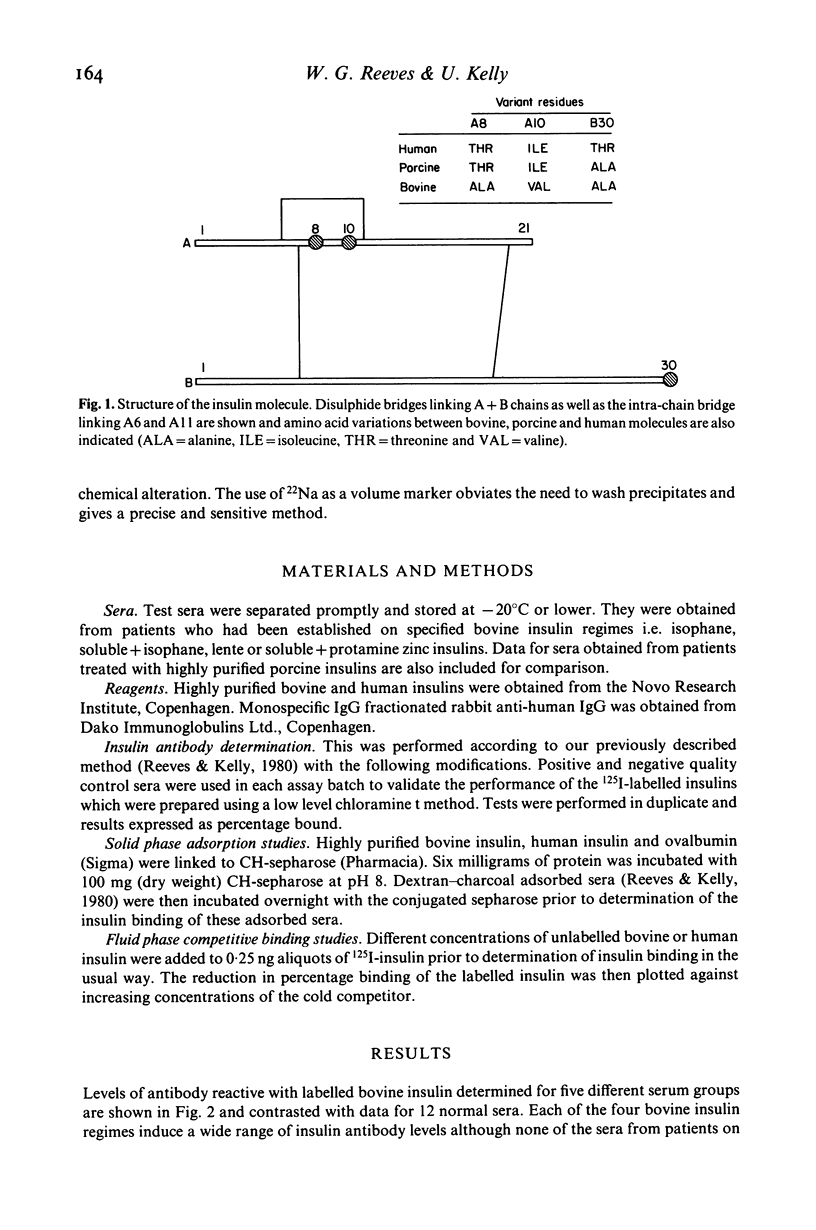
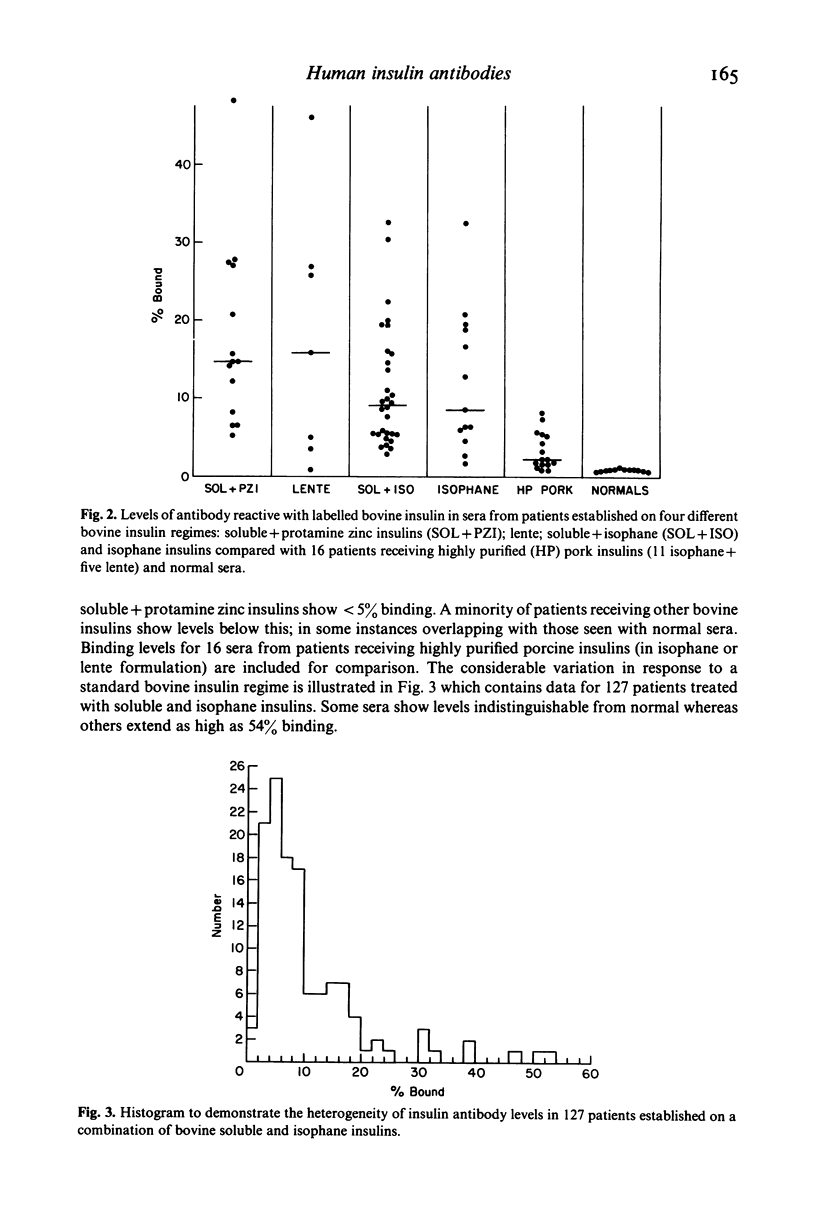
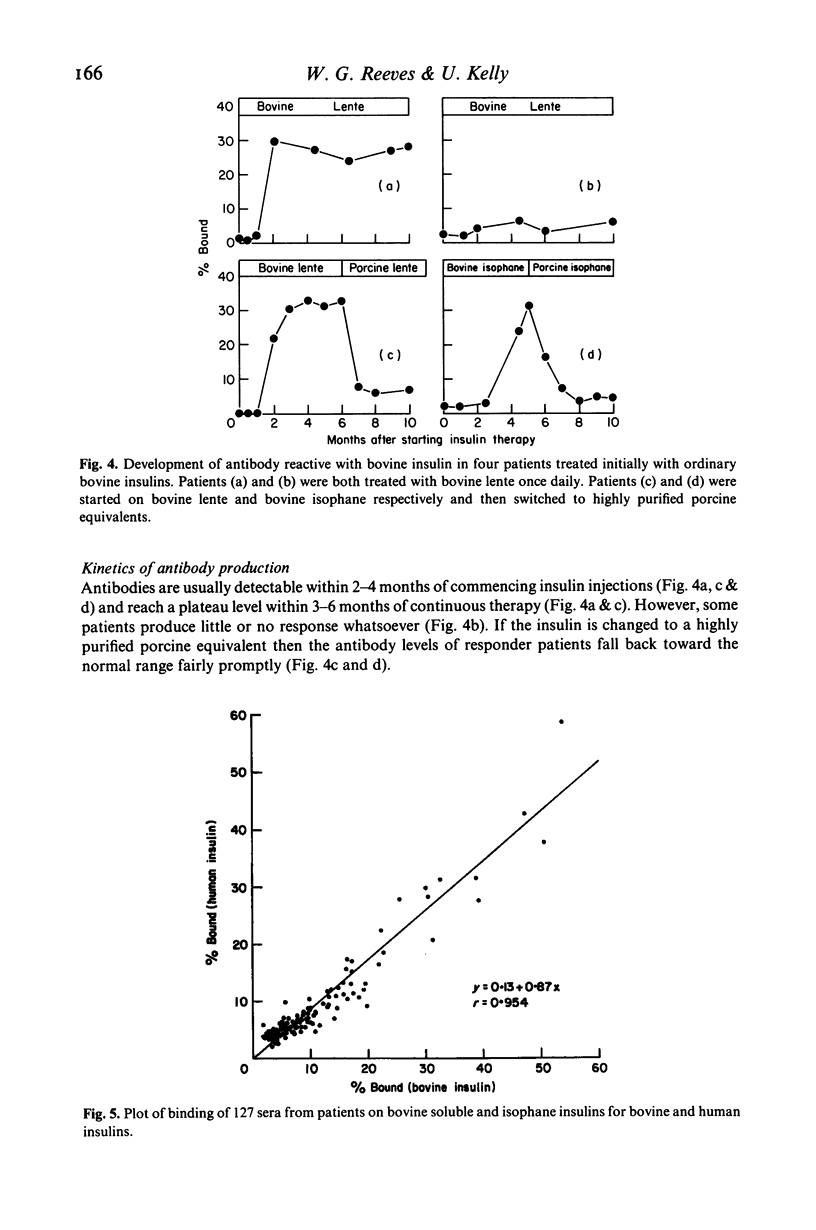
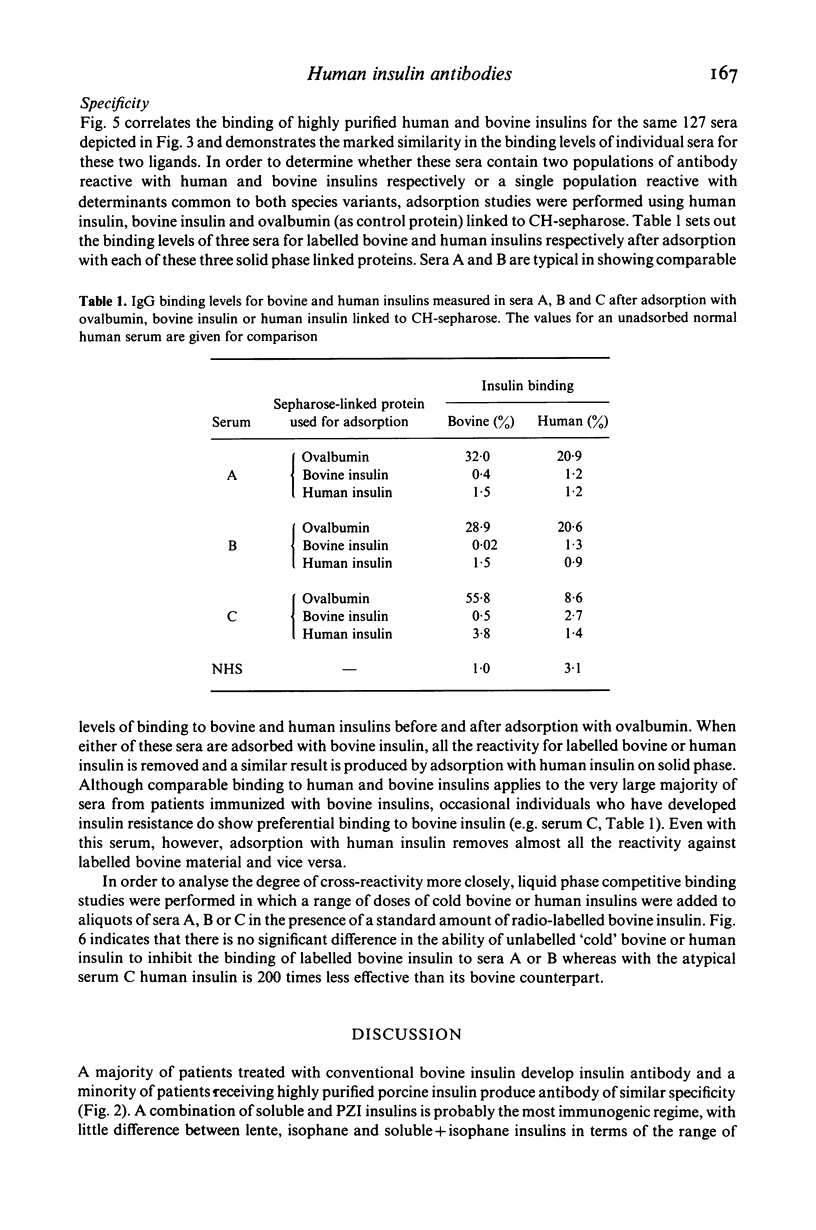
Abstract
Insulin antibodies are detectable in the sera of most patients within 3-4 months of starting treatment with conventional bovine insulins. Various factors determine the immunogenicity of insulin preparations including the genetic background of the recipient. This causes wide variation in response. Solid phase absorption studies as well as competitive binding in fluid phase indicate that the antibodies formed are almost always specific for determinants shared by the endogenous human molecule. This has important implications for the metabolic effect of insulin antibodies in vivo as well as for mechanisms of autoantibody production in man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen O. O. Clinical significance of anti-insulin-antibodies. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1976;205:231–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arquilla E. R., Thiene P., Brugman T., Ruess W., Sugiyama R. Effects of zinc ion on the conformation of antigenic determinants on insulin. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):289–297. doi: 10.1042/bj1750289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKINSHAW V. J., RANDALL S. S., RISDALL P. C. Formation of precipitin lines between insulin and anti-insulin serum produced in sheep and in guinea pigs. Nature. 