Abstract
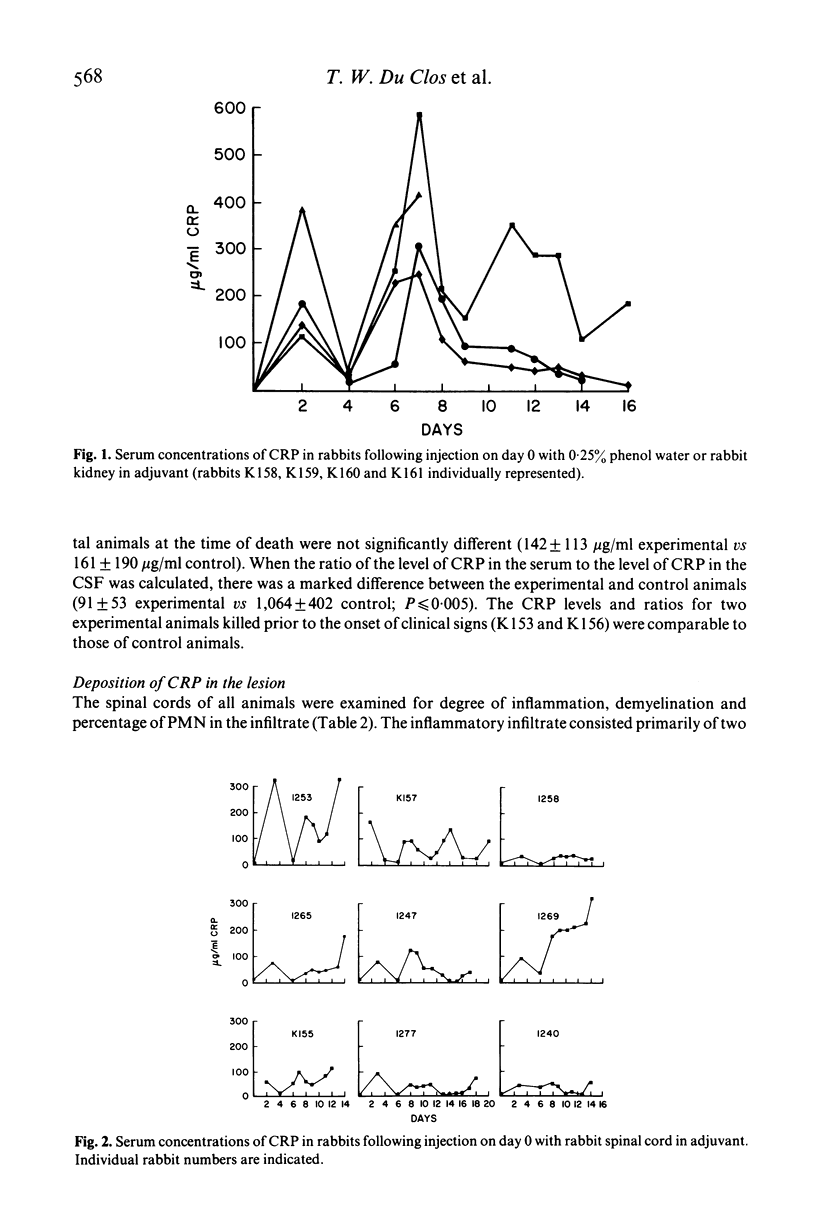
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase reactant which has been found deposited at sites of inflammation and tissue destruction. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system characterized by inflammatory cellular infiltrates. This study describes the CRP response and the deposition of CRP in the spinal cords of rabbits with EAE. EAE was induced by a single injection of rabbit spinal cord in Freund's complete adjuvant. Serum CRP levels in experimental and adjuvant control rabbits showed cyclic elevations. An additional increase in levels of CRP in the serum was observed in the experimental group coincident with the onset of clinical disease. Deposition of CRP in spinal cord lesions of six of nine animals with EAE was demonstrated by direct immunofluorescence. CRP was seen around and within a small proportion of the cells in the acute inflammatory lesion. The amount of CRP deposition was most closely correlated with the proportion of polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) in the infiltrate. No staining was observed in control animals, in experimental animals prior to the onset of clinical signs of EAE, or in clinically affected animals with exclusively mononuclear infiltration. The demonstration of CRP and PMN in acute lesions of rabbits with EAE may reflect a role for humoral mediators of inflammation in this disease.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Metzger H. Affinity labeling of a phosphorylcholine binding mouse myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):766–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin J. D., Gitlin J. I., Gitlin D. Localizing of C-reactive protein in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1491–1499. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute phase protein. I. An immunohistochemical method for the localization of Cx-reactive protein in rabbits. Association with necrosis in local inflammatory lesions. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:961–974. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., RAKITA L., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute-phase protein. II. Localization of Cx-reactive protein in heart in induced myocardial infarction in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:286–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI104715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J. A HYPERACUTE FORM OF ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jul;47:61–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Osmand A. P., Lint T. F., Gewurz H. Interaction of C-reactive protein with lymphocytes and monocytes: complement-dependent adherence and phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):774–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Adjuvants, cell-mediated immune responses and autoimmune disease. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Nov;14(5):426–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Osmand A. P., Wilson M. F., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. II. C-reactive protein-mediated consumption of complement by poly-L-lysine polymers and other polycations. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):709–721. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Feltkamp T. E. Conjugation of fluorescein isothiocyanate to antibodies. I. Experiments on the conditions of conjugation. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):865–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O. Cyclical production of antibody as a regulatory mechanism in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:87–111. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


