Abstract
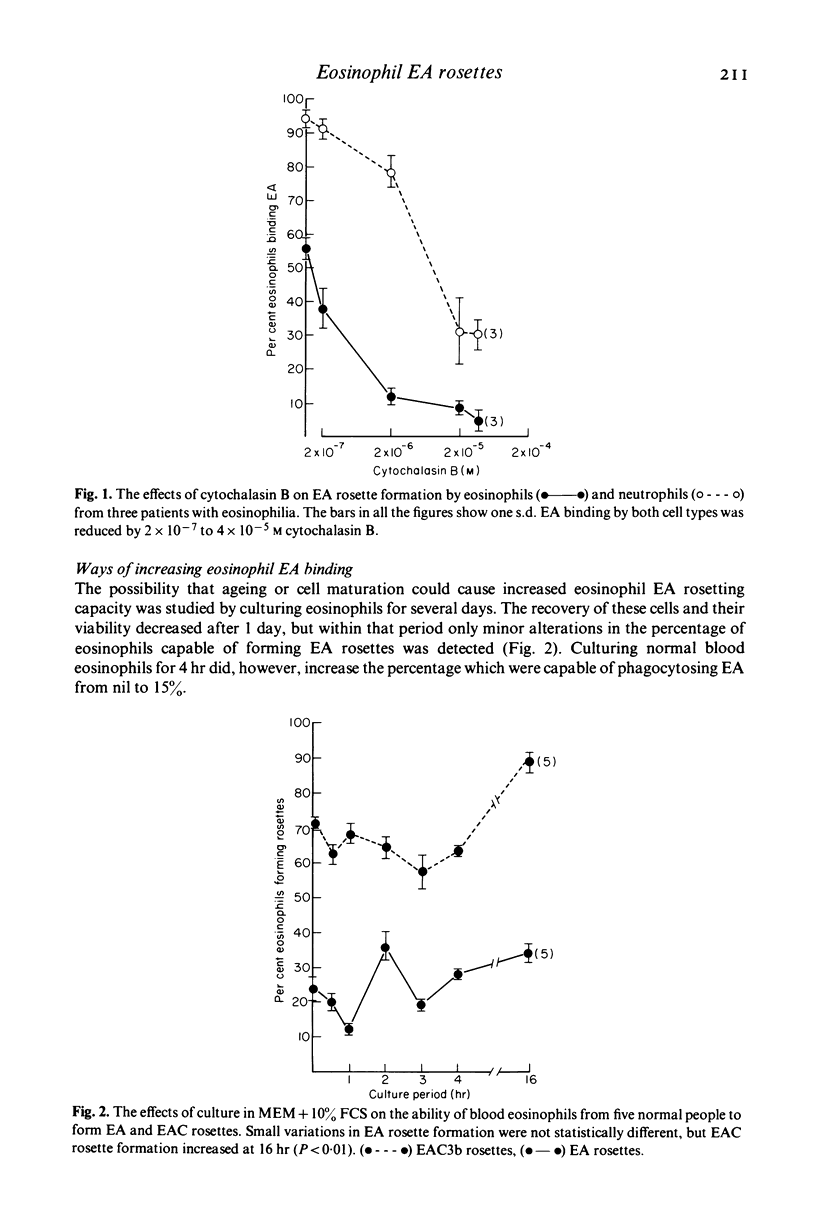
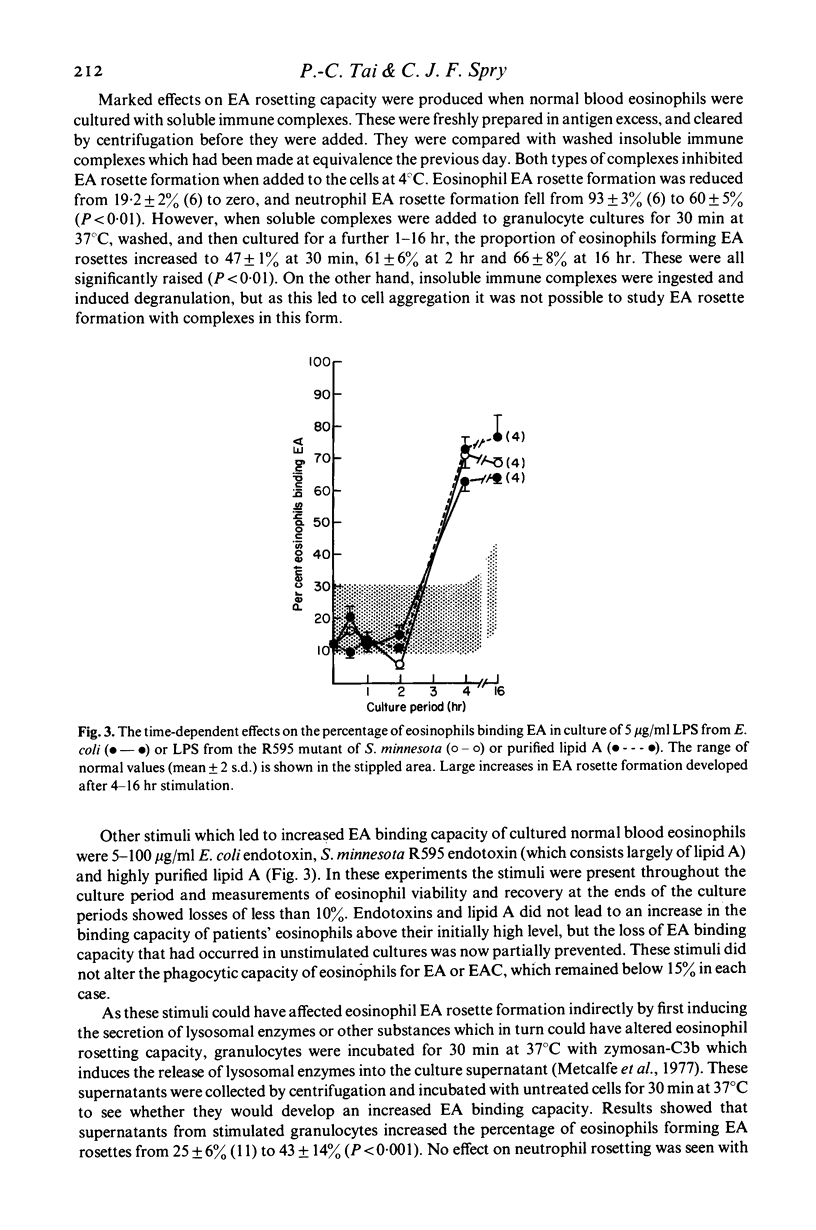
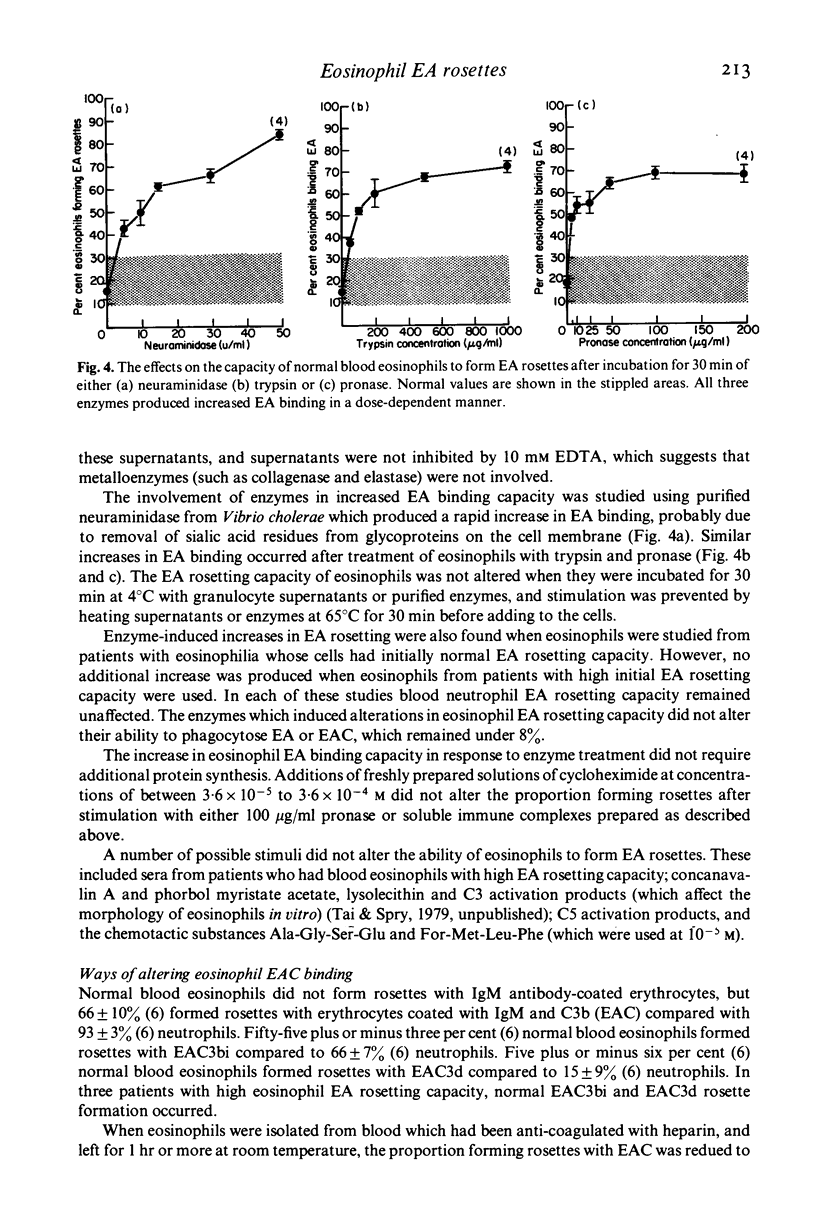
Blood eosinophils from some patients with an eosinophilia have a higher capacity to bind to IgC antibody-coated red cells (EA) than blood eosinophils from normal people. Twenty per cent of eosinophils from normal blood bound EA, whereas eight of nine patients with hypereosinophilic syndromes and all nine patients with filariasis who were studied had blood eosinophils with EA rosette-forming capacities of between 42 and 89%. High EA binding capacity was reduced in culture, and prednisolone and cytochalasins A and B inhibited normal blood eosinophil EA binding. Normal blood eosinophils developed small increases in EA binding capacity in culture, but marked increases occurred after stimulation with soluble immune complexes, endotoxins and lipid A. Supernatants from granulocytes cultured with zymosan-C3b caused rapid increases in eosinophils EA binding capacity which also occurred with neuraminidase, pronase and trypsin. In vitro alterations in EA rosetting did not require protein synthesis and did not affect eosinophil phagocytic capacity for EA. Substances in culture which did not affect eosinophil EA rosetting capacity included sera from patients with eosinophils with high EA binding capacity and chemotactic substances. Cultured eosinophils also developed an increased capacity to form rosettes with EAC3b, and soluble immune complexes stimulated this further. Conversely, blood eosinophils formed less C3b rosettes when separated from heparinized blood in which C3 activation had occurred. CytochalasinA (but not B) irreversibly inhibited eosinophils EAC3b rosette formation. Trypsin also inhibited, but this effect was reversed within 30 min after washing. It was concluded that eosinophils from normal blood have an intrinsically lwo capacity to bind EA, but that in vivo and in response to stimulation in vitro their ability to bind complexed IgG can approach that seen with blood neutrophils. It is suggested that enzymes in granulocyte secretion products may cause the membrane changes which lead to high eosinophils EA binding capacity. This increase, which can occur separately from alterations in EAC binding or phagocytic capacity, may enable eosinophils to take part more effectively in inflammatory reactions in tissues.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHER G. T., HIRSCH J. G. MOTION PICTURE STUDIES ON DEGRANULATION OF HORSE EOSINOPHILS DURING PHAGOCYTOSIS. J Exp Med. 1963 Aug 1;118:287–294. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander E. L., Titus J. A., Segal D. M. Quantitation of Fc receptors and surface immunoglobulin is affected by cell isolation procedures using plasmagel and ficoll-hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(3-4):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar A. R., Kay A. B. Membrane receptors for IgG and complement (C4, C3b and C3d) on human eosinophils and neutrophils and their relation to eosinophilia. