Abstract
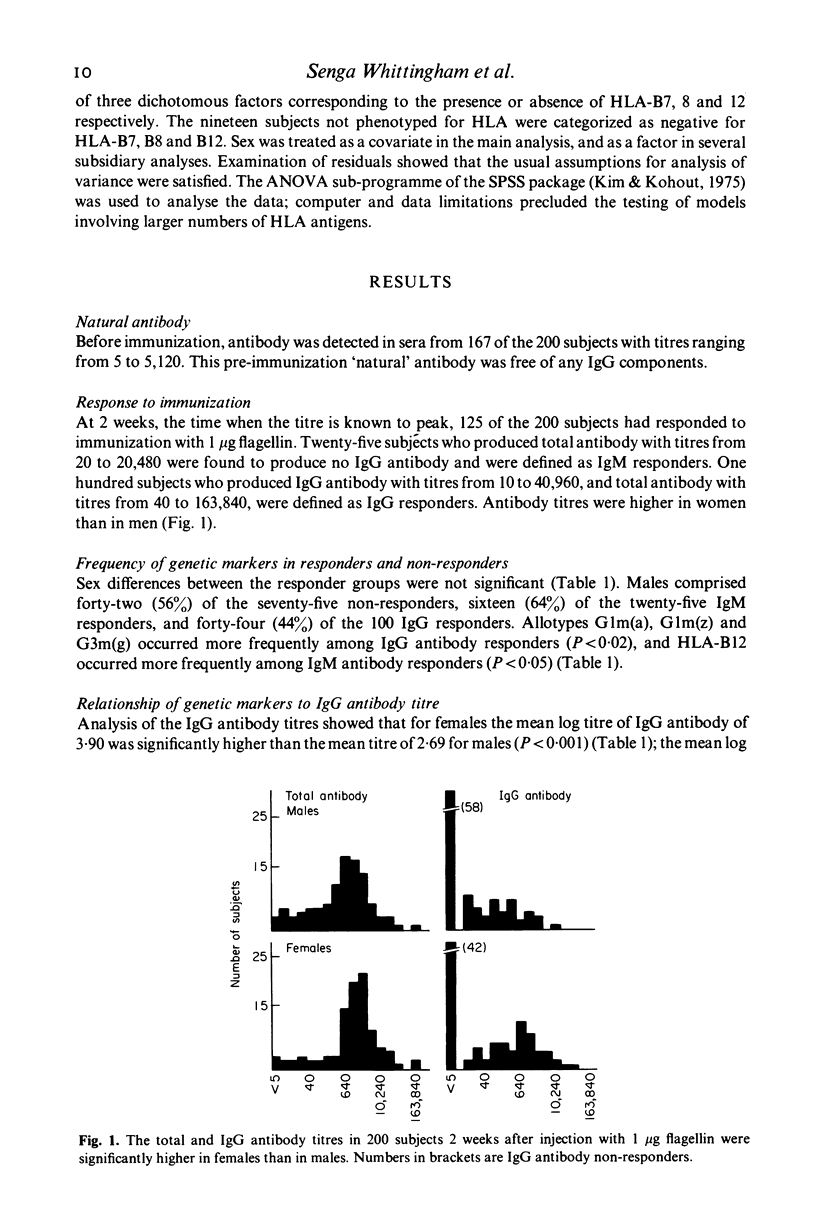
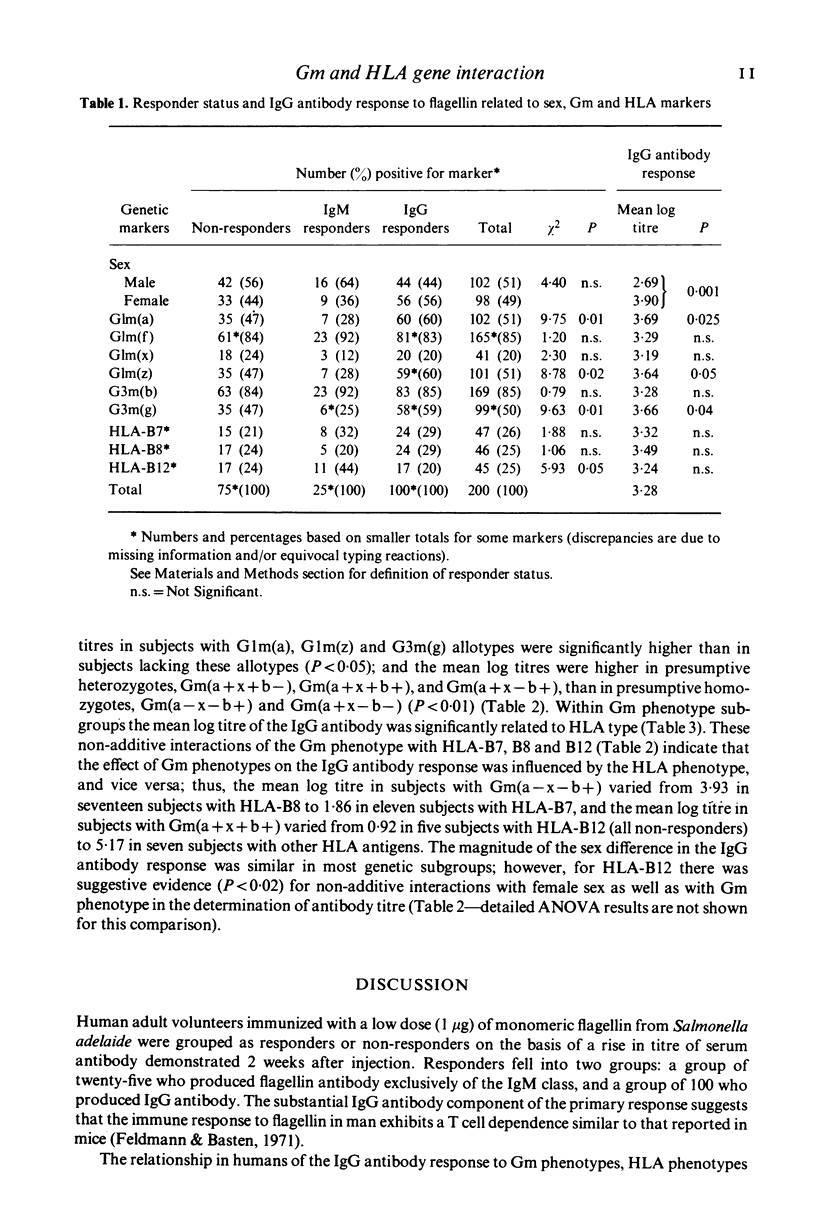
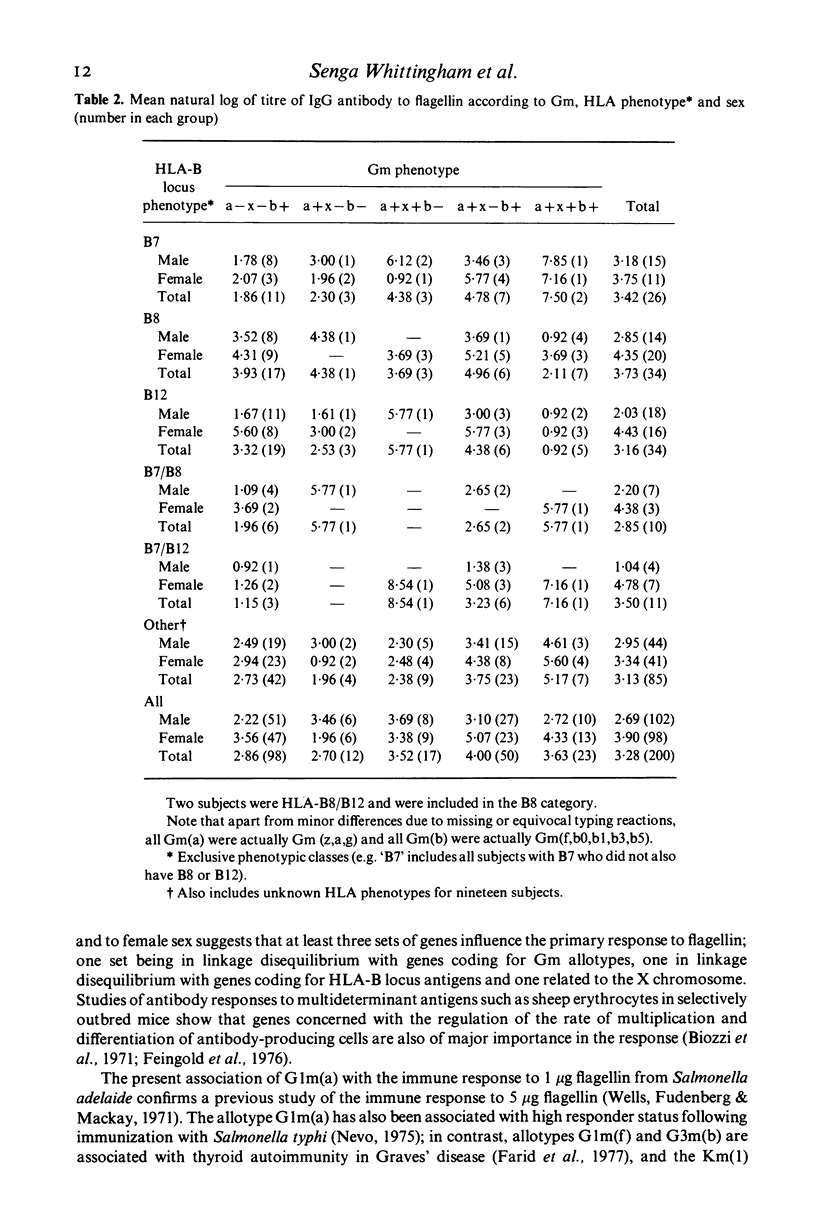
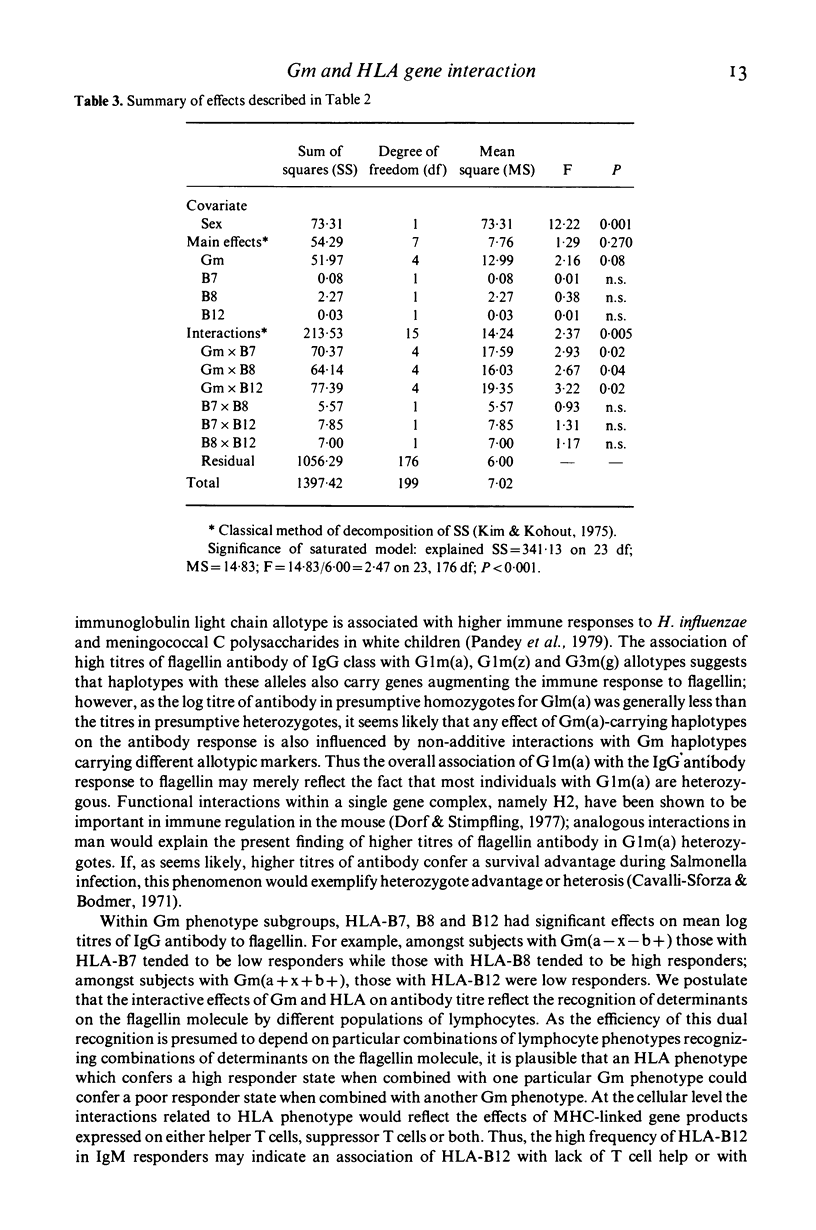
Two hundred healthy adults were immunized with 1 microgram of the bacterial antigen monomeric flagellin from Salmonella adelaide, and grouped as responders and non-responders on the basis of a rise in titre of antibody 2 weeks after immunization. Immunoglobulin allotypes G1m(a), G1m(z) and G3m(g) were more frequent among responders who made immunoglobulin (Ig)G antibody (P less than 0.02), and HLA-B12 was more frequent among responders who made IgM antibody (P less than 0.05). The mean log titre of IgG antibody was higher in females (P less than 0.001), in subjects with T1m(a), G1m(z) and G3m(g) allotypes (P less than 0.05), and in Gm heterozygotes (P less than 0.01). The mean log titre of the IgG antibody response in subjects with particular Gm phenotypes was also dependent on the HLA-B locus phenotypes HLA-B7, B8 and B12 (P less than 0.005); for example, among those with the phenotype Gm(a-x-b) subjects with HLA-B7 were low responders and those with HLA-B8 were high responders. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that there are immune response genes within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) which interact with Gm-linked genes in determining levels of serum antibodies of different isotypes and specificities.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J., ABBOT A. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. I. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF FLAGELLAR ANTIGENS FROM SALMONELLA ADELAIDE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:267–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsbaugh D. F., Hansen C. T., Prescott B., Stashak P. W., Barthold D. R., Baker P. J. Genetic control of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide in mice. I. Evidence that an X-linked gene plays a decisive role in determining responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):931–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H., Bazin H. T-cell idiotypes are linked to immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Nature. 1976 Dec 16;264(5587):639–642. doi: 10.1038/264639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B., Geckeler W. R., Weigert M. Genetics of the antibody response to dextran in mice. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorf M. E., Stimpfling J. H. Coupled complementation of immune response genes controlling responsiveness to the H-2.2 alloantigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):571–578. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K. Idiotypic identity of antibodies to streptococcal carbohydrate in inbred mice. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):301–307. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidinger D., Garrett T. J. Studies of the regulatory effects of the sex hormones on antibody formation and stem cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1098–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Newton R. M., Noel E. P., Marshall W. H. Gm phenotypes in autoimmune thyroid disease. J Immunogenet. 1977 Dec;4(6):429–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1977.tb00927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold N., Feingold J., Mouton D., Bouthillier Y., Stiffel C., Biozzi G. Polygenic regulation of antibody synthesis to sheep erythrocytes in the mouse: a genetic analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jan;6(1):43–51. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Easten A. The relationship between antigenic structure and the requirement for thymus-derived cells in the immune response. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):103–119. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Armerding D. The role of histocompatibility gene products in lymphocyte triggering and differentiation. Fed Proc. 1976 Jul;35(9):2053–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm L. U., Friedrich U., Petersen C. B., Jorgensen J., Nielsen J., Therkelsen A. J., Kissmeyer-Nielsen F. Assignment of the major histocompatibility complex to chromosome No. 6 in a family with a pericentric inversion. Hum Hered. 1974;24(3):273–284. doi: 10.1159/000152660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Fudenberg H. H., Virella G., Kyong C. U., Loadholt C. B., Galbraith R. M., Gotschlich E. C., Parke J. C., Jr Association between immunoglobulin allotypes and immune responses to Haemophilus influenzae and Meningococcus polysaccharides. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):190–192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak L. L., Nisonoff A. Distribution of a cross-reactive idiotypic specificity in inbred strains of mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):855–869. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley M. J., Mackay I. R. Measurement of antibody-producing capacity in man. I. The normal response to flagellin from Salmonella adelaide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Oct;5(4):407–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley M. J., Wistar R., Mackay I. R. Measurement of antibody-producing capacity in man. V. Immunoglobulin classes of antibodies to flagellin. Immunology. 1972 Mar;22(3):475–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Cohn M. Inheritance of an idiotype associated with the immune response of inbred mice to phosphorylcholine. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Aug;2(4):319–326. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Hirschhorn K. Location of the genes for human heavy chain immunoglobulin to chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3367–3371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting A., Morris P. J. A technique for lymphocyte preparation from stored heparinized blood. Vox Sang. 1971 Jun;20(6):561–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., May A. G., Johnston E. The linkage relationships of HL-A with other genetic marker systems. Hum Hered. 1975;25(5):337–345. doi: 10.1159/000152744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. V., Fudenberg H. H., MacKay I. R. RElation of the human antibody response to flagellin to GM genotype. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1505–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistar R., Jr Serum antibody to Salmonella flagellar antigens. I. Methods of antibody assay. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Dec;46(6):769–777. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeicher M., Mozes E., Lonai P. Lymphocytes alloantigens associated with X-chromosome-linked immune response genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):721–724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


