Abstract
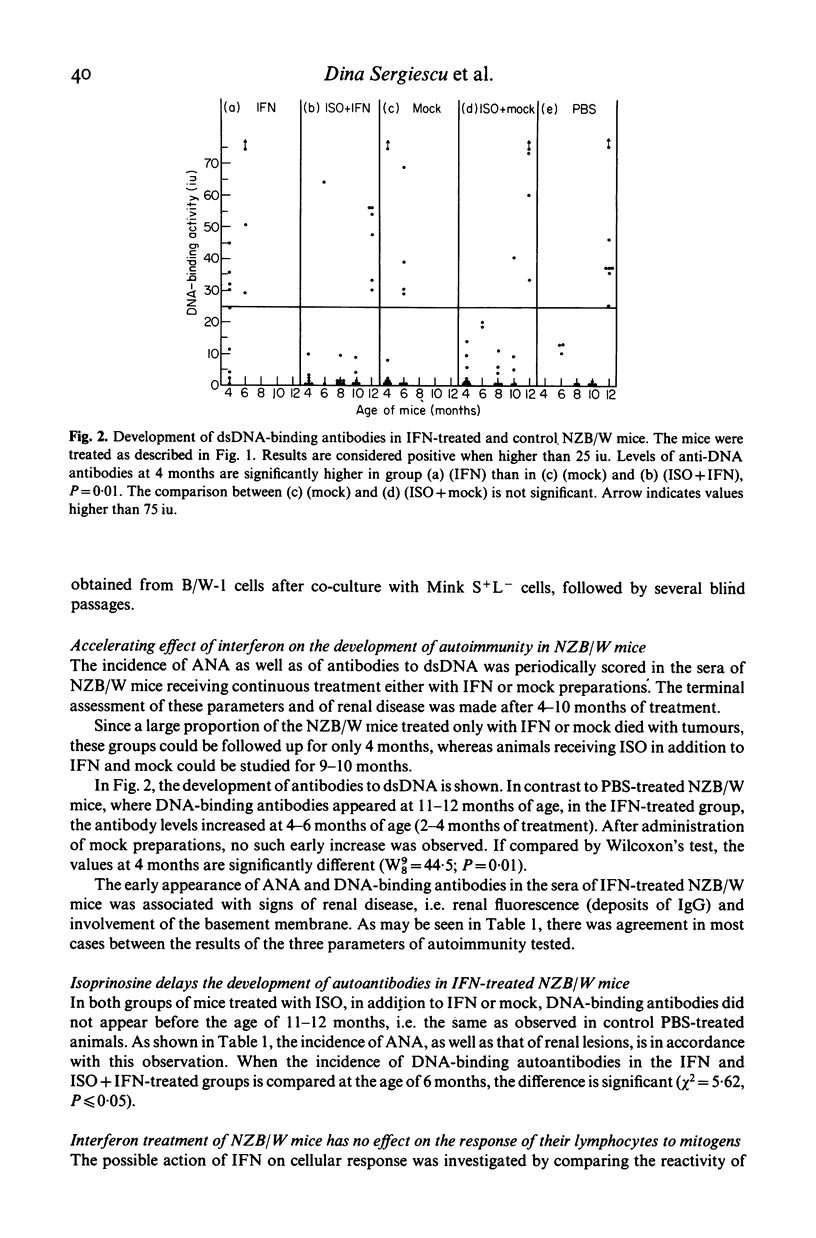
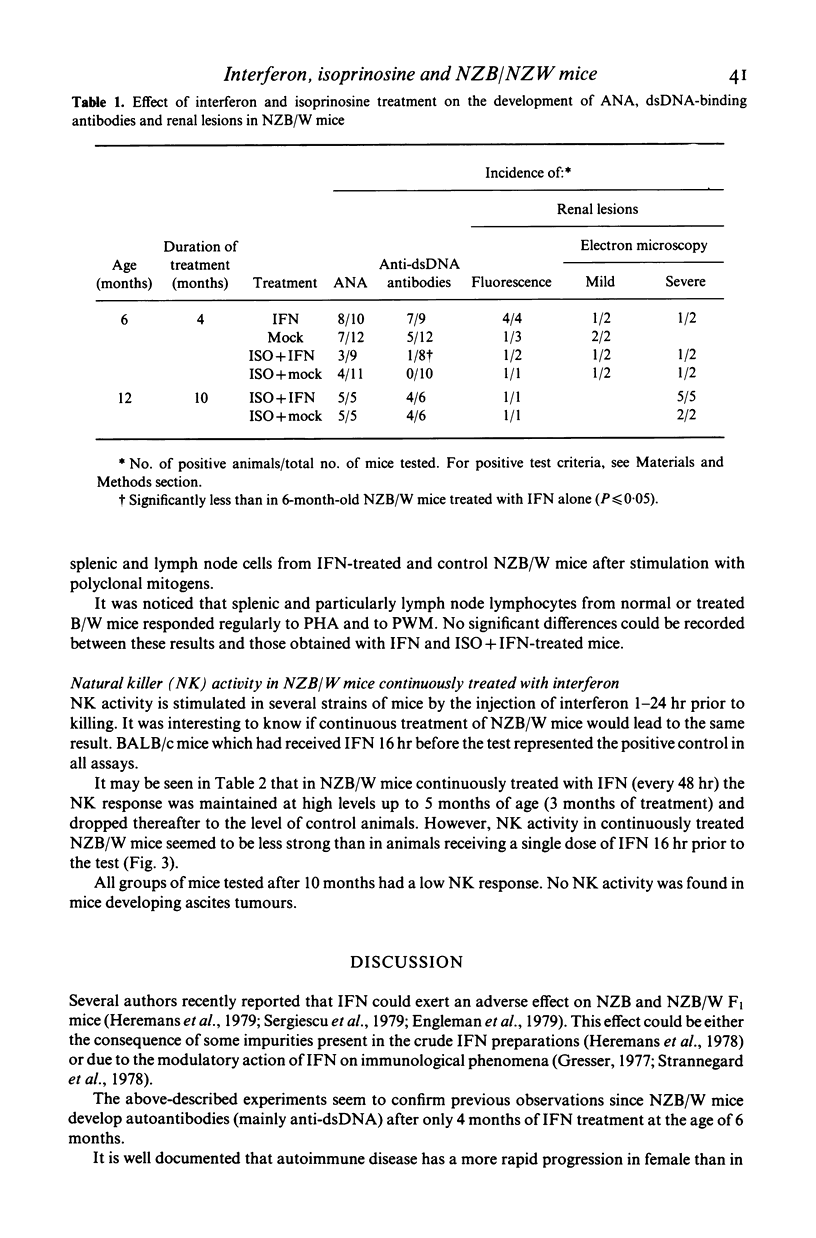
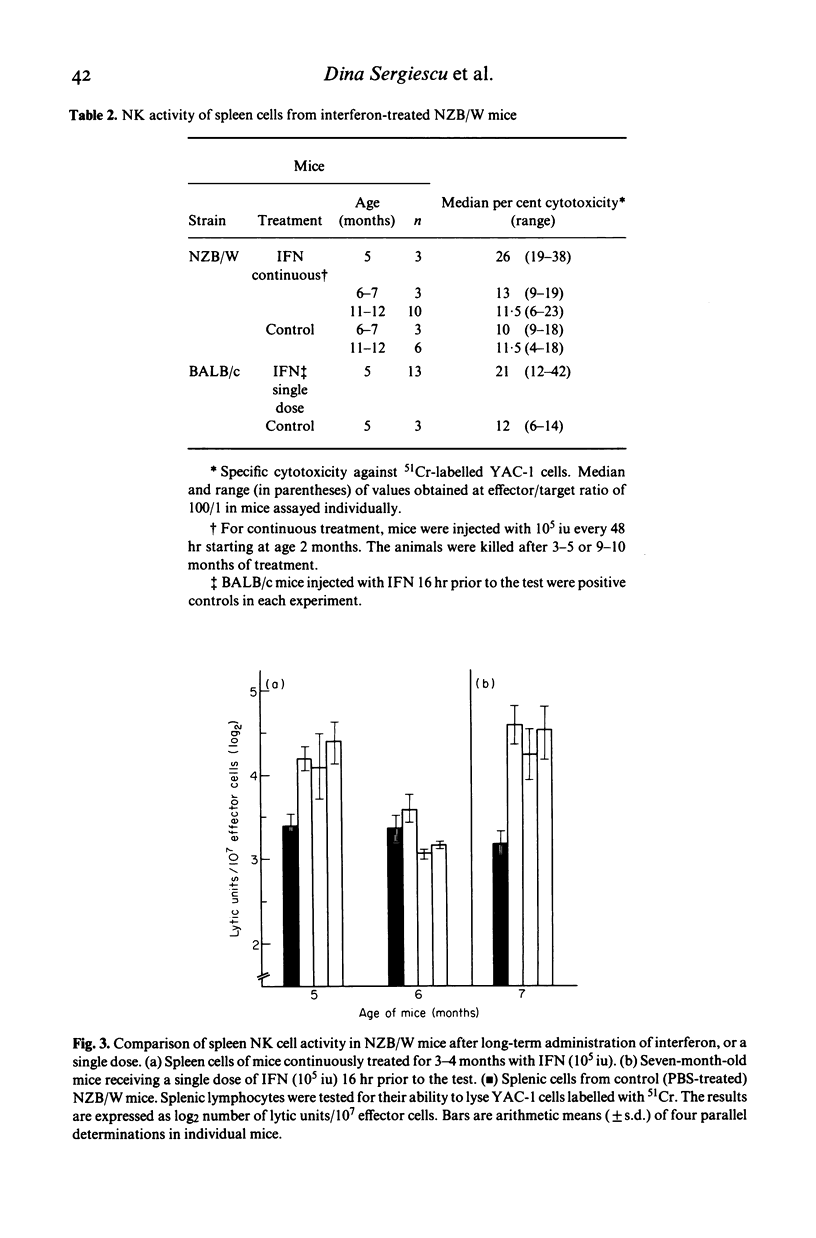
NZB/NZW F1 hybrid mice treated for long periods with type beta interferon developed early symptoms of autoimmune disease. In these animals the level of anti-dsDNA antibody begins to increase at 4-6 months while untreated NZB/NZW mice do not display similar levels until 12 months. The concomitant administration of isoprinosine and interferon delays the early appearance of autoimmune disorders. In interferon-treated NZB/NZW mice the cytotoxic activity of natural killer lymphocytes is maintained at high levels until the age of 5 months. Nevertheless, the natural killer activity is even stronger and detected until at least 7 months in NZB/NZW mice receiving a single dose of interferon 16 hr prior to the test. Lymphoblastoid ascitic tumours appeared early (2-3 months) during interferon treatment in all groups of NZB/NZW mice. However, in the presence of isoprinosine only a few animals developed tumours. Thus, isoprinosine seems to protect NZB/NZW mice both from early autoimmune disorders due to interferon and from early tumour development.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourgeade M. F., Chany C. Effect of sodium butyrate on the antiviral and anticellular action of interferon in normal and MSV-transformed cells. Int J Cancer. 1979 Sep 15;24(3):314–318. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti I., Chany C., Schlumberger J. F. Isoprinosine increases the antitumor action of interferon. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1979;1(1):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(79)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Cerutti I. Enhancement of antiviral protection against encephalomyocarditis virus by a combination of isoprinosine and interferon. Arch Virol. 