gamma globulin in mouse radiation chimaeras depends on macrophages. Nature. 1974 Dec 13;252(5484):605–607. doi: 10.1038/252605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukić M. L., Wortis H. H., Leskowitz S. A gene locus affecting tolerance to BGG in mice. Cell Immunol. 1975 Feb;15(2):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E., Kies M. W. Myelin basic proteins of the rat central nervous system. Purification, encephalitogenic properties, and amino acid compositions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Levine S., Sowindki R. The location of regions in guinea pig and bovine myelin basic proteins which induce experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):592–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. H., Lerner E. M., 2nd, Goode J. H., Jr Acute and chronic autoimmune encephalomyelitis: age, strain, and sex dependency. The importance of the source of antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):341–344. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanborg R. H. Antigen-induced inhibition of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. III. Localization of an inhibitory site distinct from the major encephalitogenic determinant of myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):191–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Swanborg R. H. Immunoregulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: conditions for induction of suppressor cells and analysis of mechanism. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1501–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Swanborg R. H. Suppressor cell control of unresponsiveness to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):631–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Miller S. D., Claman H. N. Immune suppression with supraoptimal doses of antigen in contact sensitivity. I. Demonstration of suppressor cells and their sensitivity to cyclophosphamide. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):240–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D. Further studies on B-lymphocyte suppression in delayed hypersensitivity, indicating a possible mechanism for Jones-Mote hypersensitivity. Immunology. 1973 Apr;24(4):751–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitale B., Allegretti N., Matosić M. Influence of x-irradiation on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Radiat Res. 1966 Aug;28(4):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg D. O. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat: studies on the mechanism of recovery from disease and acquired resistance to reinduction. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1145–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


