Abstract
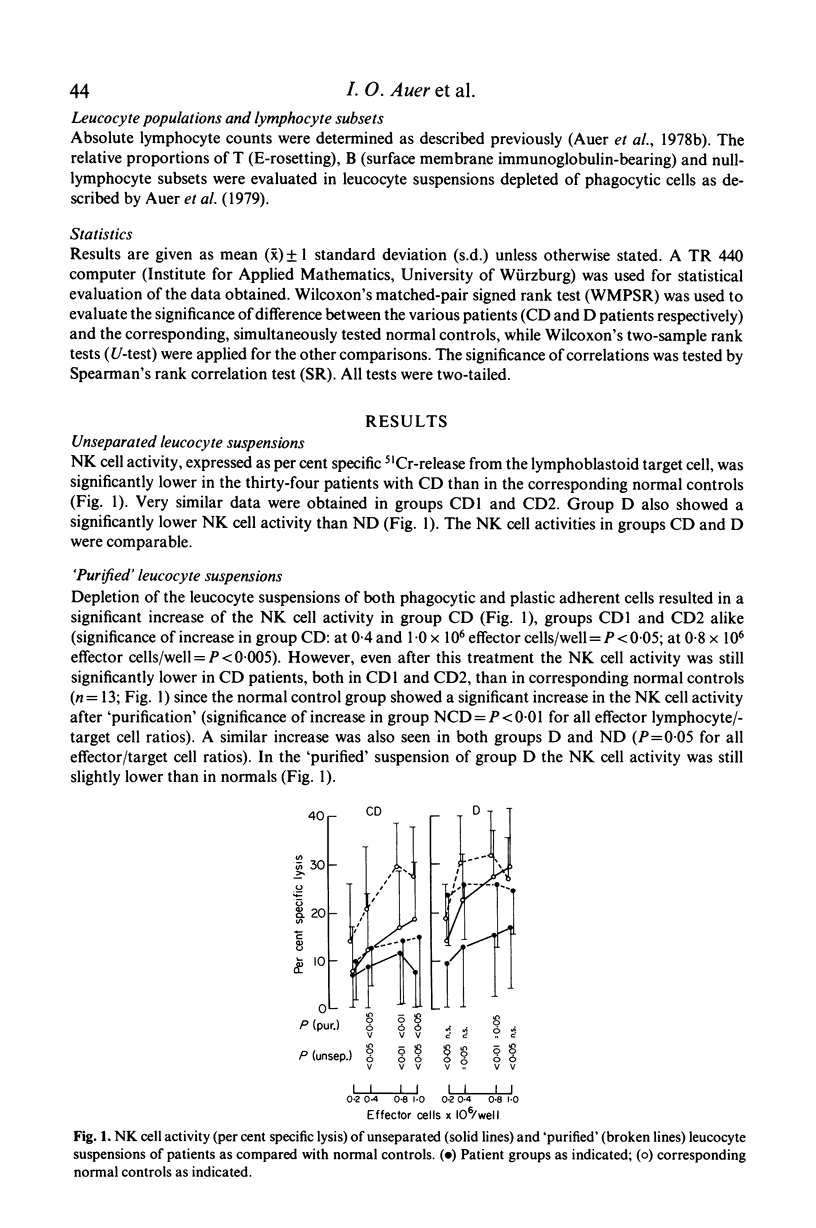
To identify and measure the spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity of natural killer cells, we used the lysis of an established lymphoblastoid cell line as target in a 4-hr 51Cr-release assay. Mononuclear cell suspensions of the peripheral blood of thirty-four patients with Crohn's disease (group CD), eleven patients with inflammatory bowel disease other than CD or ulcerative colitis (group D) and forty-five healthy subjects matched for both age and sex with the patients were studied. Depletion of phagocytic, plastic-adherent cells ('purified suspensions') led to a significant increase of the natural killer cell activity as compared with unseparated suspensions. This was seen to occur in all groups. In CD patients the natural killer cell activity was significantly below normal levels in both unseparated and 'purified' suspensions. This was independent of disease duration. In 'purified' suspensions the natural killer cell activity was inversely related to the disease activity. In group D the natural cytotoxicity was significantly lower in unseparated suspensions than that in healthy controls. In 'purified' suspensions it was still slightly lower than in healthy controls.
