Abstract
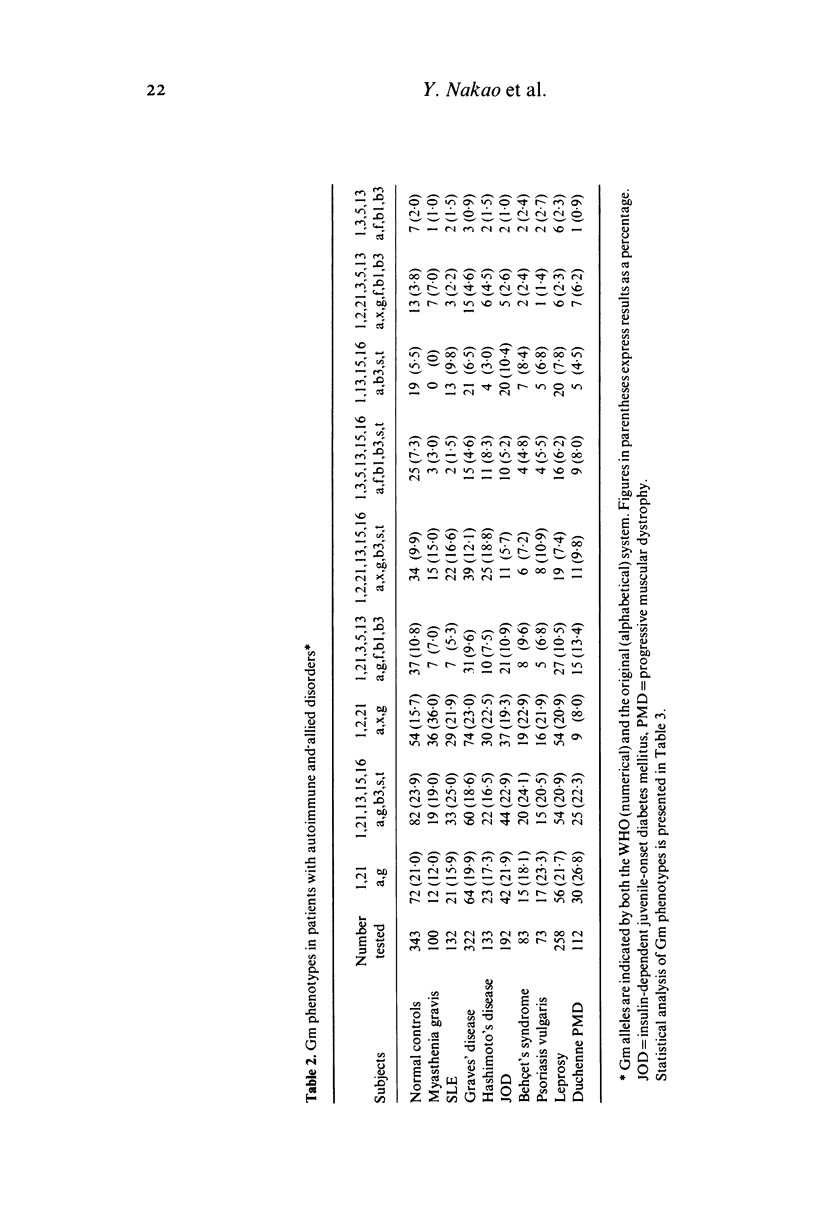
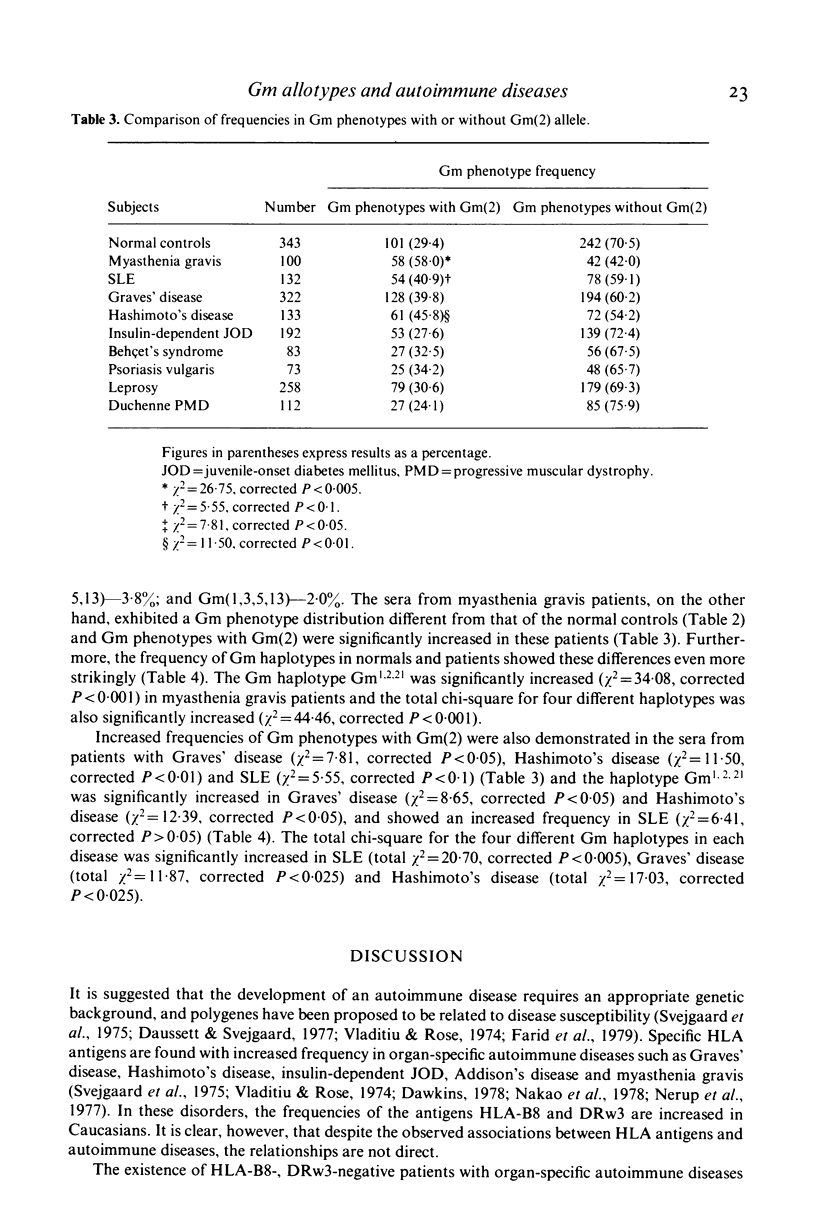
Serum samples from 100 patients with myasthenia gravis, 322 with Graves' disease, 113 with Hashimoto's disease, 132 with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 192 with insulin-dependent juvenile diabetes mellitus, 83 with Behçet's syndrome, 73 with psoriasis vulgaris, 258 with leprosy, 112 with Duchenne progressive muscular dystrophy and 343 non-related normal controls were studied for Gm allotypes. The incidence of Gm phenotypes with Gm(2) was significantly increased in patients with myasthenia gravis. Graves' disease, Hashimoto's disease, and high in SLE patients. The Gm1,2,21 haplotype was increased in patients with myasthenia gravis (chi 2 = 34 . 08, corrected P less than 0 . 001), Hashimoto's disease (chi 2 = 12 . 39, corrected P less than 0 . 05), Graves' disease (chi 2 = 8 . 65, corrected P less than 0 . 05), and SLE (chi 2 = 6 . 41, 0 . 1 greater than corrected P greater than 0 . 05). The total chi-square for the four different Gm haplotypes was significantly increased in patients with myasthenia gravis (chi 2 = 44 . 46, corrected P less than 0 . 001), SLE (chi 2 = 20 . 70, corrected P less than 0 . 005), Hashimoto's disease (chi 2 = 17 . 03, corrected P less than 0 . 025), and Graves' disease (chi 2 = 11 . 87, corrected P less than 0 . 025). Our data suggest the presence of Gm-associated pathogenic polygenes in certain autoimmune disorders.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender K., Müller C. R., Schmidt A., Strohmaier U., Wienker T. F. Linkage studies on the human Pi, Gm, GLO, and HLA genes. Hum Genet. 1979 Jun 19;49(2):159–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00277637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B., Geckeler W. R., Weigert M. Genetics of the antibody response to dextran in mice. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Shander M., Martinis J., Cicurel L., D'Ancona G. G., Dolby T. W., Koprowski H. Chromosomal location of the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3416–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Shen F. W., Cantor H., Gershon R. K. Genetic control of immunoregulatory circuits. Genes linked to the Ig locus govern communication between regulatory T-cell sets. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):44–50. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Newton R. M., Noel E. P., Marshall W. H. Gm phenotypes in autoimmune thyroid disease. J Immunogenet. 1977 Dec;4(6):429–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1977.tb00927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Sampson L., Noel E. P., Barnard J. M., Mandeville R., Larsen B., Marshall W. H., Carter N. D. A study of human leukocyte D locus related antigens in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):108–113. doi: 10.1172/JCI109263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HLA antigens in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Apr;138(4):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurczynski T. W., Steinberg A. G. A general program for maximum likelihood estimation of gene frequencies. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 Mar;19(2):178–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm L. U., Thorsen I. L., Petersen G. B., Jorgensen J., Henningsen K., Bech B., Kissmeyer-Nielsen F. Data on the HL-A linkage group. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 May;38(4):383–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Potter M., Humphrey W., Jr, Chien C. C. Idiotype of inulin-binding antibodies and myeloma proteins controlled by genes linked to the allotype locus of the mouse. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2105–2111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Takatsuki K., Matsunaga E. Gm factors in Japan: population and family studies. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1968 Jul;13(1):10–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Scherz R., Käser H., Skvaril F. Evidence for an association between uncommon Gm phenotypes and neuroblastoma. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):23–24. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91657-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao Y., Matsumoto H., Miyazaki T., Nishitani H., Ota K., Fujita T., Tsuji K. Gm allotypes in myasthenia gravis. Lancet. 1980 Mar 29;1(8170):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Asanuma T., Sugiura S., Wakisaka A., Aizawa M., Itakura K. HLA-Bw51 and Behçet's disease. JAMA. 1978 Aug 11;240(6):529–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okimoto K., Juji T., Ishiba S., Maruyama H., Tohyama H., Kosaka K. HLA--Bw54 (Bw22-J, J-1) antigen in juvenile onset diabetes mellitus in Japan. Tissue Antigens. 