1977;55(3):225–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01319908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Manny N., Andrzejewski C., André-Schwartz J., Schwartz R. S. Genetic studies of autoimmunity and retrovirus expression in crosses of New Zealand black mice I. Xenotropic virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):854–871. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald K. L., Ponzio N. M. Natural killer cell activity in reticulum cell sarcomas (RCS) of SJL/J mice. Cell Immunol. 1979 Mar 1;43(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisler R. H., Lindahl P., Gresser I. Effects of interferon on antibody synthesis in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Maury C., Tovey M., Morel-Maroger L., Pontillon F. Progressive glomerulonephritis in mice treated with interferon preparations at birth. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):420–422. doi: 10.1038/263420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser J., Morel-Maroger L., Verroust P., Rivière Y., Guillon J. C. Anti-interferon globulin inhibits the development of glomerulonephritis in mice infected at birth with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3413–3416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern B., Fray A. Déclenchement de l'anémie hémolytique autoimmune chez de jeunes souriceaux NZB par l'administration de Corynebacterium parvum. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Dec;117(6):778–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans H., Billiau A., Colombatti A., Hilgers J., de Somer P. Interferon treatment of NZB mice: accelerated progression of autoimmune disease. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):925–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.925-930.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston D. P., Steinberg A. D. Animal models of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Yale J Biol Med. 1979 May-Jun;52(3):289–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan A., Perlik F., Le Go A., Delbarre F., Giroud J. P. Adjuvant-induced arthritis in four inbred strains of rats. An in vitro study of peripheral T and B lymphocytes. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):219–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01972212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Petranyi G., Kärre K., Jondal M., Tracey D., Wigzell H. Killer cells: a functional comparison between natural, immune T-cell and antibody-dependent in vitro systems. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):772–780. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. H., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the glomerulonephritis of NZB/W mice. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):507–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Kazan P., Varnier O., Kleiman H. Murine xenotropic type C viruses I. Distribution and further characterization of the virus in NZB mice. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.844-853.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalski J. P., McCombs C. C., Talal N. Suppressor cells and immunodeficiency in (NZB x NZW)F1 hybrid mice. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):440–446. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles P. T. An in vitro focus-induction assay for xenotropic murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus C, and the feline--primate viruses RD-114/CCC/M-7. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset S. Refractory state of cells to interferon induction. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jan;22(1):9–20. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryd W., Hagmar B., Lundgren E., Strannegård O. Discrepant effects of interferon murine syngeneic ascites tumors and their solid metastasizing counterparts. Int J Cancer. 1979 Mar 15;23(3):397–401. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senik A., Gresser I., Maury C., Gidlund M., Orn A., Wigzell H. Enhancement by interferon of natural killer cell activity in mice. Cell Immunol. 1979 Apr;44(1):186–200. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergiescu D., Cerutti I., Efthymiou E., Kahan A., Chany C. Adverse effects of interferon treatment on the life span of NZB mice. Biomedicine. 1979 Apr;31(2):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Baron S., Talal N. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice, I. Induction of antinucleic acid antibodies by polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1102–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Reinertsen J. L. Lupus in New Zealand mice and in dogs. Bull Rheum Dis. 1977;28(4-5):940–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephension J. R., Reynolds R. K., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Distribution of three classes of endogenous type-C RNA viruses among inbred strains of mice. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):404–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Larsson I., Lundgren E., Miörner H., Persson H. Modulation of immune responses in newborn and adult mice by interferon. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):334–339. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.334-339.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Disordered immunologic regulation and autoimmunity. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:240–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. E. Accelerated mortality in young NZB/NZW mice treated with the interferon inducer tilorone hydrochloride. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Sep;8(2):204–212. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. E., Anver M. R. Accelerated appearance of neoplasms in female NZB/NZW mice treated with high-dose cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Dec;22(12):1338–1343. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


