Abstract
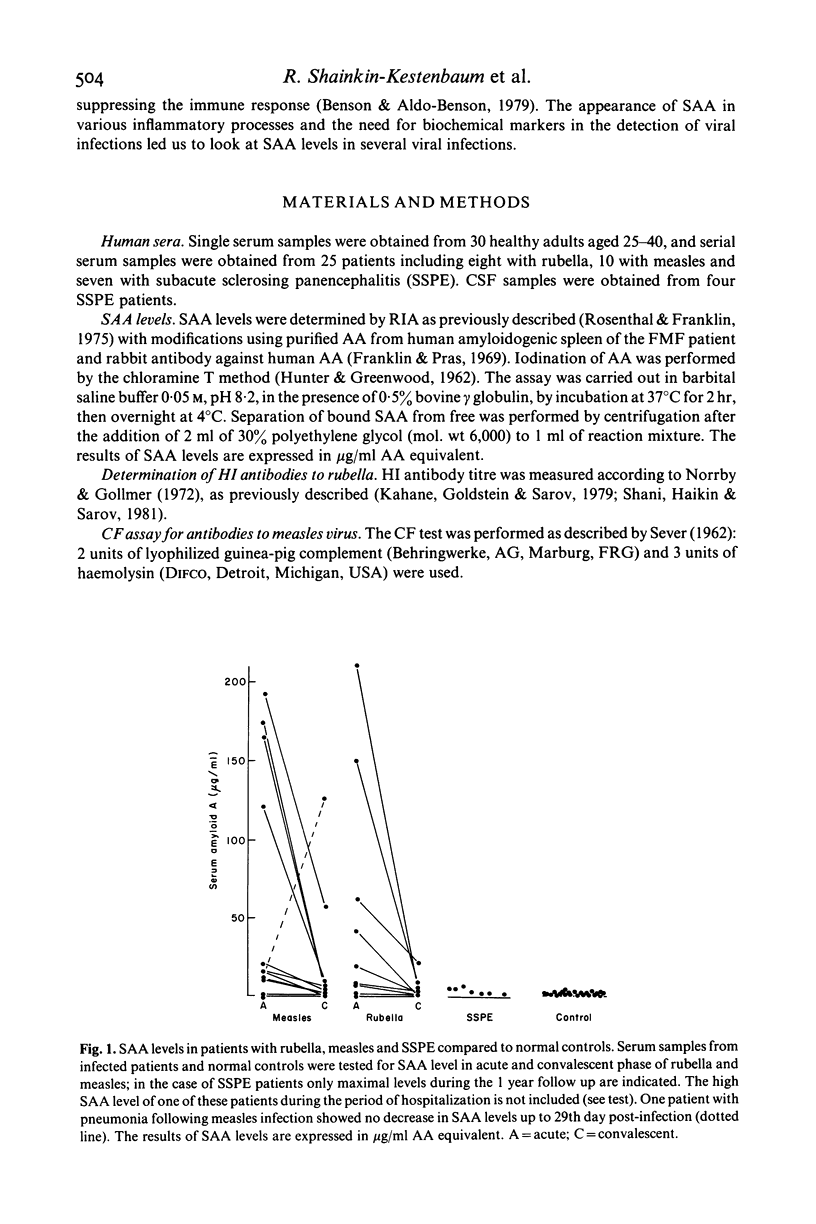
Serum amyloid A (SAA) levels were determined in the serial serum samples of eight rubella, 10 measles and seven subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) patients. An early rise in SAA levels was detected in the acute phase in rubella and measles, followed by a prompt decrease in the convalescent phase. In a number of measles and rubella patients from whom early serum samples were available, the rise of SAA levels could be demonstrated before specific viral antibodies could be detected by complement fixation (CF) (measles) and haemagglutination inhibition (HI) (rubella). In only one rubella and one measles patient was no rise of SAA level detected. In SSPE only a moderate increase in SAA levels was noted except in one patient during a temporary deterioration, at which time the SAA level was very high; it returned to close to normal shortly thereafter. The possibility that SAA levels might be of value in monitoring the severity of infections, the recovery process and effects of anti-viral agents is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumal R., Sklar S., Wilson B., Laskov R. Casein-induced murine amyloidosis: amyloidogenesis in vitro by monolayer spleen explants of casein-injected mice. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):632–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausserman L. L., Herbert P. N., McAdam K. P. Heterogeneity of human serum amyloid A proteins. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):641–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Aldo-Benson M. Effect of purified protein SAA on immune response in vitro: mechanisms of suppression. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):2077–2082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Kleiner E. Synthesis and secretion of serum amyloid protein A (SAA) by hepatocytes in mice treated with casein. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):495–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Skinner M., Lian J., Cohen A. S. "A" protein of amyloidosis. Isolation of a cross-reacting component from serum by affinity chromatography. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):315–322. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Pras M. Immunologic studies of water-soluble human amyloid fibrils. Comparative studies of eight amyloid preparations. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):797–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Natvig J. B. A serum component related to nonimmunoglobulin amyloid protein AS, a possible precursor of the fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1054–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI107642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignaczak T. F., Sipe J. D., Linke F. P., Glenner G. G. Immunochemical studies on the nature of the serum component (SAA) related to secondary amyloidosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 May;89(5):1092–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane S., Goldstein V., Sarov I. Detection of IgG antibodies specific for measles virus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Intervirology. 1979;12(1):39–46. doi: 10.1159/000149067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Elastase-type proteases on the surface of human blood monocytes: possible role in amyloid formation. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Pras M., Franklin E. C. Immunologic studies of the major nonimmunoglobulin protein of amyloid. I. Identification and partial characterization of a related serum component. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):373–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I., Stenman S., Natvig J. B. Localization of amyloid-related serum protein SAA-like material to intermediate (10 nm) filaments of cultured human embryonal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Sipe J. D. Murine model for human secondary amyloidosis: genetic variability of the acute-phase serum protein SAA response to endotoxins and casein. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1121–1127. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Gollmar Y. Appearance and persistence of antibodies against different virus components after regular measles infections. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.240-247.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Variation with age and disease of an amyloid A protein-related serum component. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):746–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI107985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Sullivan L. M. Serum amyloid A to monitor cancer dissemination. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):383–390. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Sullivan L. Serum amyloid A: evidence for its origin in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1181–1186. doi: 10.1172/JCI109237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A. C-reactive protein in acute viral infections. J Med Virol. 1981;8(3):161–167. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger M. J., McAdam K. P., Kaplan M. M., Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Rosenstreich D. L. Monokine-induced synthesis of serum amyloid A protein by hepatocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):498–500. doi: 10.1038/285498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani L., Haikin H., Sarov I. A rapid immunoperoxidase assay for determination of IgG antibodies to measles virus. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., McAdam K. P., Uchino F. Biochemical evidence for the biphasic development of experimental amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1978 Jan;38(1):110–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Ryan J. L., McAdam K. P., Rosenstreich D. L. Detection of a mediator derived from endotoxin-stimulated macrohpages that induces the acute phase serum amyloid A response in mice. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):597–606. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Vogel S. N., Sipe J. D., Murphy P. A., Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. The role of macrophages in the acute-phase response: SAA inducer is closely related to lymphocyte activating factor and endogenous pyrogen. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):164–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


