Abstract
The lectin peanut agglutinin (PNA), which interacts specifically with D-galactosyl residues, was studied for its binding to human normal and malignant lymphoid cells at various stages of differentiation. As previously reported, PNA binds to thymocytes; however, it does not interact with the prothymocytes which precede the cortical thymocyte differentiation stage. No mature peripheral cells in any of the lymphoid organs bind PNA. In contrast to the normal T differentiation pathway, the expression of the PNA-binding site does not seem to coincide with that of T cell characteristics in the various malignant lymphoid cells studied. We therefore conclude that more information is needed about the nature of the PNA-binding site before it can be used as a differentiation marker in malignant lymphoid cells.
Full text
PDF


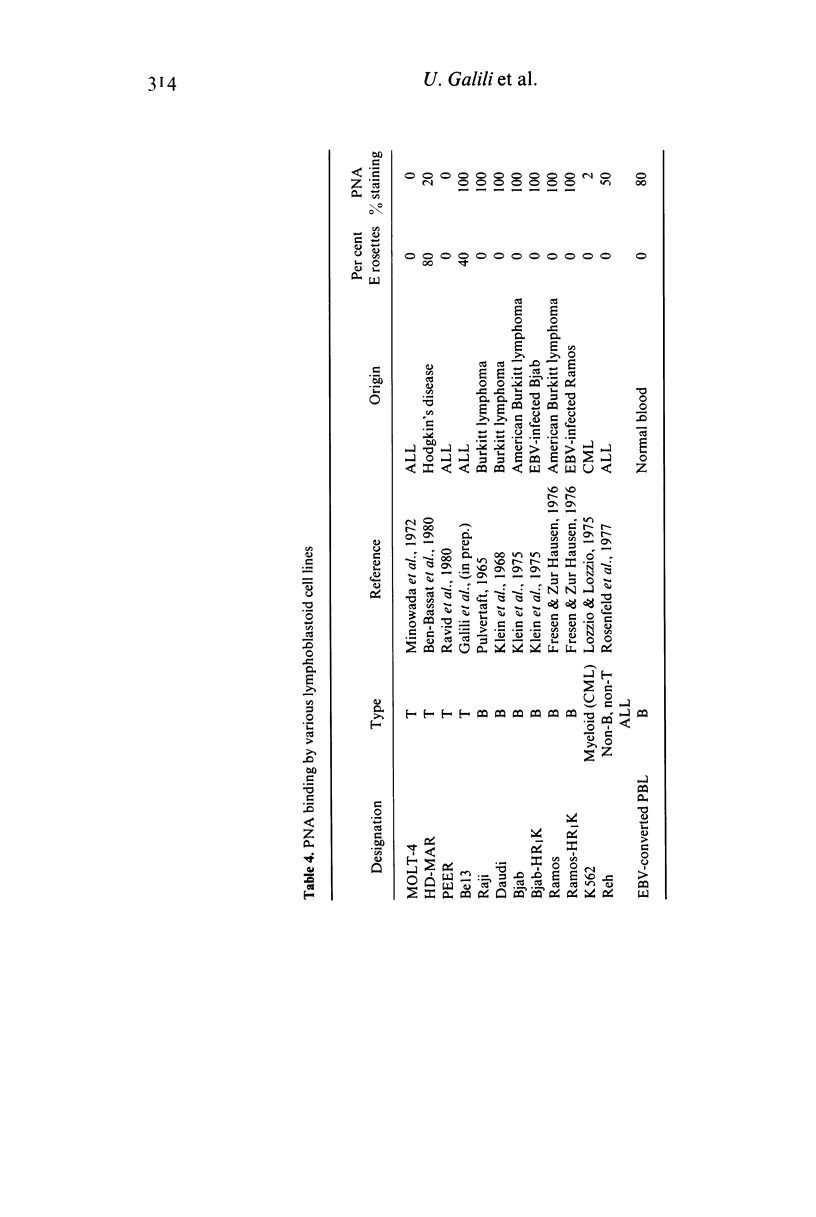

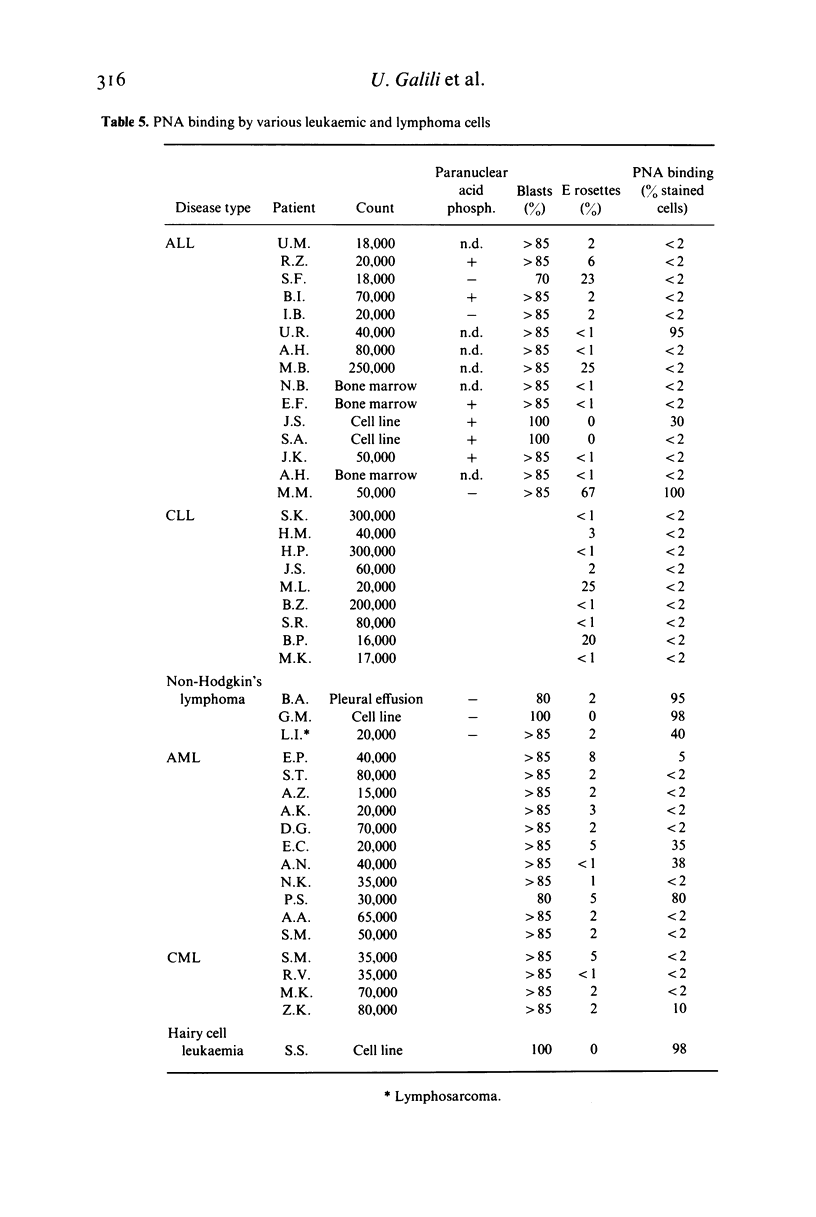


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Bassat H., Mitrani-Rosenbaum S., Gamliel H., Naparstek E., Leizerowitz R., Korkesh A., Sagi M., Voss R., Kohn G., Polliack A. Establishment in continuous culture of a T-lymphoid cell line (HD-Mar) from a patient with Hodgkin's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1980 May 15;25(5):583–590. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despont J. P., Abel C. A., Grey H. M. Sialic acids and sialyltransferases in murine lymphoid cells: indicators of T cell maturation. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jun;17(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flandrin G., Brouet J. C. The Sezary cell: cytologic, cytochemical, and immunologic studies. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Aug;49(8):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Hausen H. Establishment of EBNA-expressing cell lines by infection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-genome-negative human lymphoma cells with different EBV strains. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):161–166. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Galili N., Vánky F., Klein E. Natural species-restricted attachment of human and murine T lymphocytes to various cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Häyry P., Klein E. Loss of net negative surface charge during MLC stimulation of human T lymphocytes: correlation to "stable" E-rosette formation and natural attachment to normal and malignant target cells. Cell Immunol. 