Abstract
Human blood leucocytes were tested for their capacity to bind histamine coupled as a rabbit serum albumin conjugate (H-RSA) to formalized ox red cells. The percentage of rosette-forming target cells was directly related to the concentration of erythrocyte-bound H-RSA. Under optimal experimental conditions the average number of rosettes was 52% for monocytes, 3 for lymphocytes, 25% for neutrophils and 59% for eosinophils. Free histamine partially inhibited rosette formation by blood monocytes in a dose-dependent fashion from 10-3 to 10-5 mol/l, and complete inhibition was achieved by the H-RSA conjugate. In contrast, three amines chemically related to histamine, L-histidine, imidazoleacetic acid and N-acetylhistamine, had no inhibitory effect. The histamine H1 antagonists, mepyramine and chlorpheniramine, and the H1 receptor agonist, 2-(2-aminoethyl)-thiazole, all inhibited rosette formation by blood monocytes in a dose-dependent fashion. However, the H2 receptor antagonists, burimamide and metiamide, and the H2 receptor agonists, Dimaprit and 4-methyl-histamine, were inactive. There was no statistical difference in the percentage of histamine rosettes for monocytes. lymphocytes, neutrophils or eosinophils between atopic and non-atopic individuals.
Full text
PDF

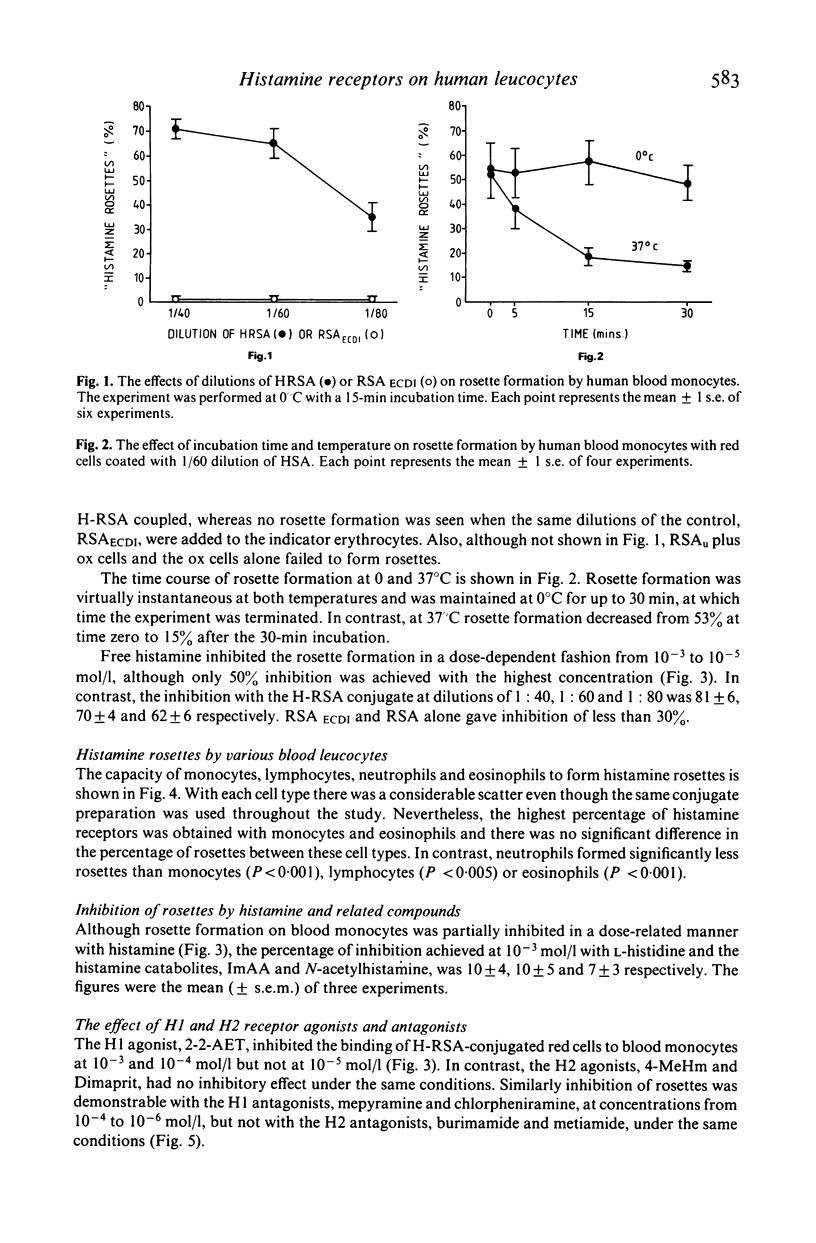