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):976–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. The macrophage receptor for IgG: number and affinity of binding sites. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J. P., Michael J. M., Chaplin H., Jr, Parker C. W. Modulation of macrophage C3b receptor function by cytochalasin-sensitive structures. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1292–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J. P., Parker C. W. Cytochalasin binding to macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1978 Nov;41(1):103–121. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(78)80031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballow M., Cochrane C. G. Two anticomplementary factors in cobra venom: hemolysis of guinea pig erythrocytes by one of them. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett Foster D. E., Dorrington K. J., Painter R. H. Structure and function of immunoglobulin domains. VII. Studies on the structural requirements of human immunoglobulin G for granulocyte binding. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1952–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett E. G., Baker J. R., BAKER P. A., MYERS D. B. Comparison of collagenase activity in eosinophil and neutrophil fractions from rat peritoneal exudates. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Oct;54(5):459–465. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Coombs R. R., Gurner B. W., Wilson A. B. Receptors for antibody-opsonic adherence on the eosinophils of guinea pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(3):368–377. doi: 10.1159/000231610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E. The eosinophil and its role in immunity to helminth infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;77:127–168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66740-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK G. M., HEARD D. H., SEAMAN G. V. Sialic acids and the electrokinetic charge of the human erythrocyte. Nature. 1961 Jul 1;191:44–47. doi: 10.1038/191044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Munck A., Smith K. A. Glucocorticoids inhibit expression of Fc receptors on the human granulocytic cell line HL-60. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):338–339. doi: 10.1038/279338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R., Butterworth A. E., Remold H. G., David P. H., Houba V., Sturrock R. F. Antibody-dependent, eosinophil-mediated damage to 51Cr-labeled schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: effect of metabolic inhibitors and other agents which alter cell function. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2221–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. T., Estensen R., Quie P. G. Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):161–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T. Effects of cytochalasin B on the pinocytosis and degradation of proteins by macrophages [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Apr;7(2):362–364. doi: 10.1042/bst0070362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Prisco-de-Fuenmayor M. C. Fc receptors for human, rabbit and pig antibodies on human eosinophils from normal persons and patients with atopic dermatitis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;59(3):249–255. doi: 10.1159/000232267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. S., Goldberg R., Ward L. Increased circulating neutrophils with surface receptor activity for immunoglobulin G in polycythemia vera and myeloid metaplasia. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauert A. M., Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V. The mechansim of antibody-dependent, eosinophil-mediated damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro: a study by phase-contrast and electron microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1978 Dec;34:173–192. doi: 10.1242/jcs.34.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M. Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte lysosomes and immune tissue injury. Prog Allergy. 1976;20:301–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal A. S., Babiuk L. A. Induction, isolation and surface marker studies on bovine eosinophils. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Ross G. D., Good R. A., Siegal F. P. Surface markers of human eosinophils. Blood. 1976 Nov;48(5):755–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegert D. G. Neuraminidase- and trypsin-induced exposure to membrane receptors for IgG and IgM molecules on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Sep;29(3):457–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegert D. G. Phagocytic peripheral blood monocytes from rabbits and humans express membrane receptors specific for IgM molecules: evidence that incubation with neuraminidase exposes cryptic IgM (Fc) receptors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Mar;35(3):484–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Zanolari B., Schwartzman N. A., Hong S. R. Intracellular control of human neutrophil secretion. I. C5a-induced stimulus-specific desensitization and the effects of cytochalasin B. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herborn H. A., Valdimarsson H., Wickramasinghe S. N. Development of human granulocyte and monocyte Fc receptors. Scand J Haematol. 