1979 Nov;48(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Klein E., Schlesinger M. Human T lymphocyte receptors for sheep red blood cells and specific antigens: are they identical sites on the cell membrane? J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):104–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Schlesinger M. The formation of stable E-rosettes by human T lymphocytes activated in mixed lymphocyte reactions. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):730–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatien J. G., Schneeberger E. E., Merler E. Analysis of human thymocyte subpopulations using discontinuous gradients of albumin: precursor lymphocytes in human thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1975 May;5(5):312–317. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoessli D., Bron C., Pink J. R. T-lymphocyte differentiation is accompanied by increase in sialic acid content of Thy-1 antigen. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):576–578. doi: 10.1038/283576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C., Roberts P., Ranki A., Nordling S. Fractionation of immunocompetent cells by free-flow cell electrophoresis. Isr J Med Sci. 1975 Dec;11(12):1299–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S., Russell E. C., Blanchard D., McWilliams N. B., Maurer H. M., Mohanakumar T. Receptors for peanut agglutinin (Arachus hypogea) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: possible clinical significance. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):37–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Berrih S., Bach J. F. Peanut agglutinin. I. A new tool for studying T lymphocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):438–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Berrih S., Papiernik M. Peanut agglutinin. III. Study of T lymphocyte differentiation during murine ontogeny. Dev Comp Immunol. 1979 Spring;3(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(79)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. A., Klein P. J., Rudland P. S. Binding of peanut lectin to breast epithelium, human carcinomas, and a cultured rat mammary stem cell: use of the lectin as a marker of mammary differentiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Dec;63(6):1339–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Lotan R., Ravid A., Sharon N. Peanut agglutinin, a new mitogen that binds to galactosyl sites exposed after neuraminidase treatment. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1243–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Kabat E. A., Lotan R., Sharon N. Immunochemical studies on the specificity of the peanut (Arachis hypogaea) agglutinin. Carbohydr Res. 1976 Oct;51(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravid Z., Goldblum N., Zaizov R., Schlesinger M., Kertes T., Minowada J., Verbi W., Greaves M. Establishment and characterization of a new leukaemic T-cell line (Peer) with an unusual phenotype. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jun 15;25(6):705–710. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Biniaminov M., Rosenthal E., Sharon N., Ramot B. Interaction of peanut agglutinin with normal human lymphocytes and with leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Biniaminov M., Rosenthal E., Sharon N., Ramot B. Interaction of peanut agglutinin with normal human lymphocytes and with leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Gachelin G., Dubois P., Nicolas J. F., Sharon N., Jacob F. Interaction of peanut agglutinin, a lectin specific for nonreducing terminal D-galactosyl residues, with embryonal carcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1977 Nov;61(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. L., Birbeck M. S., Wallis V. J., Forrester J. A., Davies A. J. Peanut lectin binding properties of germinal centres of mouse lymphoid tissue. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):364–366. doi: 10.1038/284364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld C., Goutner A., Choquet C., Venuat A. M., Kayibanda B., Pico J. L., Greaves M. F. Phenotypic characterisation of a unique non-T, non-B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):841–843. doi: 10.1038/267841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiig J. N. Effect of neuraminidase on lymphoid cells. Differences in structure of B and T cells and thymocytes of the mouse shown by cell electrophoresis and sialic acid determination. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(3):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. J., Gesner B. M. The effect of neuraminidase on the fate of transfused lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):551–567. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


