Abstract
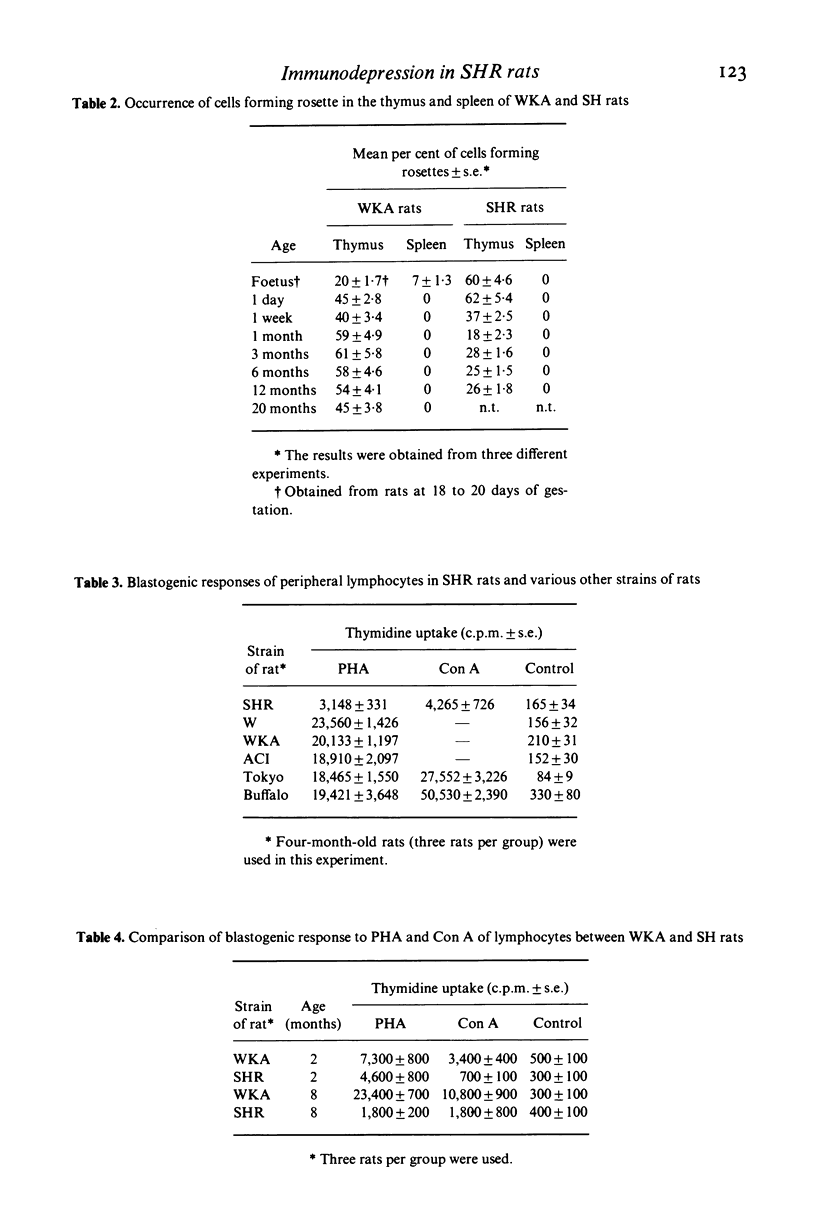
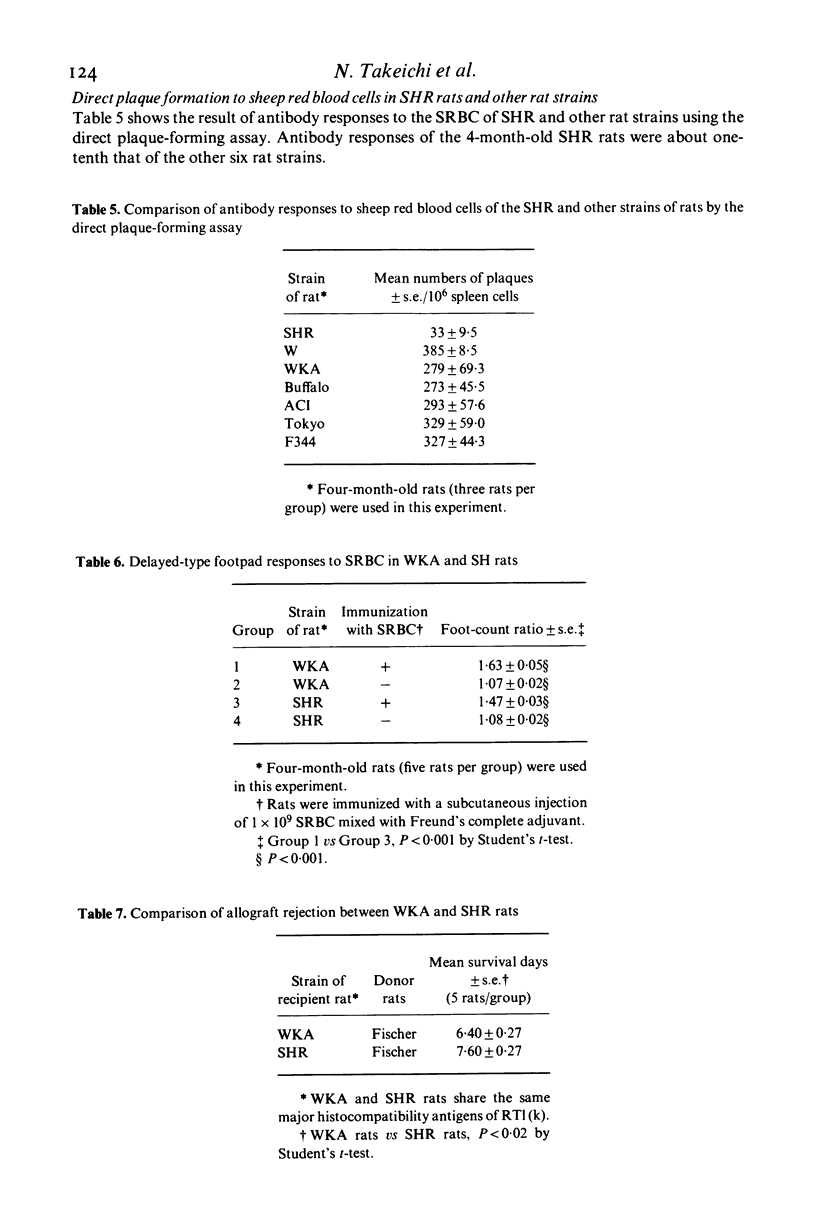
Cell-mediated immunity was investigated in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). The thymuses of young SHR rats before developing hypertension had reduced numbers of immature T lymphocytes which were detected by the rosette formation test with guinea-pig erythrocytes in the presence of foetal bovine serum, whereas the thymuses of eight other rat strains tested contained about 60% of rosetting cells. The number of rosetting cells decreased progressively with age. The blastogenic responses to PHA and Con A of the SHR rats' lymphocytes was depressed to less than one-fifth when compared to those of othe rat strains including W/7k rats, the original colony of the SHR rats. Eight-month-old SHR rats showed fewer mitogenic responses than those of 2-month-old SHR rats. Other cell-mediated immune responses, including delayed hypersensitivity, allograft rejections, and a co-operation of T and B lymphocytes to produce humoral antibody formation were depressed significantly when compared to those of other rat strains. Possible mechanisms of immunological depression in the SHR rats in relation to the devleopment of hypertension are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AOKI K. EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ENDOCRINE ORGANS AND HYPERTENSION IN SPONTANEOUSLY HYPERTENSIVE RATS. III. ROLE OF THE ENDOCRINE ORGANS AND HORMONES. Jpn Heart J. 1964 Jan;5:57–68. doi: 10.1536/ihj.5.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AOKI K., TANKAWA H., FUJINAMI T., MIYAZAKI A., HASHIMOTO Y. PATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ENDOCRINE ORGANS OF THE SPONTANEOUSLY HYPERTENSIVE RATS. Jpn Heart J. 1963 Sep;4:426–442. doi: 10.1536/ihj.4.