1979 Apr 4;22(4):364–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb00432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S., Soberman R., Goldstein I., Weissmann G. Concanavalin A induces microtubule assembly and specific granule discharge in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):781–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn D., Andreewa P., Rodt H., Thiel E., Eulitz M. Demonstration of the Fc-receptor of blood cells by soluble peroxidase-anti-peroxidase (PAP) complexes. Blut. 1978 May 18;36(5):263–273. doi: 10.1007/BF01880677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulliger L., Blazkovec A. A. A simple and efficient method of separating peripheral-blood leucocytes for in-vitro studies. Lancet. 1967 Jun 17;1(7503):1304–1305. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Wicher K., Arbesman C. E. In vitro and in vivo studies on uptake of antigen-antibody complexes by eosinophils. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;46(2):230–248. doi: 10.1159/000231126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Colley D. G. Eosinophil-mediated destruction of S. mansoni eggs IV. Effects of several inhibitory substances on eosinophil function. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jun;38(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Gallin J. I. Inhibition of neutrophil Fc receptor function by cotricosteroids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Oct;34(1):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempner M. S., Gallin J. I. Separation and functional characterization of human neutrophil subpopulations. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G., Niemetz A. H. Species specificity in the binding of IgG to macrophages. Immunology. 1979 Aug;37(4):835–840. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson N. R., Wong P. S., Travis J. Enzymatic inactivation of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor by neutrophil myeloperoxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):402–409. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeever P. E., Garvin A. J., Hardin D. H., Spicer S. S. Immune complex receptors on cell surfaces. II. Cytochemical evaluation of their abundance on different immune cells: distribution, uptake, and regeneration. Am J Pathol. 1976 Sep;84(3):437–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe D. D., Gadek J. E., Raphael G. D., Frank M. M., Kaplan A. P., Kaliner M. Human eosinophil adherence to serum-treated sepharose: granule-associated enzyme release and requirement for activation of the alternative complement pathway. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1744–1750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickenberg I. D., Root R. K., Wolff S. M. Bactericidal and metabolic properties of human eosinophils. Blood. 