Abstract
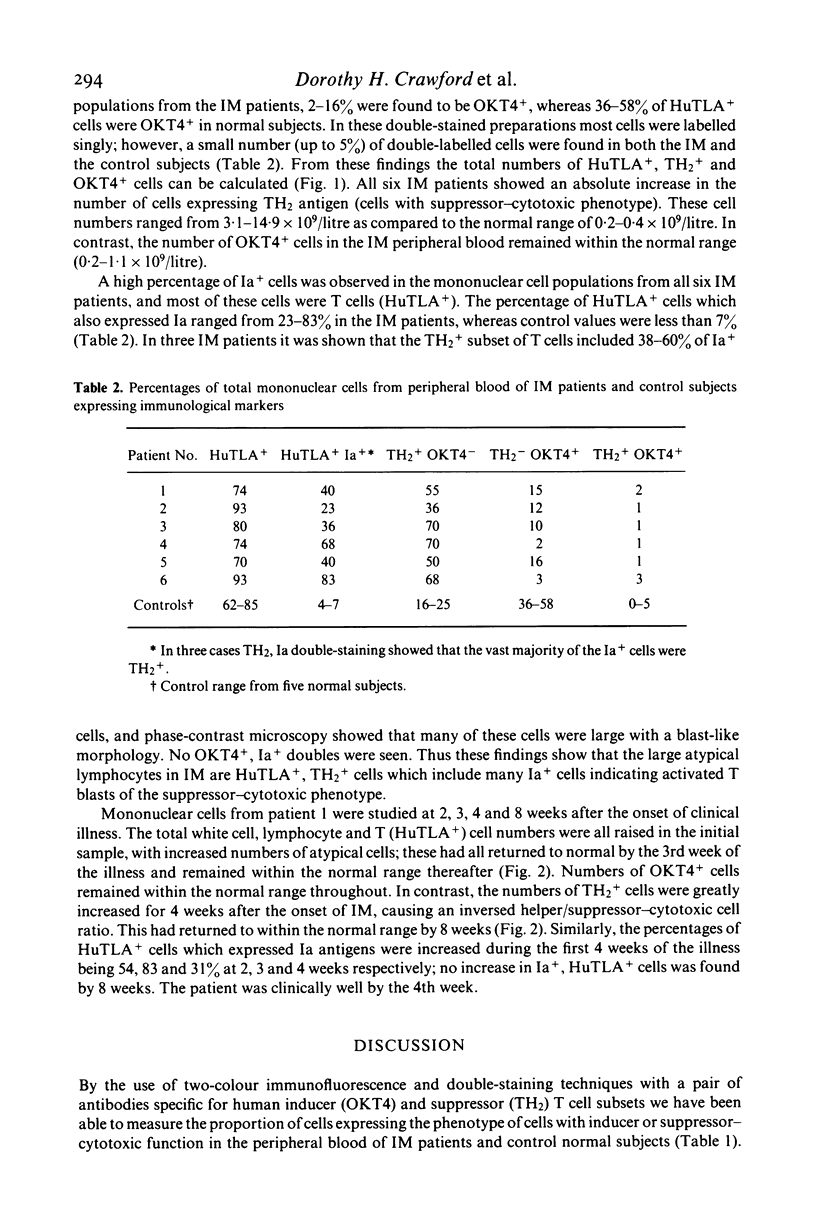
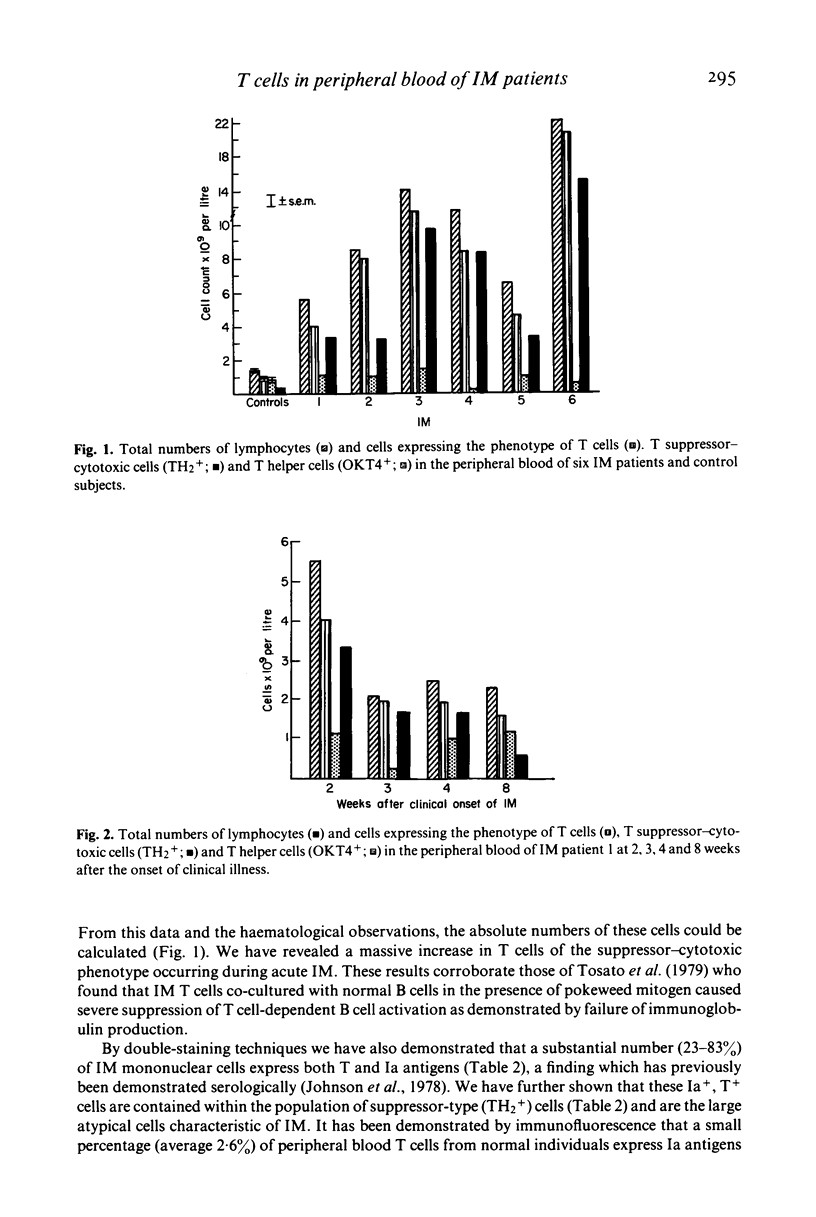
Peripheral blood cells from six patients with acute infectious mononucleosis were studied by two-colour immunofluorescence using antibodies to human T cells, inducer and suppressor-cytotoxic T cell subsets and Ia-like antigens. The absolute number of T cells with the suppressor-cytotoxic phenotype was substantially increased in each case; many of these cells also expressed Ia-like antigens and had the morphology of the large atypical cells characteristic of infectious mononucleosis. These activated suppressor T cells of infectious mononucleosis may therefore represent a control mechanism to prevent viral-induced proliferation of B cells.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denman A. M., Pelton B. K. Control mechanisms in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):13–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl V., Henle G., Henle W., Kohn G. Demonstration of a herpes group virus in cultures of peripheral leukocytes from patients with infectious mononucleosis. J Virol. 1968 Jul;2(7):663–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.7.663-669.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg R. N., Eberle B. J., Williams R. C., Jr T- and B-cells in peripheral blood during infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):104–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden H. D., Chang R. S., Prescott W., Simpson E., Cooper T. Y. Leukocyte-transforming agent: prolonged excretion by patients with mononucleosis and excretion by normal individuals. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):471–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewetson J. F., Rocchi G., Henle W., Henle G. Neutralizing antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in healthy populations and patients with infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):283–289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Svedmyr E., Jondal M., Persson P. O. EBV-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA)-positive cells in the peripheral blood of infectious mononucleosis patients. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Niederman J. C., Andrews L. L. Prolonged oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus after infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):229–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Rickinson A. B., Pope J. H. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. I. Complete regression of virus-induced transformation in cultures of seropositive donor leukocytes. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):662–668. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G. The establishment of lymphoblastoid lines from adult and fetal human lymphoid tissue and its dependence on EBV. Int J Cancer. 1971 Nov 15;8(3):443–450. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Sheldon P. J., Holborow E. J. T- and B-cell subpopulations in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Gerber P. Selective transformation of B lymphocytes by E.B. virus. Lancet. 1973 Jul 14;2(7820):93–94. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)93286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provisor A. J., Iacuone J. J., Chilcote R. R., Neiburger R. G., Crussi F. G. Acquired agammaglobulinemia after a life-threatening illness with clinical and laboratory features of infectious mononucleosis in three related male children. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 10;293(2):62–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507102930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Further characterization of the human inducer T cell subset defined by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2894–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Pesando J. M., Ritz J., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Ia determinants on human T-cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibody. Activation stimuli required for expression. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1472–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Con A-inducible suppression of MLC: evidence for mediation by the TH2 + T cell subset in man. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1335–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Strelkauskas A. J., O'Brien C., Schlossman S. F. Phenotypic and functional distinctions between the TH2+ and JRA+ T cell subsets in man. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Crawford D., Epstein M. A. Inhibition of the in vitro outgrowth of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphocytes by thymus-dependent lymphocytes from infectious mononucleosis patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):72–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Moss D. J., Pope J. H., Ahlberg N. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in man. IV. Development of T-cell memory in convalescent infectious mononucleosis patients. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jan 15;25(1):59–65. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. E., Brown N., Andiman W., Halliday K., Francke U., Robert M. F., Andersson-Anvret M., Horstmann D., Miller G. Diffuse polyclonal B-cell lymphoma during primary infection with Epstein-Barr virus. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1293–1297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Sullivan J. L., Periman P. O., Perlin E. Cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr-virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 4;293(23):1159–1163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512042932301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon P. J., Hemsted E. H., Papamichail M., Holborow E. J. Thymic origin of atypical lymphoid cells in infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1973 May 26;1(7813):1153–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E., Jondal M. Cytotoxic effector cells specific for B Cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus are present in patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Magrath I., Koski I., Dooley N., Blaese M. Activation of suppressor T cells during Epstein-Barr-virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 22;301(21):1133–1137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911223012101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim F. A., Williams R. C., Jr Studies on the macroglobulins of human serum. I. Polyclonal immunoglobulin class M (IgM) increase in infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jan 13;274(2):61–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196601132740202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. A., Frenkel E. P. The atypical lymphocyte. Am J Med. 1967 Jun;42(6):923–936. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Gibofsky A., Ko H. S., Kunkel H. G. Peripheral blood Ia-positive T cells. Increases in certain diseases and after immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):91–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