Full text
PDF


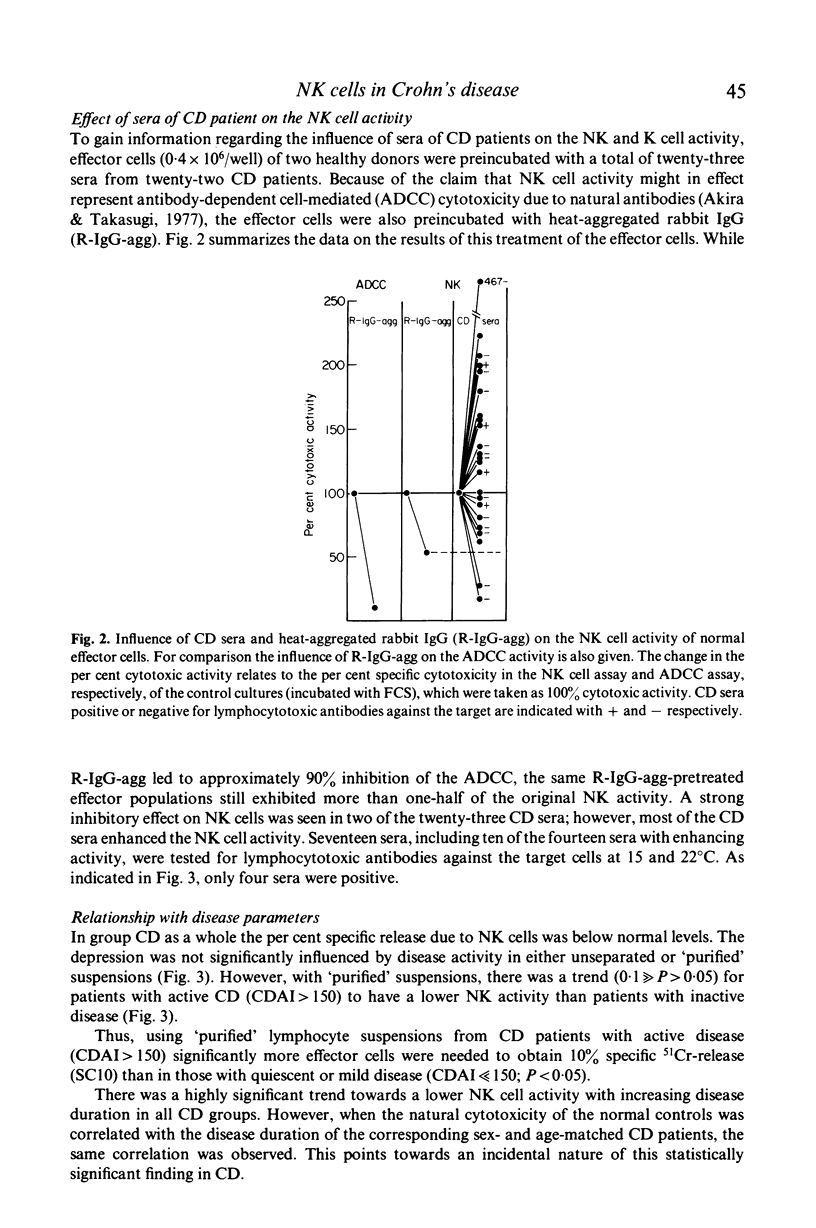



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira D., Takasugi M. Loss of specific natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity with absorption of natural antibodies from serum. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jun 15;19(6):747–755. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
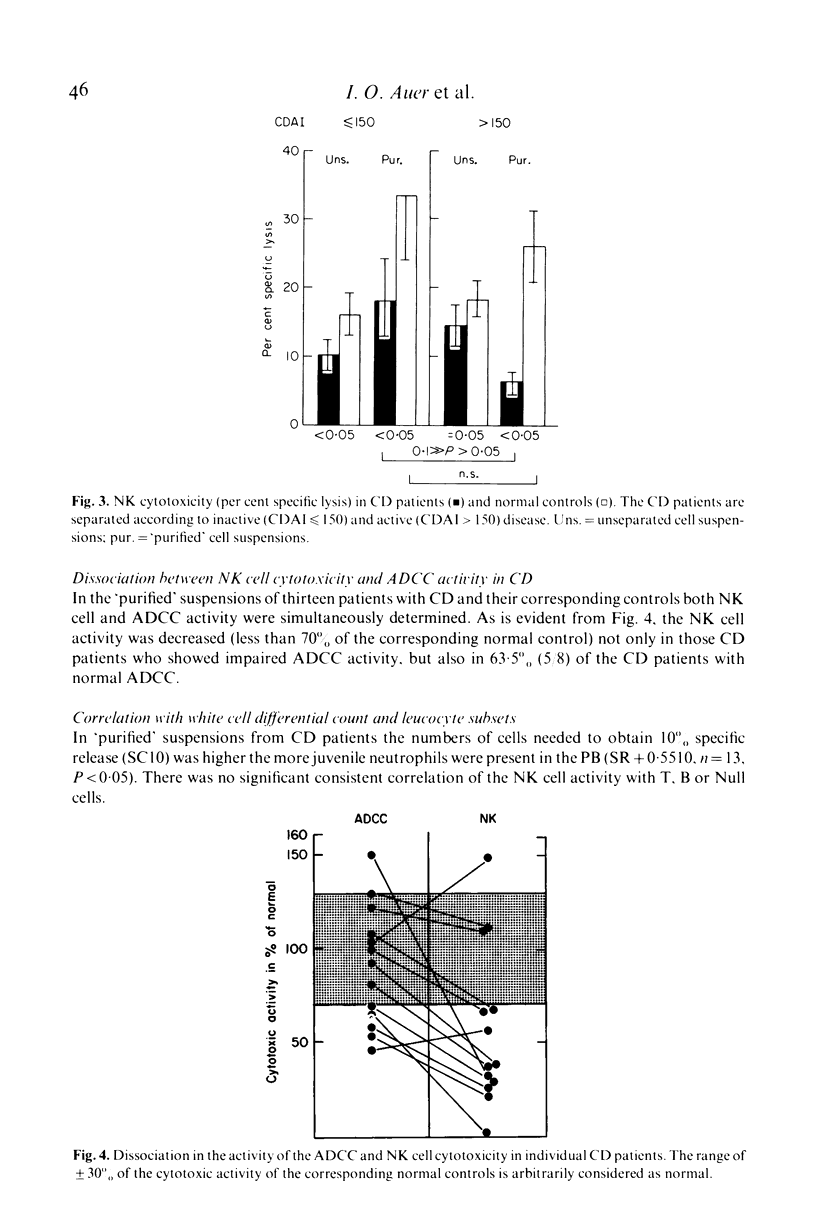
- Arnaud-Battandier F., Bundy B. M., O'Neill M., Bienenstock J., Nelson D. L. Cytotoxic activities of gut mucosal lymphoid cells in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Buschmann C., Ziemer E. Immune status in Crohn's disease. 2. Originally unimpaired primary cell mediated immunity in vitro. Gut. 1978 Jul;19(7):618–626. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.7.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Götz S., Ziemer E., Malchow H., Ehms H. Immune status in Crohn's disease. 3. Peripheral blood B lymphocytes, enumerated by means of F(ab)2-antibody fragments, Null and T lymphocytes. Gut. 1979 Apr;20(4):261–268. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Wechsler W., Ziemer E., Malchow H., Sommer H. Immune status in Crohn's disease. I. Leukocyte and lymphocyte subpopulations in peripheral blood. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(5):561–571. doi: 10.3109/00365527809181765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Ziemer E. Immune status in Crohn's disease. 4. In vitro antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity in peripheral blood. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Aug 1;58(15):779–787. doi: 10.1007/BF01478286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B. Studies of the human lymphocyte receptor for heat-aggregated or antigen-complexed immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):508–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickmeiss E., Nielsen L. S. Antibody-dependent lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in an allogeneic human system. II. Evidence for HL-A specificity. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(2):199–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droller M. J., Schneider M. U., Perlmann P. A possible role of prostaglandins in the inhibition of natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eremin O., Coombs R. R., Plumb D., Ashby J. Characterization of the human natural killer (NK) cell in blood and lymphoid organs. Int J Cancer. 1978 Jan 15;21(1):42–50. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding J. F., Prior P., Waterhouse J. A., Cooke W. T. Malignancy in Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(1):3–7. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitnick G. L., Arthur M. H., Shibata I. Cultivation of viral agents from Crohn's disease. A new sensitive system. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):215–217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey P., Edwards A., Edwards J., Adams E., Milton G. W., Nelson D. S. Specificity of cell-mediated cytotoxicity against human melanoma lines: evidence for "non-specific" killing by activated T-cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jul 15;16(1):173–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Spine C., Targan S. Human spontaneous killer cells selective for tumour-derived target cells. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):62–64. doi: 10.1038/272062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Hutt L. M., Huang Y. T. Cytotoxicity of circulating leukocytes in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Nov;8(3):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbour P. A., Bloom B. R. Absence of virus-induced lymphocyte suppression and interferon production in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):476–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Zmijewski C. M., Koprowski H. HLA-related control of spontaneous and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity in humans. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):765–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Reactivity of lymphocytes from normal persons on cultured tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2898–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Ramseyer A., Takasugi J. Decline of natural nonselective cell-mediated cytotoxicity in patients with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1977 Feb;37(2):413–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolentino P., Dianzani F., Zucca M., Giacchino R. Decreased interferon response by lymphocytes from children with chronic hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):459–461. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., De Marchi M., Mayr W., Savi M., Ceppellini R. Lymphocyte antibody lymphocytolytic interaction (LALI) with special emphasis on HL-A. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1631–1649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Santoli D. Anti-viral activity induced by culturing lymphocytes with tumor-derived or virus-transformed cells. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by interferon and antagonistic inhibition of susceptibility of target cells to lysis. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1314–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weedon D. D., Shorter R. G., Ilstrup D. M., Huizenga K. A., Taylor W. F. Crohn's disease and cancer. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 22;289(21):1099–1103. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311222892101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Cannon G. B., Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes against a myeloid cell line: characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorwell P. J., Phillips C. A., Beeken W. L., Little P. K., Roessner K. D. Isolation of reovirus-like agents from patients with Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1977 Jun 4;1(8023):1169–1171. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92714-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Nowinski R. C., Bach F. H. Lysis of leukemia cells by spleen cells of normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2780–2784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries J. E., Cornain S., Rumke P. Cytotoxity of non-T versus T-lymphocytes from melanoma patients and healthy donors on short- and long-term cultured melanoma cells,. Int J Cancer. 1974 Oct 15;14(4):427–434. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