1972 Jan;39(1):67–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Olsson I. The extracellular release of granulocyte collagenase and elastase during phagocytosis and inflammatory processes. Scand J Haematol. 1977 Aug;19(2):145–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1977.tb02339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottesen E. A., Stanley A. M., Gelfand J. A., Gadek J. E., Frank M. M., Nash T. E., Cheever A. W. Immunoglobulin and complement receptors on human eosinophils and their role in cellular adherence to schistosomules. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):134–141. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. E., Folds J. D., Spitznagel J. K. Proteolysis of human IgG by human polymorphonuclear leucocyte elastase produces an Fc fragment with in vitro biological activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):162–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Atkinson J. P., Newball H. H., Frank M. M. Receptors for immunoglobulin and complement on human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1813–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. Macrophage heterogeneity in receptor activity: the activation of macrophage Fc receptor function in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):976–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D., Loos J. A. Changes in the carbohydrate metabolism of mitogenically stimulated human peripheral lymphocytes. I. Stimulation by phytohaemagglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 29;222(3):565–582. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spry C. J., Tai P. C. Studies on blood eosinophils. II. Patients with Löffler's cardiomyopathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):423–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Phagocytosis: recognition and ingestion. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jan;12(1):83–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Studies on blood eosinophils. I. Patients with a transient eosinophilia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):415–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Kaplan G., Plutner H., Cohn Z. A. Fc-receptor variants of a mouse macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1400–1404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Action of sphingomyelinase C and other lipid-specific agents as inhibitors of Fc binding and locomotion in human leucocytes. Immunology. 1977 Sep;33(3):407–412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Winfield J. B., Kunkel H. G. Immunofluorescent studies on antibodies directed to a buried membrane structure present in lymphocytes and erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):410–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