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfenbein G. J., Santos G. W. Rosette formation between rat thymocytes and guinea pig erythrocytes requires "active" fetal calf serum. II. Characterization of the receptor-bearing thymocytes. Cell Immunol. 1978 Apr;37(1):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfenbein G. J., Winkelstein J. A. Rosette formation between rat thymocytes and guinea pig erythrocytes requires "active" fetal calf serum. I. Characteristics of "active" serum factors and receptors on thymocytes and erythrocytes. Cell Immunol. 1978 Apr;37(1):188–198. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliss N., Suter R. B. Altered survival times of murine skin allografts from cancer-bearing donors. Transplantation. 1968 Oct;6(7):844–848. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196810000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO K., AOKI K. Development of a strain of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Jpn Circ J. 1963 Mar;27:282–293. doi: 10.1253/jcj.27.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi N., Boone C. W. Local adoptive transfer of the antitumor cellular immune response in syngeneic and allogeneic mice studied with a rapid radioisotopic footpad assay. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jul;55(1):183–187. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi N., Boone C. W. Spontaneous rosette formation of rat thymus cells with guinea pig erythrocytes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Nov;27(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi N., Suzuki K., Kobayashi H. A thymus cell marker in murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas of rats. Cancer Res. 1979 Sep;39(9):3749–3751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


