Abstract
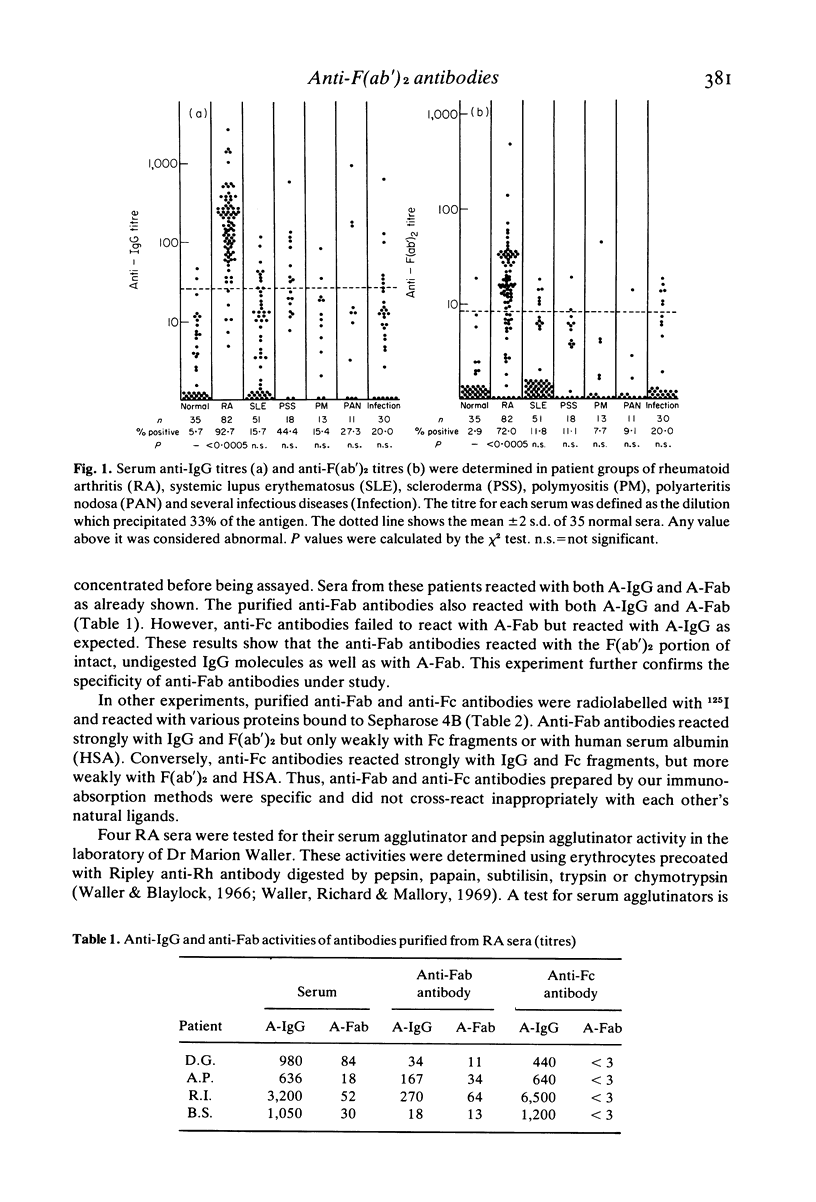
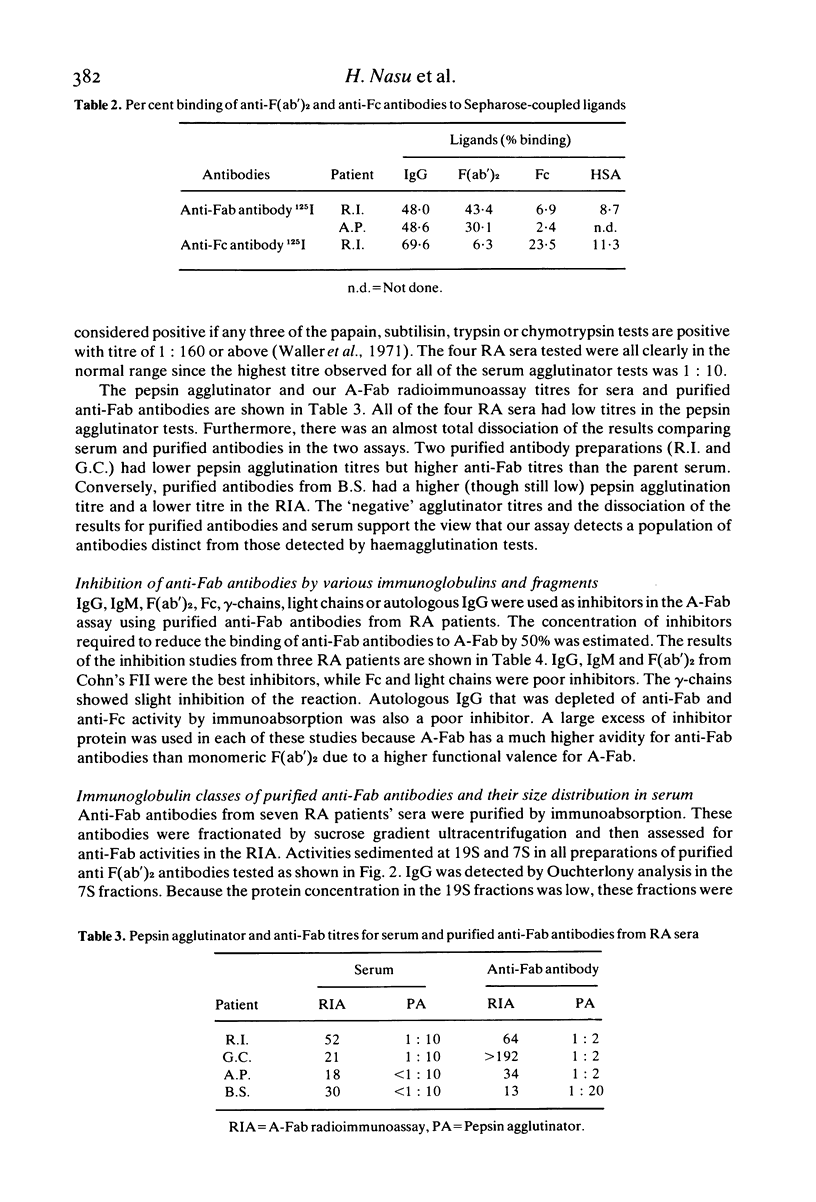
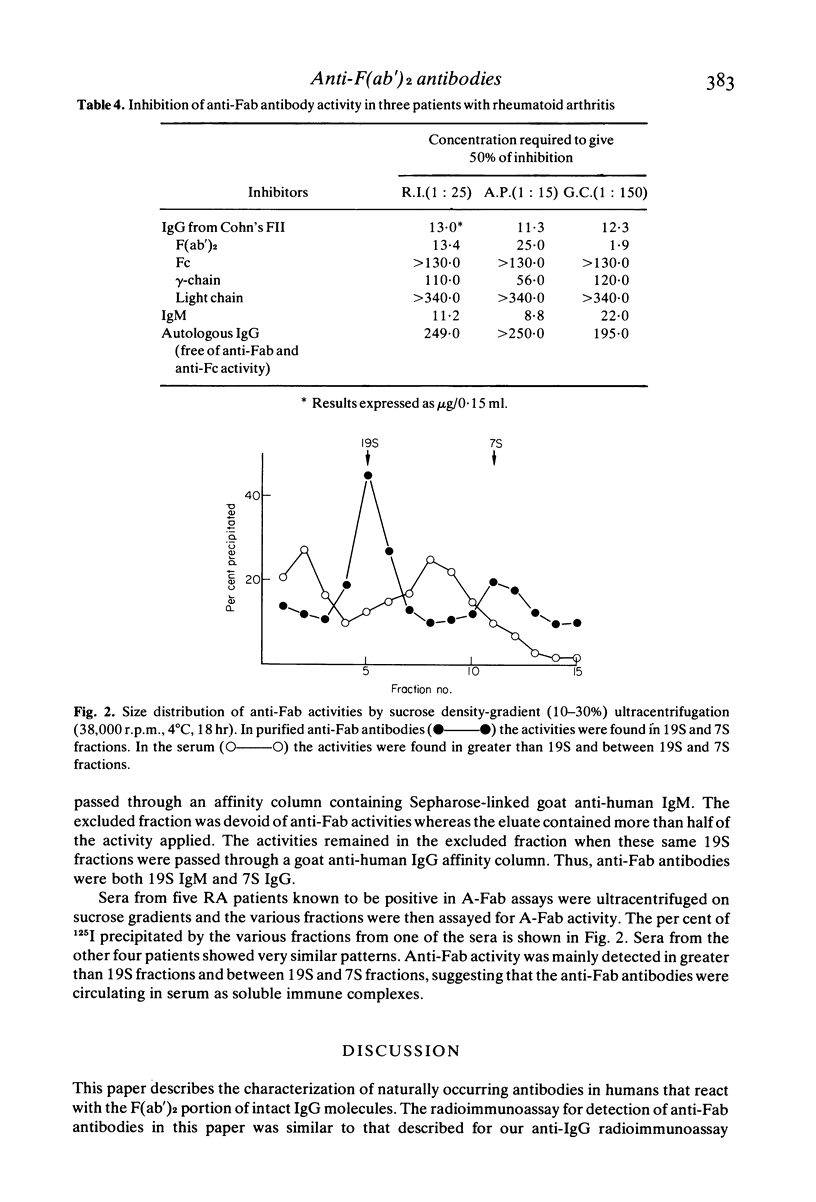
Antibodies to the F(ab')2 portion of IgG were detected in the sera of patients and normals using a heat-aggregated F(ab')2 fragment in a liquid-phase radioimmunoassay. The antibodies were found in 72% of 82 rheumatoid arthritis patients, in less than 20% of patients with other diseases and in a few normal subjects. Anti-F(ab')2 antibodies were distinct from previously described anti-Fc antibodies and 'serum agglutinators'. They reacted with intact IgG, F(ab')2 and IgM in binding and inhibition assays and they appeared to have specificity for the Fd portion of IgG molecules, possibly to the VH region. The anti-F(ab')2 antibodies were of both 7S IgG and 19S IgM classes and were found in sera as components of intermediate size (between 7S and 19S) and large size (greater than 19S) immune complexes. The possible contribution of autologous anti-F(ab')2 to abnormal immunoregulation is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brazier D. M., Goldsmith K. L., Gunson H. H., van Loghem E. The first human example of anti-Gm(17): Gm(z). Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):558–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Hypervariable regions, idiotypy, and the antibody-combining site. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosenza H., Köhler H. Specific inhibition of plaque formation to phosphorylcholine by antibody against antibody. Science. 1972 Jun 2;176(4038):1027–1029. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4038.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosenza H., Köhler H. Specific suppression of the antibody response by antibodies to receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAN J. B., PAIN R. H., PORTER R. R. Reduction of gamma-globulins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C. Structural units of human 7S gamma globulin. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1933–1941. doi: 10.1172/JCI104218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD E. R., ROPARTZ C., RIVAT L., ROUSSEAR P. Y. GM(F)--A DETERMINANT OF HUMAN GAMMA-GLOBULIN. Vox Sang. 1965 May-Jun;10:299–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausset P., Delespesse G., Hubert C., Kennes B., Govaerts A. In vitro response of subpopulations of human lymphocytes. II. DNA synthesis induced by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):446–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F. Biological effects of anti-immunoglobulins: evidence for immunoglobulin receptors on 'T' and 'B' lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1970;5:45–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1970.tb00356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb R., Kronvall G., Mårtensson L. Some aspects of the relations between rheumatoid arthritis, antigamma-globulin factors and the polymorphism of human gamma globulin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(2):865–872. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb19009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARBOE M., RAU B., AHO K. PROPERTIES OF VARIOUS ANTI-GAMMA-GLOBULIN FACTORS IN HUMAN SERA. J Exp Med. 1965 Apr 1;121:503–519. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Garrett M. A. Lymphocyte reactivity to mitogens in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jan;27(1):92–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Lentz H., van Es L. A. Isolation of stable aggregates of IgG by zonal ultracentrifugation in sucrose gradients containing albumin. Immunol Commun. 1979;8(3):337–345. doi: 10.3109/08820137909050047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormeier L. C., Ing J. T., Mandy W. J. Specificity of antiglobulin factors in normal human serum reacting with enzyme digested gamma-G-globulin. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):612–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler H., Rowley D. A., DuClos T., Richardson B. Complementary idiotypy in the regulation of the immune response. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G. Effects of anti-immunoglobulin sera on B lymphocyte functions. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(6):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B. Heterogeneity of anti-gamma-globulin factors detected by pepsin-digested human gamma G-globulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):369–382. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman H. A., Johnson J. S., Vaughan J. H., McGlamory J. C. Altered lymphocyte reactivity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19(3):509–515. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller M., Duma R. J., Farley E. D., Jr, Atkinson J. The influence of infection on titres of antiglobulin antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Mar;8(3):451–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller M., Richard A. J., Mallory J. Immunochemical and serological studies of enzymaatically fragmented human IgG globulins. II. Hydrolysis with subtilisin, elastase, trypsin, and chymotrypsin. Immunochemistry. 1969 Mar;6(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata J., Barnett E. V., Knutson D. W., Nasu H., Chia D. Characterization and measurement of anti-IgG antibodies in human sera by radioimmunoassay (RIA). J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


