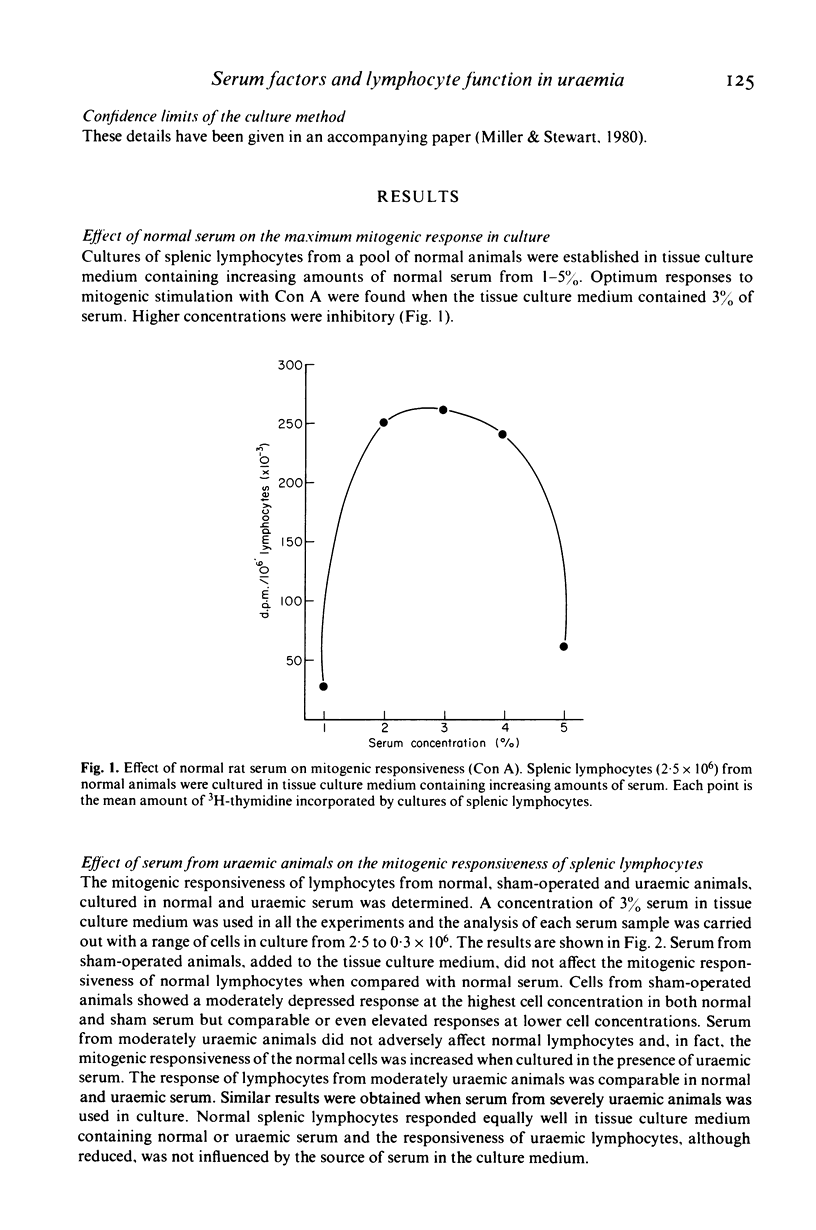
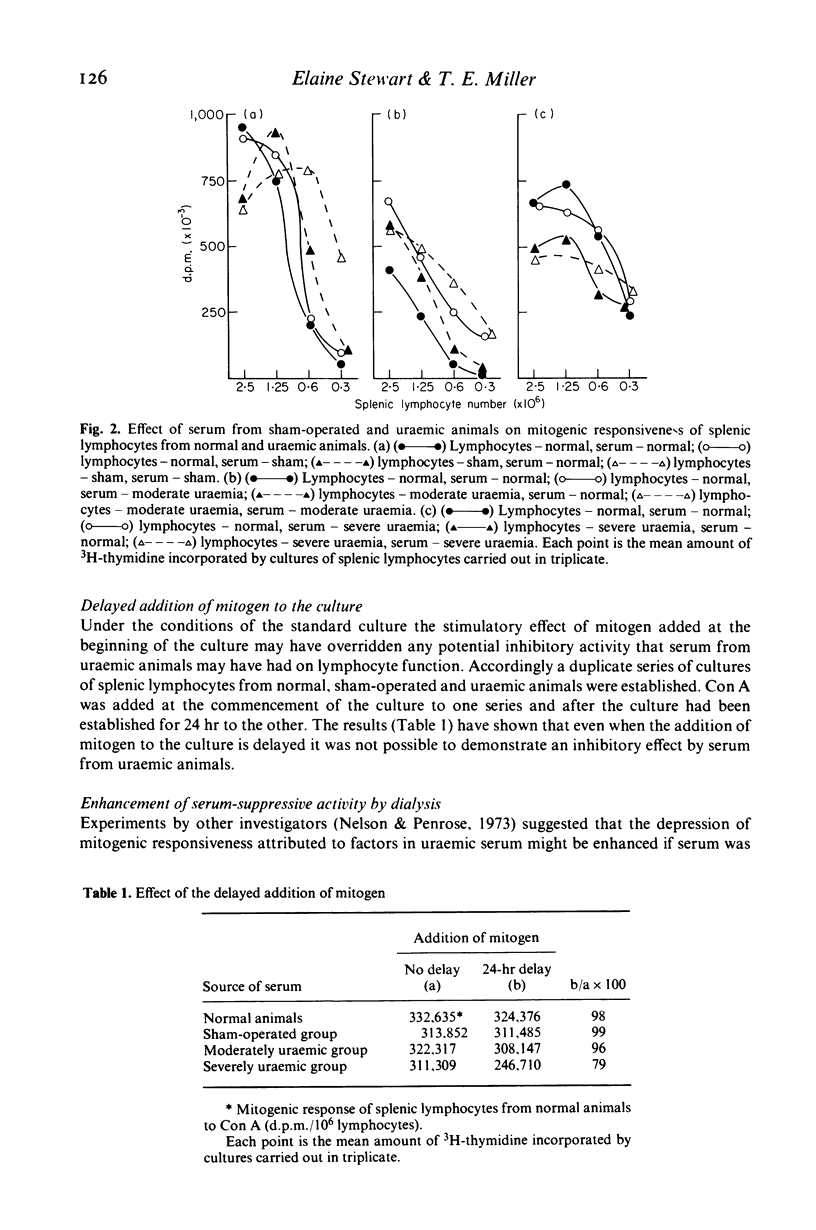
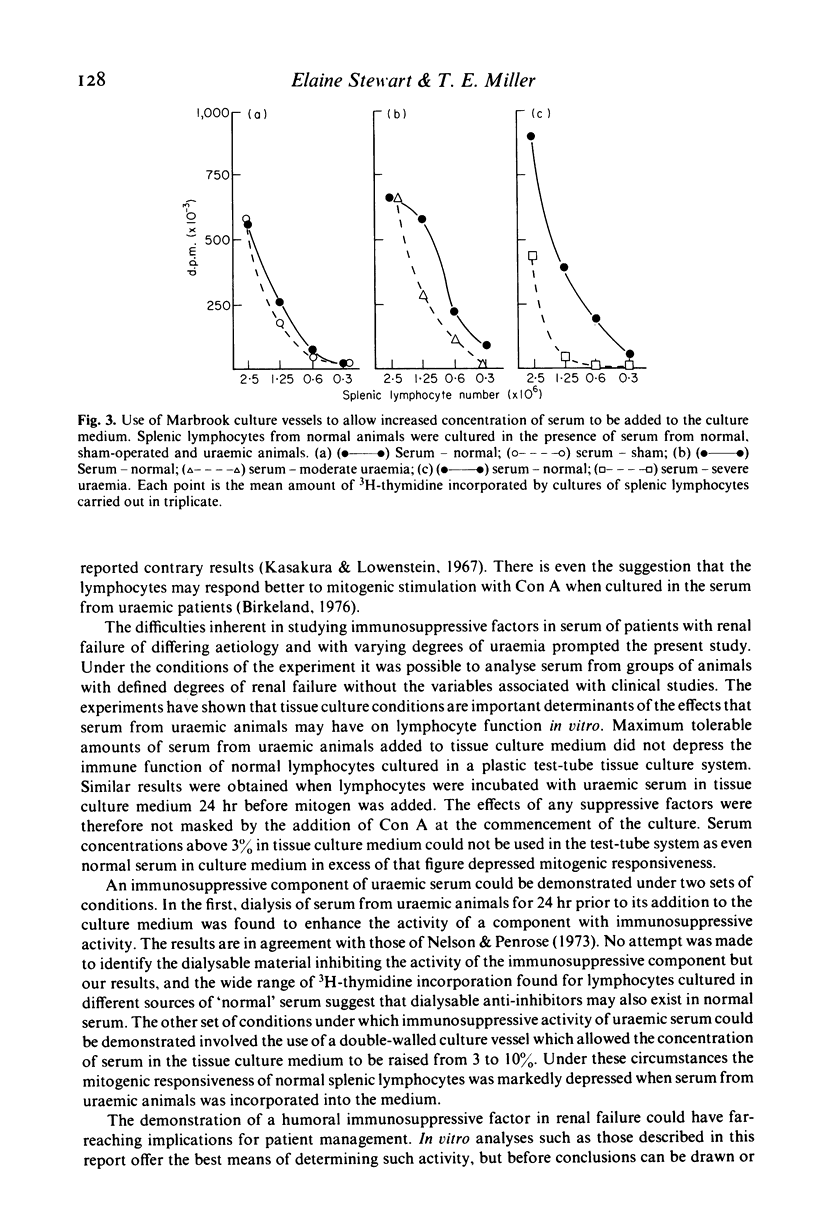
Abstract
A model of experimentally induced uraemia has been used to study the effect of serum from uraemic rats on the immune responsiveness of thymus-derived (T) lymphocytes. Splenic lymphocytes from normal or uraemic animals responded to mitogenic stimulation with concanavalin A to a similar degree when cultured in a tissue culture medium containing the maximum non-toxic concentration of normal or uraemic serum in the culture system (3%). Serum from uraemic animals, however, had an immunosuppressive effect if the serum was first dialysed for 24 hr before being added to the tissue culture medium. When an alternative vessel was used which allowed the concentration of serum in the medium to be increased to 10%, serum from severely uraemic animals markedly suppressed the capacity of lymphocytes from normal animals to respond to Con A. Thus while serum from uraemic animals can be shown to be immunosuppressive, the results of the experiments are influenced by the conditions in vitro. The type of culture vessel and the concentration of serum in the culture medium are particularly critical determinants. It is likely that variations in laboratory procedures have contributed to the differences of opinion on the effect of serum from uraemic individuals on lymphocyte function.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkeland S. A. Uremia as a state of immune deficiency. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(1-2):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb02997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAMMIN G. J., COUCH N. P., MURRAY J. E. Prolonged survival of skin homografts in uremic patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Mar 22;64(5):967–976. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb52488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelstein H., Körner W. F., Mempel W., Grosse-Wilde H., Edel H. H. Vitamin B6 deficiency in uremia and its implications for the depression of immune responses. Kidney Int. 1974 Mar;5(3):233–239. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanicki Z., Cichocki T., Sarnecka-Keller M., Klein A., Komorowska Z. Influence of middle-sized molecule aggregates from dialysate of uremic patients on lymphocyte transformation in vitro. Nephron. 1976;17(1):73–80. doi: 10.1159/000180713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. E., Pagé D., Posen G., Stewart T. Suppression of in vitro lymphocyte function by uremic toxins. J Urol. 1972 Aug;108(2):312–313. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)60723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. F., Slavin R. G. Mechanism of inhibition of adoptive transfer of tuberculin sensitivity in acute uremia. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Mar;87(3):457–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbrook J. Primary immune response in cultures of spleen cells. Lancet. 1967 Dec 16;2(7529):1279–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Creaghe E. Bacterial interference as a factor in renal infection. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 May;87(5):792–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Stewart E. Host immune status in uraemia. I. Cell-mediated immune mechanisms. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jul;41(1):115–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munster A. M., Loadholdt C. B., Leary A. G., Barnes M. A. The effect of antibiotics on cell-mediated immunity. Surgery. 1977 Jun;81(6):692–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S., Penrose J. M. Macromolecular inhibitor of lymphocyte transformation in serum from patients with chronic renal failure. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Apr;51(2):259–262. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry W. M., Sanford J. P. Defective cellular immunity in renal failure: depression of reactivity of lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin by renal failure serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1262–1271. doi: 10.1172/JCI106604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk M. R. The effect of uremic plasma on lymphocyte transformation. Invest Urol. 1967 Sep;5(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin R. G., Fitch C. D. Inhibition of lymphocyte transformation by guanidinosuccinic acid, a surplus metabolite in uremia. Experientia. 1971;27(11):1340–1341. doi: 10.1007/BF02136727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Smith J., Bradfield J. W. The effect of uraemia on organ graft survival in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Apr;54(2):183–191. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnawski A., Batko B. Antibiotics and immune processes. Lancet. 1973 Mar 24;1(7804):674–675. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