1962 Mar 17;193:1089–1090. doi: 10.1038/1931089b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLINGER R. E., MORRIS J. H., MCKNIGHT F. G., DIEDERICH D. A. DISAPPEARANCE OF I-131-LABELED INSULIN FROM PLASMA AS A GUIDE TO MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES. N Engl J Med. 1964 Apr 9;270:767–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196404092701504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcinski M. A., Rosenthal A. S. Immune response gene control of determinant selection. I. Intramolecular mapping of the immunogenic sites on insulin recognized by guinea pig T and B cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):726–742. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Deamidation of insulin during storage in frozen state. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):875–879. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutton R. F., Harington C. R., Yuill M. E. Studies in synthetic immunochemistry: Serological investigation of O-beta-glucosidotyrosyl derivatives of proteins. Biochem J. 1938 Jul;32(7):1111–1118. doi: 10.1042/bj0321111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckert T., Andersen O. O., Grundahl E., Kerp L. Isoimmunization of man by recrystallized human insulin. Diabetologia. 1972 Nov;8(5):358–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01218497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J. Autoimmunity in endocrine disease. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1980;36:509–556. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571136-4.50020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Strayer D. S. H-2 linked Ir gene control of antibody responses to porcine insulin. I. Development of insulin-specific antibodies in some but not all nonresponder strains injected with proinsulin. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):978–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar D. Immunoreactivity of insulin antibodies in insulin-treated diabetics: significance of the beta-chain carboxy-terminal amino acid (B-30) of insulin. Diabetes. 1979 Nov;28(11):994–1000. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.11.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Knospe S., Ziegler M., Wilke W., Michael R. Failure of appearance of insulin antibodies in dogs adapted to bovine-porcine insulin. Diabetologia. 1971 Oct;7(5):386–390. doi: 10.1007/BF01219475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer H. P., Schöne H. H. The immunogenicity of different insulins in several animal species. Diabetes. 1978 Jan;27(1):8–15. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Allen B. R., Tattersall R. B. Insulin-induced lipoatrophy: evidence for an immune pathogenesis. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 21;280(6230):1500–1503. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6230.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Douglas C. A. C-peptide antibodies induced by bovine insulin therapy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):171–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. G., Kelly U. An immunochemical method for the quantitation of insulin antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1980;34(4):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendell M., Hamilton R. G., Drew H. M., Adkinson N. F., Jr Exacerbation of diabetes mellitus by antibodies to exogenous insulin. Am J Med Sci. 1981 Jul-Aug;282(1):18–26. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198107000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I. The modes of inheritance of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or the genetics of IDDM, no longer a nightmare but still a headache. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Nov;33(6):835–851. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walford S., Allison S. P., Reeves W. G. The effect of insulin antibodies on insulin dose and diabetic control. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):106–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00254838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Ohman J. L., Weir G. C., Raymond L. W., Lowell F. C. Insulin antibodies in the pathogenesis of insulin allergy and resistance. Am J Med. 1977 Nov;63(5):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pirro R., Fusco A., Spallone L., Magnatta R., Lauro R. Insulin antibodies prevent insulin-receptor interactions. Diabetologia. 1980 Aug;19(2):118–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00421857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