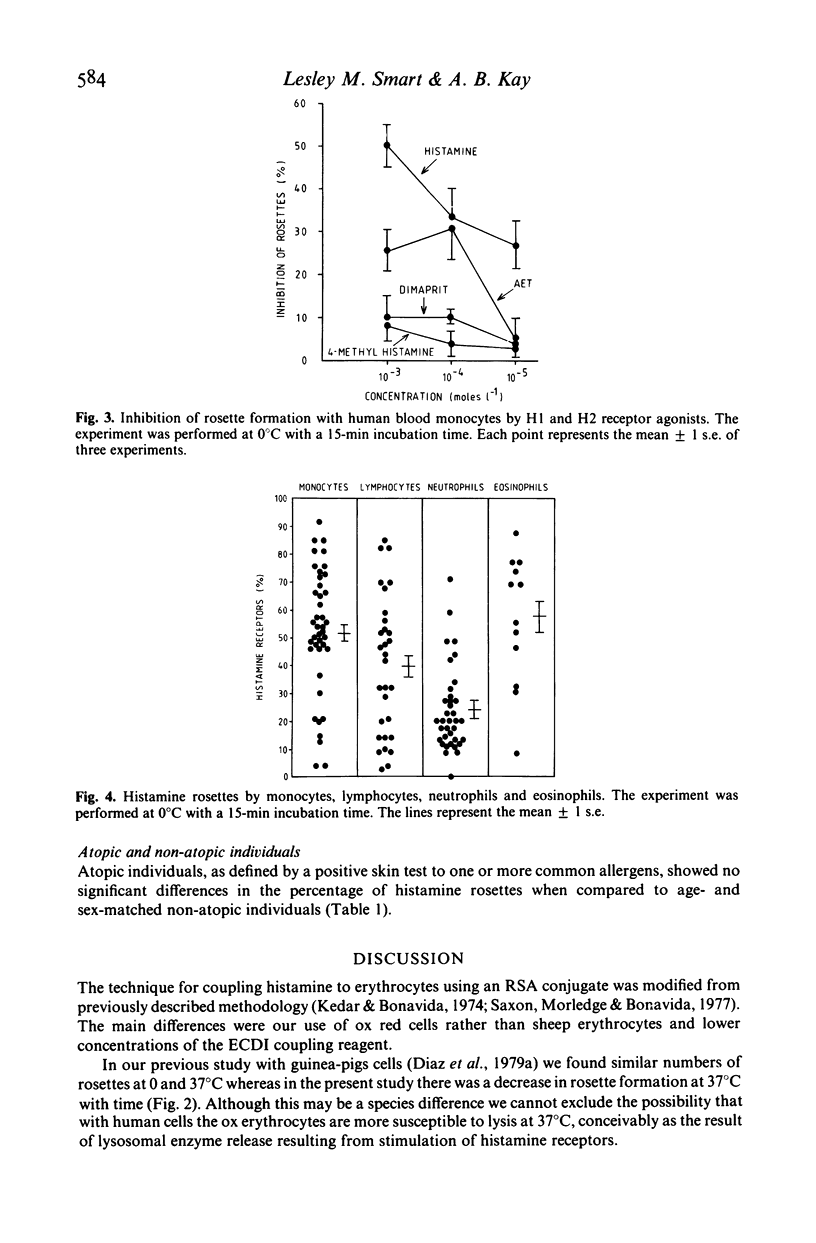
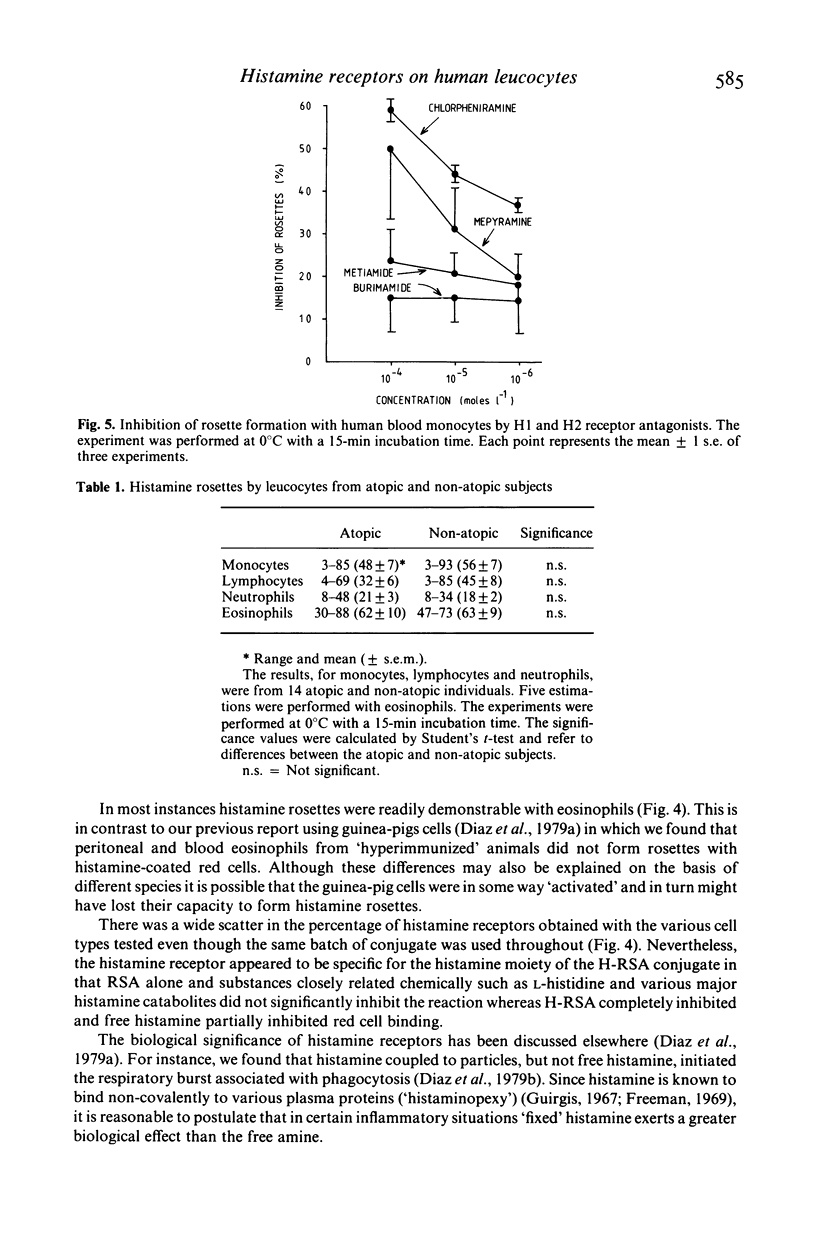

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R., Glover A., Rabson A. R. The in vitro effects of histamine and metiamide on neutrophil motility and their relationship to intracellular cyclic nucleotide levels. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1690–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse W. W., Sosman J. Histamine inhibition of neutrophil lysosomal enzyme release: an H2 histamine receptor response. Science. 1976 Nov 12;194(4266):737–738. doi: 10.1126/science.185696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz P., Jones D. G., Kay A. B. Histamine receptors on guinea-pig alveolar macrophages: chemical specificity and the effects of H1- and H2-receptor agonists and antagonists. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Mar;35(3):462–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz P., Jones D. G., Kay A. B. Histamine-coated particles generate superoxide (O-2) and chemiluminescence in alveolar macrophages. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):454–456. doi: 10.1038/278454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirgis H. M. Separation of a histamine-binding fraction from normal human serum. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1967;31(6):587–593. doi: 10.1159/000229905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedar E., Bonavida B. Histamine receptor-bearing leukocytes (HRL). I. Detection of histamine receptor-bearing cells by rosette formation with histamine-coated erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1544–1552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmon K. L., Bourne H. R., Weinstein J., Sela M. Receptors for histamine can be detected on the surface of selected leukocytes. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):707–709. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Lichtenstein L. M., Henney C. S. Increase in histamine receptors on thymus-derived effector lymphocytes during the primary immune response to alloantigens. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):284–287. doi: 10.1038/244284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Modulation of cellular-immune responses in vivo and in vitro by histamine receptor-bearing lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1051–1058. doi: 10.1172/JCI108347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Morledge V. D., Bonavida B. Histamine-receptor leucocytes (HRL). Organ and lymphoid subpopulation distribution in man. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):394–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


