Abstract
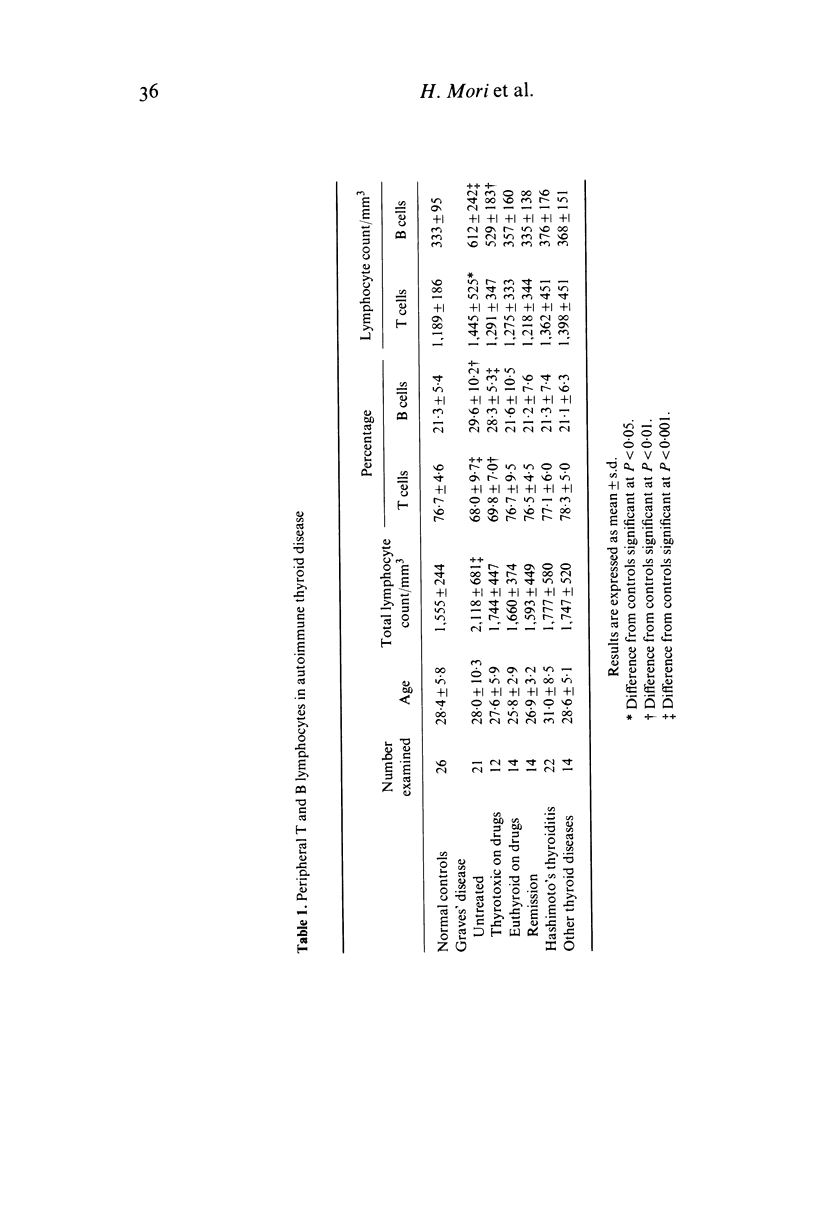
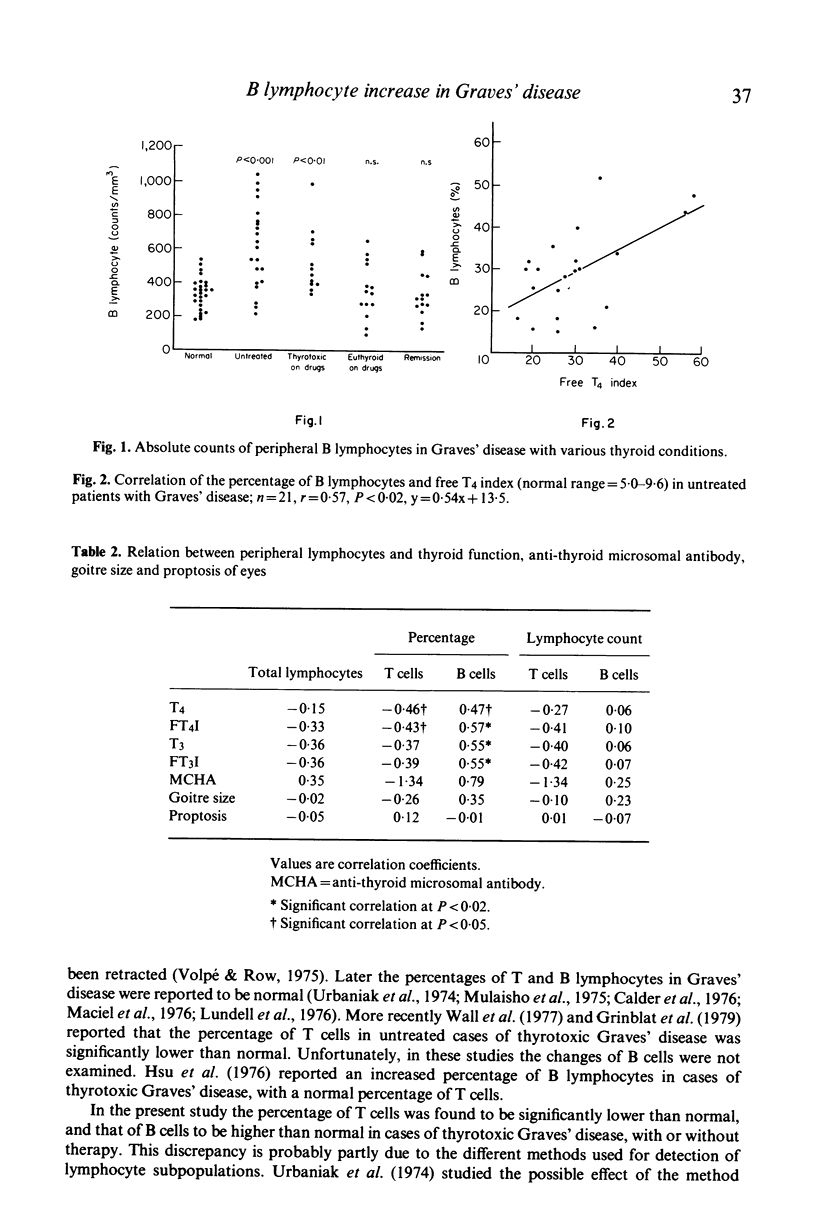
Peripheral T and B lymphocytes were examined in autoimmune thyroid diseases. The percentages of T and B lymphocytes were calculated from the proportions of E and EAC rosette-forming cells and peroxidase-positive cells determined by micromethods. In thyrotoxic Graves' disease, the percentage of T cells was significantly lower, and the percentage of B cells was higher than in normal controls. The absolute count of B lymphocytes was also markedly increased. The serum levels of thyroid hormones showed a significant correlation with the percentage of B cells and an inverse correlation with that of T cells in untreated cases of Graves' disease. Similar abnormalities of lymphocyte subpopulations were observed in patients with thyrotoxic Graves' disease under drug therapy, but the proportions and absolute counts of T and B lymphocytes were normal in euthyroid patients with Graves' disease, either under drug therapy or in remission. No abnormalities in T and B cells were found in Hashimoto's disease. The data indicate that the main feature of the abnormality of the lymphocyte subpopulations in thyrotoxic Graves' disease is an increase of B lymphocytes. The reasons for the discrepancy between our results and those of earlier reports and for the B cell abnormality in Graves' disease are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. Self-tolerance and autoimmunity in the thyroid. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 7;295(15):821–827. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610072951508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amino N., DeGroot L. J. Concentration of cultured medium to detect small amounts of lymphotoxin induced by PHA, PPD, and thyroid antigens. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):188–197. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amino N., Degroot L. J. Insoluble particulate antigen(s) in cell-mediated immunity of autoimmune thyroid disease. Metabolism. 1975 Jan;24(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amino N., Hagen S. R., Yamada N., Refetoff S. Measurement of circulating thyroid microsomal antibodies by the tanned red cell haemagglutination technique: its usefulness in the diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976 Mar;5(2):115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb02822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amino N., Kuro R., Tanizawa O., Tanaka F., Hayashi C., Kotani K., Kawashima M., Miyai K., Kumahara Y. Changes of serum anti-thyroid antibodies during and after pregnancy in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):30–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amino N., Yabu Y., Miyai K., Fujie T., Azukizawa M., Onishi T., Kumahara Y. Differentiation of thyrotoxicosis induced by thyroid destruction from Graves' disease. Lancet. 1978 Aug 12;2(8085):344–346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92943-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Wakisaka G., Nagata I. Increase of T cells in Graves' disease. Lancet. 1973 Jul 7;2(7819):49–50. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91993-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Irvine W. J., Davidson N. M., Wu F. T, B and K cells in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. The effect of thyroid antigens on the in vitro migration of leucocytes from patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):429–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Penhale W. J., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):153–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Duchateau J., Collet H., Govaerts A., Bastenie P. A. Lymphocyte transformation with thyroglobulin in thyroid diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):439–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F., Russell R. C. Goitrous autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's disease). Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;8(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(79)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Munro R. E., Row V. V., Volpé R. Peripheral thymus-dependent (T) lymphocytes in Graves's disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 21;288(25):1313–1317. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306212882502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folb P. I., Bank H. Evidence for an active immune response in acute hyperthyroidism (Graves' disease). Am J Med Sci. 1976 Nov-Dec;272(3):269–276. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197611000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. F., Hellman L., Finkelstein J., Yoshida K., Weitzman E. D., Roffwarg H. D., Fukushima D. K. Hyperthyroidism and cortisol secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jun;34(6):919–927. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-6-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinblat J., Shohat B., Lewitus Z., Joshua H. Quantitative and functional assessment of peripheral T-lymphocytes in thyroid diseases. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Jan;90(1):52–61. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0900052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. C., Chen Y., Patterson R. Peripheral blood B-lymphocyte abnormalities associated with hyperthyroidism of Graves' disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):431–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., Wu F. C., Urbaniak S. J., Toolis F. Peripheral blood leucocytes in thyrotoxicosis (Graves' disease) as studied by conventional light microscopy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Feb;27(2):216–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamki L., Row V. V., Volpé R. Cell-mediated immunity in Graves' disease and in Hashimoto's thyroiditis as shown by the demonstration of migration inhibition factor (MIF). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):358–364. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell G., Wasserman J., Granberg P. O., Blomgren H. Lymphocyte populations in peripheral blood in hyperthyroid and euthyroid subjects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jan;23(1):33–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciel R. M., Miki S. S., Nicolau W., Mendes N. F. Peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes, in vitro stimulation with phytohemagglutinin, and sensitization with 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in Grave's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):583–587. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulaisho C., Abdou N. I., Utiger R. D. Lack of T-cell immune abnormalities in peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with Graves' disease or hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Aug;41(2):266–270. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podleski W. K. Cytotoxic lymphocytes in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):543–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana T., Ishikawa M. A new micro-method for quantitation of human T- and B-lymphocytes. Jpn J Exp Med. 1973 Jun;43(3):227–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman T. H. Distribution of T-, B-, and thyroglobulin-binding lymphocytes infiltrating the gland in Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and de Quervain's thyroiditis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jul;10(3):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman T. H., Mäenpä J., Gordin A., Mäkinen T., Taskinens E., Andersson L. C., Häyry P. Blood and thyroid-infiltrating lymphocyte subclasses in juvenile autoimmune thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaniak S. J., Penhale W. J., Irvine W. J. Circulating lymphocyte subpopulations in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Nov;15(3):345–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaniak S. J., Penhale W. J., Irvine W. J. Peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes in patients with thyrotoxicosis and Hashimoto's thyroiditis and in normal subjects. A comparison of lymphocyte separation methods. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Dec;18(4):449–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpé R., Row V. V. Letter: Proportion of E rosettes normal in Graves's and Hashimoto's disease: a retraction. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 3;293(1):44–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507032930115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpé R. The role of autoimmunity in hypoendocrine and hyperendocrine function: with special emphasis on autoimmune thyroid disease. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jul;87(1):86–99. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. R., Gray B., Greenwoood D. M. Total and "activated" peripheral blood T lymphocytes in patients with thyroid disorders. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1977 Aug;85(4):753–759. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0850753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartenberg J., Doniach D., Brostoff J., Roitt I. M. Leucocyte migration inhibition in thyroid disease. Effect of human thyroid microsomes and thyroglobulin. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(3):396–408. doi: 10.1159/000230947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Fudenberg H. H. Thymus-derived rosette-forming cells. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 17;288(20):1072–1073. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305172882011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Clements P. J., Paulus H. E., Peter J. B., Levy J., Barnett E. V. Human lymphocyte subpopulations. Effect of corticosteroids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):565–571. doi: 10.1172/JCI107591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


