Abstract
The technical details of a fixation procedure with formaldehyde which was applied in a direct membrane immunofluorescence technique to mononuclear cells from normal human blood are described. After separation of the cells with Ficoll--Isopaque according to Böyum (1963) they were washed and fixed with 0 . 04% formaldehyde in PBS for 10 min and washed again. This cell suspension can be stored at 4 degrees C for at least 24 hr and the slides prepared from them at -20 degrees C for at least some months. In practice, this fixation procedure not only appeared to be effective in the preservation of cells but also showed a number of additional advantages, such as the short handling period, including the fixation procedure and the avoidance of loss of cells. Moreover, true B lymphocytes, as defined by the synthesis of immunoglobulins and the incorporation of these molecules into their cell membrane, are recognized convincingly.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
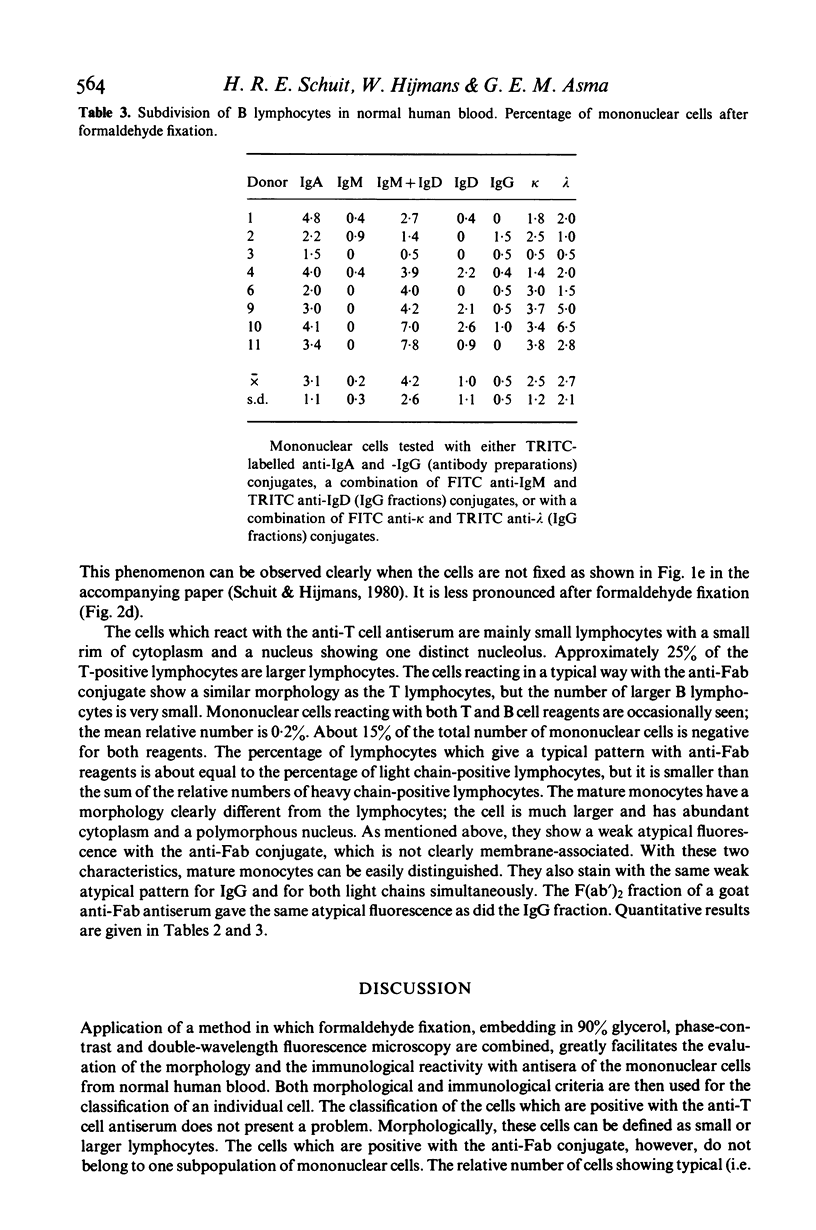
- Asma G. E., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The determination of numbers of T and B lymphocytes in the blood of children and adults by the direct immunofluorescence technique. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):286–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B. Identification of three different human lymphocyte populations by surface markers. Transplant Rev. 1973;16:114–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathings W. E., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Immunofluorescent studies of the development of pre-B cells, B lymphocytes and immunoglobulin isotype diversity in humans. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Nov;7(11):804–810. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Klein F. An immunofluorescence procedure for the detection of intracellular immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):457–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Lobo P. I. Characterizaiton of two populations of human lymphocytes bearing easily detectable surface immunoglobulin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1464–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI108227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Identification, enumeration, and isolation of B and T lymphocytes from human peripheral blood. Report of a WHO-IARC-sponsored workshop on human B and T cells, London, 15-17 July 1974. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(5):521–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamelin J. P., Thomasset N., Andre C., Brochier J., Revillard J. P. Study of human T and B lymphocytes with heterologous antisera. III. Immunofluorescence studies on tonsil sections. Immunology. 1978 Sep;35(3):463–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Horwitz D. A. An appraisal of Fc receptors on human peripheral blood B and L lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):939–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Westervelt F. B., Horwitz D. A. Identification of two populations of immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes in man. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):116–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploem J. S. The use of a vertical illuminator with interchangeable dichroic mirrors for fluorescence microscopy with incidental light. Z Wiss Mikrosk. 1967 Nov;68(3):129–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Flandrin G. Identification by peroxidase staining of monocytes in surface immunofluorescence tests. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1650–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbarth P. H., Hendriks-Sturkenboom I., Ploem J. S. Identification of monocytes in suspensions of mononuclear cells. Blood. 1976 Jul;48(1):139–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. Identification of mononuclear cells in human blood. II. Evaluation of morphological and immunological aspects of native and formaldehyde-fixed cell populations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):567–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessière-Louveaux F. M., Hijmans W., Schuit H. R. Presence of multiple isotypes on the surface of human tonsillar lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):186–191. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The percentage of monocytes among "mononuclear" cell fractions obtained from normal human blood. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]