Abstract
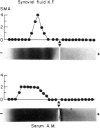
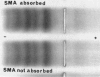
In twelve synovial fluid/serum pairs from patients with various types of seronegative polyarthritis, homogeneous gamma-bands by agarose gel electrophoresis were found in seven of the synovial fluids and in only one of the sera. In six of the fluids with gamma-bands, smooth muscle antibodies (SMA) were also present, usually in a titre identical to that in serum. In fluids with no gamma-bands, no SMA were detected. In forty synovial fluid/serum pairs from paitients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, no gamma-bands were detected in the synovial fluids, and SMA were present in only three pairs. Absorption and inhibition experiments did not give evidence that the SMA activity in seronegative polyarthritis was confined to the gamma-bands in the synovial fluids. The SMA activity in the fluids seemed to be directed against both actin and 'non-actin' muscular antigens. The association between locally produced oligoclonal immunoglobulins and possible locally produced SMA with differnet electrophoretic mobility suggests that in some of thes patients there is a local synovial production of oligoclonal antibodies with different specificities. Thus, even if the results may indicate a local virus infection in some arthritic joints, they may also be dur to an unspecific local stimulation of B cells or to a specific antigen stimulation combined with an unspecific co-activation of other antibody-producing cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen P., Andersen H. K. Smooth-muscle antibodies and other tissue antibodies in cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):22–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Sterner G. Smooth muscle antibodies in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):287–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobloug J. H., Førre O., Thorsby E. HLA-DRw4 and rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1979 Mar 10;1(8115):548–549. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90963-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Ryan G. B., Lamelin J. P., Vassalli P., Majno G., Bouvier C. A., Cruchaud A., Lüscher E. F. Human smooth muscle autoantibody. Its identification as antiactin antibody and a study of its binding to "nonmuscular" cells. Am J Pathol. 1973 Sep;72(3):473–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedberg H. A. Faint, narrow bands in the -region visible at agarose electrophoresis. The occurrence in various forms of arthritis. Ann Clin Res. 1971 Oct;3(5):281–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J., Hemsted E. H., Mead S. V. Smooth muscle autoantibodies in infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1973 Aug 11;3(5875):323–325. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5875.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J., Glynn L. E. Antibody to smooth muscle in patients with liver disease. Lancet. 1965 Oct 30;2(7418):878–879. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause R. M. The search for antibodies with molecular uniformity. Adv Immunol. 1970;12:1–56. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Linder E., Miettinen A., Alfthan O. Smooth muscle antibodies of actin and "non-actin" specificity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Apr;9(4):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidman K., Biberfeld G., Fagraeus A., Norberg R., Torstensson R., Utter G., Carlsson L., Luca J., Lindberg U. Anti-actin specificity of human smooth muscle antibodies in chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):266–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Sasazuki T., McDevitt H. O., Payne R. O. Increased frequency of HLA-Cw3 and HLA-Dw4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jun;20(5):1037–1042. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcmillan S. A., Haire M. Smooth muscle antibody in patients with warts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Aug;21(2):339–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Natvig J. B. Experimentally produced antibodies to the pepsin site of IgG due to untreated autologous IgG in immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):257–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moticka E. J., Streilein J. W. Hypothesis: nonspecific polyclonal activation of memory B cells by antigen as a mechanism for the preservation of long term immunologic anamnesis. Cell Immunol. 1978 Dec;41(2):406–413. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordal G. J., Vandvik B. Evidence of local synthesis of smooth-muscle antibodies in the central nervous system in isolated cases of multiple sclerosis and chronic lymphocytic meningoencephalitis. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(4):327–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):869–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandvik B., Mellbye O. J., Norrby E. Local synovial synthesis of oligoclonal measles virus antibodies and of smooth muscle antibodies in a case of atypical rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Aug;36(4):302–310. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.4.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]