1978 May;11(5):418–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Fudenberg H. H., Virella G., Kyong C. U., Loadholt C. B., Galbraith R. M., Gotschlich E. C., Parke J. C., Jr Association between immunoglobulin allotypes and immune responses to Haemophilus influenzae and Meningococcus polysaccharides. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):190–192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisetsky D. S., Riordan S. E., Sachs D. H. Genetic control of the immune response to staphylococcal nuclease. IX. Recombination between genes determining BALB/c antinuclease idiotypes and the heavy chain allotype locus. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):842–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B., Hertel-Wulff B., Kimura A. Alloantigen-specific idiotype-bearing receptors on mouse T lymphocytes. I. Specificity characterization and genetic association with the heavy-chain IgG allotype. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):307–321. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., David C. S. The H-2 major histocompatibility complex and the I immune response region: genetic variation, function, and organization. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:125–195. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Hirschhorn K. Location of the genes for human heavy chain immunoglobulin to chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3367–3371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao B., Ahmed A., Paul W. E., Scher I., Lieberman R., Mosier D. E. Lyb-7, a new B cell alloantigen controlled by genes linked to the IgCH locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2279–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M. HL-A and disease associations--a survey. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:3–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. V., Fudenberg H. H., MacKay I. R. RElation of the human antibody response to flagellin to GM genotype. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1505–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Seligmann M., Hong R., Good R., Kunkel H. G. Imbalances of gamma globulin subgroups and gene defects in patients with primary hypogammaglobulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):1957–1966. doi: 10.1172/JCI106415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


